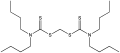
Dithiocarbamate
Dithiocarbamate is a class of organic compounds characterized by the functional group R2NCS2^-, where R can be hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, or other substituents. These compounds are widely used in various applications, including agriculture as pesticides, in rubber industry as vulcanization accelerators, and in medicine for their therapeutic properties. Dithiocarbamates are known for their fungicidal, bactericidal, and chelating properties.
Chemistry[edit]
Dithiocarbamates are derived from carbon disulfide and amines. The general synthesis involves the reaction of carbon disulfide with amines in the presence of an alkali, leading to the formation of dithiocarbamate salts. These salts can be further modified to produce various derivatives with different properties and applications. The versatility of dithiocarbamates stems from the ability to alter the R groups, which significantly affects their chemical behavior and utility.
Applications[edit]
Agriculture[edit]
In agriculture, dithiocarbamates serve primarily as fungicides to protect crops against a wide range of fungal diseases. They are among the oldest classes of fungicides, with mancozeb, maneb, and zineb being some of the most commonly used examples. These compounds act by disrupting the normal metabolism of fungal cells, effectively controlling disease spread in crops.
Rubber Industry[edit]
Dithiocarbamates are employed as vulcanization accelerators in the rubber industry. They enhance the cross-linking efficiency between rubber molecules, improving the mechanical properties and durability of rubber products. Their fast curing rates and ability to produce rubber with excellent aging properties make them valuable in manufacturing tires, seals, and other rubber goods.
Medicine[edit]
In the medical field, certain dithiocarbamate derivatives exhibit therapeutic activities, including antifungal, antibacterial, and anticancer effects. For example, disulfiram, a dithiocarbamate derivative, is used in the treatment of alcohol dependence by inhibiting the enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, leading to unpleasant effects when alcohol is consumed.
Environmental and Health Concerns[edit]
Despite their beneficial uses, dithiocarbamates raise environmental and health concerns. They can decompose to form ethylene thiourea (ETU), a potential carcinogen, under certain conditions. The use of dithiocarbamate fungicides in agriculture has been scrutinized for their potential to leave residues on food and in the environment, leading to regulatory restrictions in some countries.
Conclusion[edit]
Dithiocarbamates play a significant role in various industries due to their fungicidal, bactericidal, and chelating properties. While they offer considerable benefits, their environmental and health impacts necessitate careful management and regulatory oversight to ensure safe use.
-
Dithiocarbamate structure
-
Dithiocarbamate reaction scheme
-
Zinc dithiocarbamate complex
-
Dithiocarbamate ligand
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian