Ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Slide2xzxzxz.JPG|thumb|Anatomical slide showing the ulnar collateral ligament.]] | [[File:Slide2xzxzxz.JPG|thumb|Anatomical slide showing the ulnar collateral ligament.]] | ||
[[File:Anatomy_of_the_ulnar_collateral_ligament_in_the_pitcher's_elbow.png|left|thumb|Anatomy of the ulnar collateral ligament in a pitcher's elbow.]] | [[File:Anatomy_of_the_ulnar_collateral_ligament_in_the_pitcher's_elbow.png|left|thumb|Anatomy of the ulnar collateral ligament in a pitcher's elbow.]] | ||
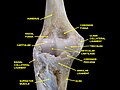
[[File:Elbow_joint_-_deep_dissection_(anterior_view,_human_cadaver).jpg|left|thumb|Deep dissection of the elbow joint, anterior view.]] | |||
The '''ulnar collateral ligament''' (UCL) of the elbow joint is a critical structure that provides stability to the elbow, particularly during overhead throwing activities. It is located on the medial side of the elbow and connects the [[humerus]] to the [[ulna]]. | The '''ulnar collateral ligament''' (UCL) of the elbow joint is a critical structure that provides stability to the elbow, particularly during overhead throwing activities. It is located on the medial side of the elbow and connects the [[humerus]] to the [[ulna]]. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Injuries to the ulnar collateral ligament are common in athletes, especially those involved in throwing sports. Such injuries can lead to pain, instability, and decreased performance. The most well-known surgical procedure to repair a torn UCL is the [[Tommy John surgery]], named after the first baseball player to undergo the procedure. | Injuries to the ulnar collateral ligament are common in athletes, especially those involved in throwing sports. Such injuries can lead to pain, instability, and decreased performance. The most well-known surgical procedure to repair a torn UCL is the [[Tommy John surgery]], named after the first baseball player to undergo the procedure. | ||
== Diagnosis and Treatment == | == Diagnosis and Treatment == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 28: | ||
* [[Tommy John surgery]] | * [[Tommy John surgery]] | ||
* [[Valgus stress]] | * [[Valgus stress]] | ||
{{human anatomy}} | |||
[[Category:Ligaments of the upper limb]] | [[Category:Ligaments of the upper limb]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Elbow_joint_-_deep_dissection_(anterior_view,_human_cadaver).jpg|Deep dissection of the elbow joint, anterior view, human cadaver | |||
File:Slide2xzxzxz.JPG|Ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:17, 18 February 2025



The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) of the elbow joint is a critical structure that provides stability to the elbow, particularly during overhead throwing activities. It is located on the medial side of the elbow and connects the humerus to the ulna.
Anatomy[edit]
The ulnar collateral ligament is composed of three distinct bands: the anterior, posterior, and transverse bands. The anterior band is the strongest and most significant for providing stability. It originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserts onto the sublime tubercle of the ulna. The posterior band is weaker and fan-like, while the transverse band, also known as Cooper's ligament, does not contribute significantly to joint stability.

Function[edit]
The primary function of the ulnar collateral ligament is to resist valgus stress at the elbow, which occurs when the forearm is forced away from the body. This is particularly important in athletes who perform repetitive overhead motions, such as baseball pitchers.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Injuries to the ulnar collateral ligament are common in athletes, especially those involved in throwing sports. Such injuries can lead to pain, instability, and decreased performance. The most well-known surgical procedure to repair a torn UCL is the Tommy John surgery, named after the first baseball player to undergo the procedure.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of UCL injuries typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies such as MRI, and sometimes diagnostic ultrasound. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's activity level. Conservative management includes rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. Surgical intervention, such as Tommy John surgery, may be necessary for complete tears or in athletes who wish to return to high-level competition.
Related Pages[edit]
| Anatomy and morphology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
-
Deep dissection of the elbow joint, anterior view, human cadaver
-
Ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint