Cataract: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Cataract | |||
| image = [[File:Cataract_in_human_eye.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = A human eye with a cataract | |||
| field = [[Ophthalmology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Blurred vision]], [[glare]], [[halos around lights]], [[difficulty seeing at night]] | |||
| complications = [[Blindness]] | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Long term | |||
| causes = [[Aging]], [[trauma]], [[radiation]], [[genetic factors]], [[diabetes]], [[smoking]] | |||
| risks = [[Age]], [[diabetes]], [[smoking]], [[alcohol consumption]], [[prolonged exposure to sunlight]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Eye examination]] | |||
| differential = [[Glaucoma]], [[macular degeneration]] | |||
| prevention = [[Sunglasses]], [[smoking cessation]], [[control of diabetes]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]] | |||
| medication = None | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
| deaths = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Cataract''' is a condition characterized by the clouding of the [[lens]] in the [[eye]] that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging, and they are very common in older people. A cataract can occur in either or both eyes, but it cannot spread from one eye to the other. | '''Cataract''' is a condition characterized by the clouding of the [[lens]] in the [[eye]] that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging, and they are very common in older people. A cataract can occur in either or both eyes, but it cannot spread from one eye to the other. | ||
[[File:Cataract in human eye.png|Cataract in human eye|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Cataract in human eye.png|Cataract in human eye|thumb]] | |||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The primary cause of cataracts is the age-related degeneration of the proteins within the lens of the eye, leading to the clouding of the lens. Other factors that may contribute to the development of cataracts include: | The primary cause of cataracts is the age-related degeneration of the proteins within the lens of the eye, leading to the clouding of the lens. Other factors that may contribute to the development of cataracts include: | ||
[[File:Cataract (28464844371).png|Cataract|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Cataract (28464844371).png|Cataract|thumb]] | |||
* [[Diabetes mellitus|Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes mellitus|Diabetes]] | ||
* Exposure to [[ultraviolet]] (UV) radiation | * Exposure to [[ultraviolet]] (UV) radiation | ||
| Line 16: | Line 34: | ||
* Other medical conditions, such as [[hypertension]] or [[obesity]] | * Other medical conditions, such as [[hypertension]] or [[obesity]] | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Cataract symptoms typically develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include: | Cataract symptoms typically develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include: | ||
* Blurred or hazy vision | * Blurred or hazy vision | ||
* Increased sensitivity to glare and bright lights | * Increased sensitivity to glare and bright lights | ||
| Line 26: | Line 42: | ||
* Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription | * Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
A comprehensive eye examination by an [[ophthalmologist]] or [[optometrist]] is necessary to diagnose cataracts. Diagnostic tests may include: | A comprehensive eye examination by an [[ophthalmologist]] or [[optometrist]] is necessary to diagnose cataracts. Diagnostic tests may include: | ||
* Visual acuity test: This test measures how well a patient can see at various distances. | * Visual acuity test: This test measures how well a patient can see at various distances. | ||
* Slit-lamp examination: A slit lamp uses a high-intensity light source and a microscope to examine the structures at the front of the eye, including the lens. | * Slit-lamp examination: A slit lamp uses a high-intensity light source and a microscope to examine the structures at the front of the eye, including the lens. | ||
* Retinal examination: After dilating the pupils with eye drops, the doctor uses a special instrument to examine the retina and optic nerve at the back of the eye. | * Retinal examination: After dilating the pupils with eye drops, the doctor uses a special instrument to examine the retina and optic nerve at the back of the eye. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment for cataracts depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on the patient's daily activities. Early-stage cataracts may be managed with non-surgical interventions, such as: | The treatment for cataracts depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on the patient's daily activities. Early-stage cataracts may be managed with non-surgical interventions, such as: | ||
* Updating eyeglass or contact lens prescription | * Updating eyeglass or contact lens prescription | ||
* Using magnifying lenses for reading or other close-up work | * Using magnifying lenses for reading or other close-up work | ||
* Wearing sunglasses to reduce glare | * Wearing sunglasses to reduce glare | ||
When cataracts significantly impair vision and interfere with daily activities, [[cataract surgery]] may be recommended. This procedure involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Cataract surgery is generally safe and effective, with a high success rate in improving vision. | When cataracts significantly impair vision and interfere with daily activities, [[cataract surgery]] may be recommended. This procedure involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Cataract surgery is generally safe and effective, with a high success rate in improving vision. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
While cataracts cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and precautions may help reduce the risk of developing them: | While cataracts cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and precautions may help reduce the risk of developing them: | ||
* Protecting the eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses with UV protection | * Protecting the eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses with UV protection | ||
* Managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension | * Managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension | ||
| Line 52: | Line 60: | ||
* Having regular eye examinations to monitor eye health and detect cataracts early | * Having regular eye examinations to monitor eye health and detect cataracts early | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* [[American Academy of Ophthalmology]]: [https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-are-cataracts What Are Cataracts?] | * [[American Academy of Ophthalmology]]: [https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-are-cataracts What Are Cataracts?] | ||
* [[National Eye Institute]]: [https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/cataracts Cataracts] | * [[National Eye Institute]]: [https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/cataracts Cataracts] | ||
[[Category:Ophthalmology]] | [[Category:Ophthalmology]] | ||
[[Category:Eye diseases]] | [[Category:Eye diseases]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:19, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Cataract | |
|---|---|
| File:Cataract in human eye.png | |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Blurred vision, glare, halos around lights, difficulty seeing at night |
| Complications | Blindness |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Aging, trauma, radiation, genetic factors, diabetes, smoking |
| Risks | Age, diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, prolonged exposure to sunlight |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Glaucoma, macular degeneration |
| Prevention | Sunglasses, smoking cessation, control of diabetes |
| Treatment | Surgery |
| Medication | None |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Rare |
Cataract is a condition characterized by the clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging, and they are very common in older people. A cataract can occur in either or both eyes, but it cannot spread from one eye to the other.
Causes[edit]
The primary cause of cataracts is the age-related degeneration of the proteins within the lens of the eye, leading to the clouding of the lens. Other factors that may contribute to the development of cataracts include:
- Diabetes
- Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Prolonged use of corticosteroid medications
- Previous eye surgery or injuries
- Family history of cataracts
- Other medical conditions, such as hypertension or obesity
Symptoms[edit]
Cataract symptoms typically develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred or hazy vision
- Increased sensitivity to glare and bright lights
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Double vision in one eye
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
Diagnosis[edit]
A comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist is necessary to diagnose cataracts. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Visual acuity test: This test measures how well a patient can see at various distances.
- Slit-lamp examination: A slit lamp uses a high-intensity light source and a microscope to examine the structures at the front of the eye, including the lens.
- Retinal examination: After dilating the pupils with eye drops, the doctor uses a special instrument to examine the retina and optic nerve at the back of the eye.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for cataracts depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on the patient's daily activities. Early-stage cataracts may be managed with non-surgical interventions, such as:
- Updating eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Using magnifying lenses for reading or other close-up work
- Wearing sunglasses to reduce glare
When cataracts significantly impair vision and interfere with daily activities, cataract surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Cataract surgery is generally safe and effective, with a high success rate in improving vision.
Prevention[edit]
While cataracts cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and precautions may help reduce the risk of developing them:
- Protecting the eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses with UV protection
- Managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension
- Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, including fruits and vegetables
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
- Having regular eye examinations to monitor eye health and detect cataracts early
External links[edit]
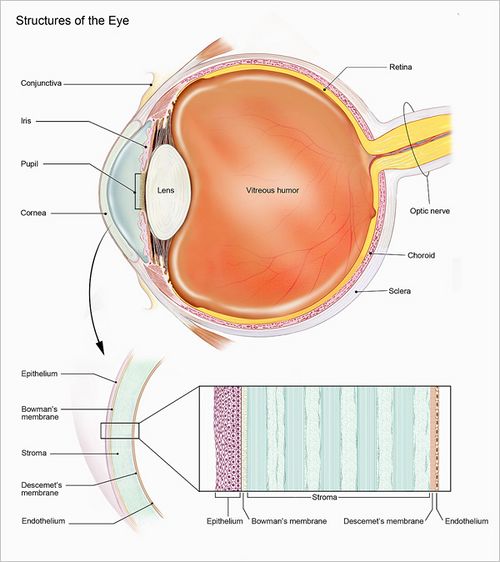
Topics in Ophthalmology[edit]
- Macular degeneration (AMD)
- Amblyopia
- Anophthalmia and * Microphthalmia
- Astigmatism
- Blepharitis
- Cataract
- Color blindness
- Cornea and Corneal disease
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Dry eye
- Floaters
- Glaucoma
- Hyperopia
- Intracranial hypertension
- Low vision
- Macular edema
- Myopia
- Pink Eye or Conjunctivitis
- Presbyopia
- Refractive errors
- Retinal detachment
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Retinoblastoma
- Retinopathy of prematurity
- Uveitis
- Vitreous detachment


