B-cell lymphoma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma affecting B cells}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) | {{Infobox medical condition (new) | ||
| name = B-cell lymphoma | | name = B-cell lymphoma | ||
| synonyms = | | synonyms = B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, B-NHL | ||
| image = Large b cell lymphoma - cytology small.jpg | | image = Large b cell lymphoma - cytology small.jpg | ||
| caption = [[Micrograph]] showing a large B cell lymphoma. [[Field stain]]. | | caption = [[Micrograph]] showing a large B cell lymphoma. [[Field stain]]. | ||
| pronounce = | | pronounce = | ||
| field = [[Hematology]], [[ | | field = [[Hematology]], [[Oncology]] | ||
| symptoms = | | symptoms = Swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue | ||
| complications = | | complications = Immunodeficiency, bone marrow suppression, organ infiltration, secondary cancers | ||
| onset = | | onset = Variable; often middle-aged or older adults | ||
| duration = | | duration = Chronic or progressive if untreated | ||
| types = | | types = [[Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma]], [[Follicular lymphoma]], [[Mantle cell lymphoma]], [[Burkitt lymphoma]], [[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia|CLL]] | ||
| causes = | | causes = Unknown; may involve [[genetic mutations]], [[Epstein-Barr virus]], or [[immunosuppression]] | ||
| risks = | | risks = Family history, age, autoimmune diseases, organ transplantation, HIV/AIDS | ||
| diagnosis = | | diagnosis = [[Lymph node biopsy]], [[Immunophenotyping]], [[Flow cytometry]], [[PET-CT]] | ||
| differential = | | differential = [[T-cell lymphoma]], [[Hodgkin lymphoma]], [[Infectious mononucleosis]], [[Reactive lymphadenopathy]] | ||
| prevention = | | prevention = None specific; managing underlying risk factors may help | ||
| treatment = | | treatment = [[Chemotherapy]], [[Radiation therapy]], [[Immunotherapy]] (e.g. rituximab), [[Stem cell transplantation]] | ||
| medication = | | medication = [[Rituximab]], [[Cyclophosphamide]], [[Doxorubicin]], [[Vincristine]], [[Prednisone]] (R-CHOP regimen) | ||
| prognosis = | | prognosis = Varies by subtype; can range from indolent to aggressive forms | ||
| frequency = | | frequency = Common subtype of [[non-Hodgkin lymphoma]]; over 80% of cases | ||
| deaths = | | deaths = Depends on type and response to treatment; aggressive forms can be fatal without therapy | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Image:Hodgkin lymphoma cytology large.jpg|thumb|left|[[Micrograph]] showing [[Hodgkin's lymphoma]], a type of B cell lymphoma that is usually considered separate from other B cell lymphomas. [[Field stain]].]] | |||
[[File:CT of primary B-cell lymphoma left ilium.jpg|thumb|left|CT scan of primary B cell lymphoma in the left [[ilium (bone)|ilium]], as diffuse cortical and trabecular thickening of the hemipelvis, mimicking [[Paget's disease of bone|Paget's disease]].]] | |||
B-cell | '''B-cell lymphoma''' is a type of [[non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] (NHL) that originates in [[B lymphocytes]], which are a type of [[white blood cell]] responsible for producing [[antibodies]]. B-cell lymphomas are the most common form of NHL and can vary significantly in their presentation, behavior, and response to treatment. | ||
==Classification== | |||
B-cell lymphomas are classified based on their appearance under the microscope, their genetic features, and their clinical behavior. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification system is commonly used to categorize these lymphomas. Major types include: | |||
* [[Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma]] (DLBCL) | |||
* [[Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma]] (DLBCL) | |||
* [[Follicular lymphoma]] | * [[Follicular lymphoma]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]]/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) | ||
* [[ | * [[Mantle cell lymphoma]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Burkitt lymphoma]] | ||
* [[Marginal zone lymphoma]] | |||
* [[Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma]] | |||
== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
B-cell lymphomas arise from the malignant transformation of B cells at various stages of their development. Genetic mutations, chromosomal translocations, and other molecular abnormalities can lead to uncontrolled proliferation of these cells. For example, the translocation t(14;18) is commonly associated with follicular lymphoma, leading to overexpression of the BCL2 gene, which inhibits apoptosis. | |||
== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of B-cell lymphoma can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common symptoms include: | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] (swollen lymph nodes) | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* [[Night sweats]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
* [[Fatigue]] | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] (enlarged liver and spleen) | |||
== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of B-cell lymphoma typically involves a combination of: | |||
* [[Physical examination]] | |||
[[ | * [[Blood tests]] | ||
* [[Imaging studies]] such as [[CT scan]] or [[PET scan]] | |||
* [[Lymph node biopsy]] | |||
* [[Immunophenotyping]] and [[flow cytometry]] | |||
* [[Cytogenetic analysis]] | |||
== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment options for B-cell lymphoma depend on the specific type and stage of the disease, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatments include: | |||
* [[Chemotherapy]] | |||
* [[Radiation therapy]] | |||
* [[Immunotherapy]], such as [[rituximab]] | |||
* [[Targeted therapy]] | |||
* [[Stem cell transplantation]] | |||
== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for patients with B-cell lymphoma varies widely based on the type of lymphoma, stage at diagnosis, and response to treatment. Some types, like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, can be aggressive but are often curable with appropriate therapy. Others, like follicular lymphoma, tend to be indolent but may require long-term management. | |||
* [ | ==Related pages== | ||
* [ | * [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] | ||
* [[Hodgkin lymphoma]] | |||
* [[Leukemia]] | |||
* [[Immunotherapy]] | |||
{{Hematological malignancy histology}} | |||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Lymphoma]] | [[Category:Lymphoma]] | ||
[[Category:Hematology]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:56, 24 March 2025
A type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma affecting B cells
| B-cell lymphoma | |
|---|---|
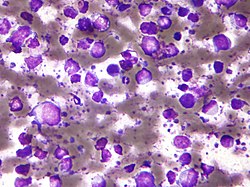
| |
| Synonyms | B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, B-NHL |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Hematology, Oncology |
| Symptoms | Swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue |
| Complications | Immunodeficiency, bone marrow suppression, organ infiltration, secondary cancers |
| Onset | Variable; often middle-aged or older adults |
| Duration | Chronic or progressive if untreated |
| Types | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Follicular lymphoma, Mantle cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, CLL |
| Causes | Unknown; may involve genetic mutations, Epstein-Barr virus, or immunosuppression |
| Risks | Family history, age, autoimmune diseases, organ transplantation, HIV/AIDS |
| Diagnosis | Lymph node biopsy, Immunophenotyping, Flow cytometry, PET-CT |
| Differential diagnosis | T-cell lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, Infectious mononucleosis, Reactive lymphadenopathy |
| Prevention | None specific; managing underlying risk factors may help |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, Radiation therapy, Immunotherapy (e.g. rituximab), Stem cell transplantation |
| Medication | Rituximab, Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, Prednisone (R-CHOP regimen) |
| Prognosis | Varies by subtype; can range from indolent to aggressive forms |
| Frequency | Common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma; over 80% of cases |
| Deaths | Depends on type and response to treatment; aggressive forms can be fatal without therapy |


B-cell lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that originates in B lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell responsible for producing antibodies. B-cell lymphomas are the most common form of NHL and can vary significantly in their presentation, behavior, and response to treatment.
Classification[edit]
B-cell lymphomas are classified based on their appearance under the microscope, their genetic features, and their clinical behavior. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification system is commonly used to categorize these lymphomas. Major types include:
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Follicular lymphoma
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- Burkitt lymphoma
- Marginal zone lymphoma
- Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma
Pathophysiology[edit]
B-cell lymphomas arise from the malignant transformation of B cells at various stages of their development. Genetic mutations, chromosomal translocations, and other molecular abnormalities can lead to uncontrolled proliferation of these cells. For example, the translocation t(14;18) is commonly associated with follicular lymphoma, leading to overexpression of the BCL2 gene, which inhibits apoptosis.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of B-cell lymphoma can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes)
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen)
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of B-cell lymphoma typically involves a combination of:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Imaging studies such as CT scan or PET scan
- Lymph node biopsy
- Immunophenotyping and flow cytometry
- Cytogenetic analysis
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options for B-cell lymphoma depend on the specific type and stage of the disease, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatments include:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Immunotherapy, such as rituximab
- Targeted therapy
- Stem cell transplantation
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with B-cell lymphoma varies widely based on the type of lymphoma, stage at diagnosis, and response to treatment. Some types, like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, can be aggressive but are often curable with appropriate therapy. Others, like follicular lymphoma, tend to be indolent but may require long-term management.
Related pages[edit]
| Leukaemias, lymphomas and related disease | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|


