Peroxisomal disorder: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Peroxisomal disorder | |||
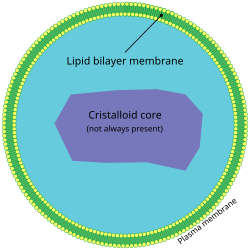
| image = [[File:Peroxisome.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram of a peroxisome | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Developmental delay]], [[neurological abnormalities]], [[liver dysfunction]], [[hearing loss]], [[vision problems]] | |||
| onset = [[Infancy]] or [[childhood]] | |||
| duration = [[Chronic (medicine)|Chronic]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]]s affecting peroxisome biogenesis or function | |||
| risks = [[Family history]] of peroxisomal disorders | |||
| diagnosis = [[Genetic testing]], [[biochemical assays]] | |||
| differential = [[Mitochondrial disorder]]s, [[lysosomal storage disorder]]s | |||
| treatment = [[Symptomatic treatment]], [[dietary management]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies depending on specific disorder and severity | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Peroxisomal disorder}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Peroxisomal disorder}} | ||
A '''peroxisomal disorder''' is a type of [[metabolic disorder]] that results from dysfunctions in the [[peroxisome]], an organelle found in virtually all [[eukaryotic cells]]. Peroxisomes play a crucial role in the metabolism of [[lipids]] and the detoxification of [[reactive oxygen species]]. Disorders of peroxisomes can lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations, often affecting multiple [[organ systems]]. | A '''peroxisomal disorder''' is a type of [[metabolic disorder]] that results from dysfunctions in the [[peroxisome]], an organelle found in virtually all [[eukaryotic cells]]. Peroxisomes play a crucial role in the metabolism of [[lipids]] and the detoxification of [[reactive oxygen species]]. Disorders of peroxisomes can lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations, often affecting multiple [[organ systems]]. | ||
== Function of Peroxisomes == | == Function of Peroxisomes == | ||
Peroxisomes are involved in several key metabolic pathways, including the [[beta-oxidation]] of very long chain [[fatty acids]], the biosynthesis of [[plasmalogens]], and the detoxification of [[hydrogen peroxide]]. They also play a role in the metabolism of [[bile acids]] and the synthesis of [[cholesterol]]. | Peroxisomes are involved in several key metabolic pathways, including the [[beta-oxidation]] of very long chain [[fatty acids]], the biosynthesis of [[plasmalogens]], and the detoxification of [[hydrogen peroxide]]. They also play a role in the metabolism of [[bile acids]] and the synthesis of [[cholesterol]]. | ||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
Peroxisomal disorders can be classified into two main categories: | Peroxisomal disorders can be classified into two main categories: | ||
=== Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders (PBDs) === | === Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders (PBDs) === | ||
PBDs are caused by defects in the assembly of peroxisomes. The most well-known PBD is [[Zellweger syndrome]], which is characterized by severe neurological impairment, [[liver dysfunction]], and craniofacial abnormalities. | PBDs are caused by defects in the assembly of peroxisomes. The most well-known PBD is [[Zellweger syndrome]], which is characterized by severe neurological impairment, [[liver dysfunction]], and craniofacial abnormalities. | ||
=== Single Enzyme Deficiencies === | === Single Enzyme Deficiencies === | ||
These disorders result from the deficiency of a single peroxisomal enzyme. Examples include [[X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy]] and [[Refsum disease]]. | These disorders result from the deficiency of a single peroxisomal enzyme. Examples include [[X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy]] and [[Refsum disease]]. | ||
== Clinical Manifestations == | == Clinical Manifestations == | ||
The clinical presentation of peroxisomal disorders can vary widely, but common features include: | The clinical presentation of peroxisomal disorders can vary widely, but common features include: | ||
| Line 23: | Line 32: | ||
* [[Skeletal abnormalities]] and [[craniofacial dysmorphism]]. | * [[Skeletal abnormalities]] and [[craniofacial dysmorphism]]. | ||
* [[Vision and hearing impairments]]. | * [[Vision and hearing impairments]]. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, biochemical tests, and genetic testing. Biochemical tests may include the measurement of very long chain fatty acids, plasmalogens, and bile acid intermediates in the blood. | Diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, biochemical tests, and genetic testing. Biochemical tests may include the measurement of very long chain fatty acids, plasmalogens, and bile acid intermediates in the blood. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Currently, there is no cure for peroxisomal disorders, and treatment is primarily supportive. Management may include dietary modifications, physical therapy, and symptomatic treatment for seizures and other complications. | Currently, there is no cure for peroxisomal disorders, and treatment is primarily supportive. Management may include dietary modifications, physical therapy, and symptomatic treatment for seizures and other complications. | ||
== Research and Future Directions == | == Research and Future Directions == | ||
Research into peroxisomal disorders is ongoing, with efforts focused on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying these conditions and developing potential therapies. Gene therapy and enzyme replacement therapy are areas of active investigation. | Research into peroxisomal disorders is ongoing, with efforts focused on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying these conditions and developing potential therapies. Gene therapy and enzyme replacement therapy are areas of active investigation. | ||
== See also == | |||
== | |||
* [[Zellweger syndrome]] | * [[Zellweger syndrome]] | ||
* [[X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy]] | * [[X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy]] | ||
* [[Refsum disease]] | * [[Refsum disease]] | ||
* [[Metabolic disorder]] | * [[Metabolic disorder]] | ||
[[Category:Genetic disorders]] | [[Category:Genetic disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Metabolic disorders]] | [[Category:Metabolic disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:24, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Peroxisomal disorder | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Developmental delay, neurological abnormalities, liver dysfunction, hearing loss, vision problems |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Infancy or childhood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations affecting peroxisome biogenesis or function |
| Risks | Family history of peroxisomal disorders |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, biochemical assays |
| Differential diagnosis | Mitochondrial disorders, lysosomal storage disorders |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Symptomatic treatment, dietary management, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on specific disorder and severity |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A peroxisomal disorder is a type of metabolic disorder that results from dysfunctions in the peroxisome, an organelle found in virtually all eukaryotic cells. Peroxisomes play a crucial role in the metabolism of lipids and the detoxification of reactive oxygen species. Disorders of peroxisomes can lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations, often affecting multiple organ systems.
Function of Peroxisomes[edit]
Peroxisomes are involved in several key metabolic pathways, including the beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids, the biosynthesis of plasmalogens, and the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide. They also play a role in the metabolism of bile acids and the synthesis of cholesterol.
Classification[edit]
Peroxisomal disorders can be classified into two main categories:
Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders (PBDs)[edit]
PBDs are caused by defects in the assembly of peroxisomes. The most well-known PBD is Zellweger syndrome, which is characterized by severe neurological impairment, liver dysfunction, and craniofacial abnormalities.
Single Enzyme Deficiencies[edit]
These disorders result from the deficiency of a single peroxisomal enzyme. Examples include X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy and Refsum disease.
Clinical Manifestations[edit]
The clinical presentation of peroxisomal disorders can vary widely, but common features include:
- Neurological symptoms such as hypotonia, seizures, and developmental delay.
- Liver dysfunction leading to hepatomegaly and jaundice.
- Skeletal abnormalities and craniofacial dysmorphism.
- Vision and hearing impairments.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, biochemical tests, and genetic testing. Biochemical tests may include the measurement of very long chain fatty acids, plasmalogens, and bile acid intermediates in the blood.
Treatment[edit]
Currently, there is no cure for peroxisomal disorders, and treatment is primarily supportive. Management may include dietary modifications, physical therapy, and symptomatic treatment for seizures and other complications.
Research and Future Directions[edit]
Research into peroxisomal disorders is ongoing, with efforts focused on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying these conditions and developing potential therapies. Gene therapy and enzyme replacement therapy are areas of active investigation.