Nateglinide
An oral antidiabetic medication
| Nateglinide | |
|---|---|
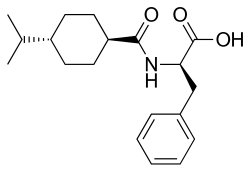
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Nateglinide is an oral antidiabetic drug used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to the class of medications known as meglitinides, which stimulate the pancreas to release insulin.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Nateglinide works by closing the ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the beta cells of the pancreas. This action leads to the opening of calcium channels, resulting in an influx of calcium ions and subsequent release of insulin. The drug is particularly effective in controlling postprandial blood glucose levels.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Nateglinide is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and has a quick onset of action. It is metabolized primarily in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, particularly CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. The drug has a short half-life, which minimizes the risk of hypoglycemia.
Clinical Use[edit]
Nateglinide is indicated for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in conjunction with diet and exercise. It is often used in combination with other antidiabetic agents such as metformin or thiazolidinediones.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of nateglinide include:
Contraindications[edit]
Nateglinide is contraindicated in patients with:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Known hypersensitivity to the drug
Administration[edit]
Nateglinide is administered orally, typically taken before meals to optimize its effect on postprandial glucose levels.
Related pages[edit]
-
Nateglinide
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
