Meesmann corneal dystrophy: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Meesmann corneal dystrophy''' ([[ICD-10]]: H18.5) is a rare form of [[corneal dystrophy]], a group of genetic, often progressive, eye disorders characterized by the accumulation of abnormal material in the [[cornea]]. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Meesmann corneal dystrophy | |||
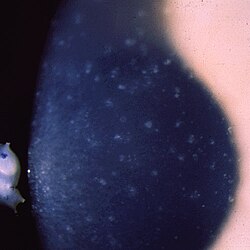
| image = [[File:Meesmann_corneal_dystrophy_-_Multiple_opaque_spots_in_the_corneal_epithelium.JPEG|250px]] | |||
| caption = Multiple opaque spots in the corneal epithelium characteristic of Meesmann corneal dystrophy | |||
| synonyms = Meesmann epithelial corneal dystrophy, Meesmann dystrophy | |||
| field = [[Ophthalmology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Corneal epithelium]] microcysts, [[vision]] disturbances | |||
| complications = [[Corneal erosion]], [[photophobia]] | |||
| onset = Early childhood | |||
| duration = Lifelong | |||
| causes = Mutations in [[KRT3]] or [[KRT12]] genes | |||
| risks = Genetic predisposition | |||
| diagnosis = [[Slit-lamp examination]], [[genetic testing]] | |||
| differential = Other [[corneal dystrophies]] | |||
| treatment = [[Lubricating eye drops]], [[contact lenses]], [[keratoplasty]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with management | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = None directly attributable | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Wiki_Drawing_-_Autosomal_Dominant_(1).svg|Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Meesmann corneal dystrophy''' ([[ICD-10]]: H18.5) is a rare form of [[corneal dystrophy]], a group of genetic, often progressive, eye disorders characterized by the accumulation of abnormal material in the [[cornea]]. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. | |||
Meesmann corneal dystrophy is caused by mutations in the [[KRT3]] or [[KRT12]] gene. These genes provide instructions for making proteins that are part of intermediate filaments, tough, resilient fibers that provide support and strength to cells. The KRT3 and KRT12 genes are specifically involved in the production of keratins, a type of intermediate filament protein, in corneal epithelial cells. Mutations in these genes alter the structure and function of these proteins, leading to the formation of abnormal, blister-like lesions in the cornea. | Meesmann corneal dystrophy is caused by mutations in the [[KRT3]] or [[KRT12]] gene. These genes provide instructions for making proteins that are part of intermediate filaments, tough, resilient fibers that provide support and strength to cells. The KRT3 and KRT12 genes are specifically involved in the production of keratins, a type of intermediate filament protein, in corneal epithelial cells. Mutations in these genes alter the structure and function of these proteins, leading to the formation of abnormal, blister-like lesions in the cornea. | ||
Symptoms of Meesmann corneal dystrophy typically appear in early childhood and may include [[photophobia]] (light sensitivity), a gritty sensation in the eyes, and mild [[visual impairment]]. However, many affected individuals are asymptomatic and the condition is often discovered during a routine eye examination. | Symptoms of Meesmann corneal dystrophy typically appear in early childhood and may include [[photophobia]] (light sensitivity), a gritty sensation in the eyes, and mild [[visual impairment]]. However, many affected individuals are asymptomatic and the condition is often discovered during a routine eye examination. | ||
Treatment for Meesmann corneal dystrophy is typically supportive and may include the use of lubricating eye drops or ointments to relieve discomfort. In severe cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary. | Treatment for Meesmann corneal dystrophy is typically supportive and may include the use of lubricating eye drops or ointments to relieve discomfort. In severe cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary. | ||
[[Category:Eye diseases]] | [[Category:Eye diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Genetic diseases]] | [[Category:Genetic diseases]] | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Corneal dystrophy]] | * [[Corneal dystrophy]] | ||
* [[Keratin]] | * [[Keratin]] | ||
* [[Corneal transplantation]] | * [[Corneal transplantation]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
* [https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/meesmann-corneal-dystrophy Genetics Home Reference: Meesmann corneal dystrophy] | * [https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/meesmann-corneal-dystrophy Genetics Home Reference: Meesmann corneal dystrophy] | ||
* [https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7050/meesmann-corneal-dystrophy National Organization for Rare Disorders: Meesmann corneal dystrophy] | * [https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7050/meesmann-corneal-dystrophy National Organization for Rare Disorders: Meesmann corneal dystrophy] | ||
{{Eye diseases}} | {{Eye diseases}} | ||
{{Genetic disorders}} | {{Genetic disorders}} | ||
{{Rare diseases}} | {{Rare diseases}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:36, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Meesmann corneal dystrophy | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Meesmann epithelial corneal dystrophy, Meesmann dystrophy |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Corneal epithelium microcysts, vision disturbances |
| Complications | Corneal erosion, photophobia |
| Onset | Early childhood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Mutations in KRT3 or KRT12 genes |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Slit-lamp examination, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Other corneal dystrophies |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Lubricating eye drops, contact lenses, keratoplasty |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with management |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | None directly attributable |

Meesmann corneal dystrophy (ICD-10: H18.5) is a rare form of corneal dystrophy, a group of genetic, often progressive, eye disorders characterized by the accumulation of abnormal material in the cornea. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Meesmann corneal dystrophy is caused by mutations in the KRT3 or KRT12 gene. These genes provide instructions for making proteins that are part of intermediate filaments, tough, resilient fibers that provide support and strength to cells. The KRT3 and KRT12 genes are specifically involved in the production of keratins, a type of intermediate filament protein, in corneal epithelial cells. Mutations in these genes alter the structure and function of these proteins, leading to the formation of abnormal, blister-like lesions in the cornea. Symptoms of Meesmann corneal dystrophy typically appear in early childhood and may include photophobia (light sensitivity), a gritty sensation in the eyes, and mild visual impairment. However, many affected individuals are asymptomatic and the condition is often discovered during a routine eye examination. Treatment for Meesmann corneal dystrophy is typically supportive and may include the use of lubricating eye drops or ointments to relieve discomfort. In severe cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
- Genetics Home Reference: Meesmann corneal dystrophy
- National Organization for Rare Disorders: Meesmann corneal dystrophy
| Eye diseases and disorders | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This eye diseases related article is a stub.
|
| Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit]
Meesmann corneal dystrophy is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Meesmann corneal dystrophy
|


