Frontonasal dysplasia

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Frontonasal dysplasia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Median cleft face syndrome, frontonasal malformation |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hypertelorism, broad nasal bridge, cleft lip, cleft palate, craniofacial anomalies |
| Complications | Developmental delay, intellectual disability, vision problems |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history of the condition |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Oculoauriculofrontonasal syndrome, craniofrontonasal dysplasia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention, speech therapy, occupational therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on severity |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Frontonasal dysplasia (FND), also known as Median cleft face syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the head and face before birth. The condition is characterized by abnormalities that can affect the nose, eyes, and upper lip.
Symptoms and Signs[edit]
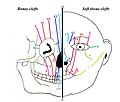
The most common features of frontonasal dysplasia are widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), a broad nose, a slit (cleft) in one or both nostrils (bifid nose), and a cleft lip and palate. Other features can include a widow's peak hairline, a flat or absent nasal bridge, and skin-covered gaps in the bones of the forehead (anterior cranial fossa meningocele).
Causes[edit]
Frontonasal dysplasia is caused by mutations in the ALX3, ALX4, and ZSWIM6 genes. These genes provide instructions for making proteins that are involved in the development of tissues and organs before birth. Mutations in these genes disrupt the normal development of the head and face, leading to the features of frontonasal dysplasia.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of frontonasal dysplasia is based on a clinical examination and confirmed by genetic testing. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI can also be used to assess the severity of the condition.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for frontonasal dysplasia is symptomatic and supportive. It often involves surgery to correct the facial abnormalities. Other treatments may include speech therapy for those with a cleft palate and special education services for those with learning disabilities.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with frontonasal dysplasia varies. Some individuals have normal intelligence and lead normal lives, while others may have learning disabilities and require special education services.
Gallery[edit]
-
Frontonasal dysplasia
-
Tessier classification of craniofacial clefts
-
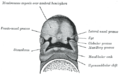
Diagram of the human skull
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian