Atlantic Ocean
File:Atlantic Ocean to Africa.ogv



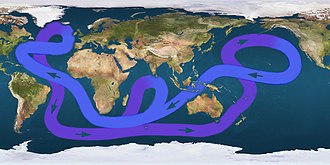
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 square kilometers (41,100,000 square miles). It covers approximately 20 percent of the Earth's surface and about 29 percent of its water surface area. It separates the "Americas" to the west from Europe and Africa to the east.
Geography[edit]
The Atlantic Ocean extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south. It is bounded by North and South America on the western side and by Europe and Africa on the eastern side. The equator subdivides it into the North Atlantic Ocean and South Atlantic Ocean.
Major Features[edit]
The Atlantic Ocean is known for its large Gulf Stream, a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates at the tip of Florida, flowing along the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the east coast of North America from Florida to Newfoundland, and the west coast of Europe. Other notable features of the Atlantic Ocean include the Baltic Sea, Black Sea, Caribbean Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea which are some of the seas that border the ocean.
History[edit]
The name "Atlantic" is derived from the Atlantis myth as described by the ancient Greek philosopher Plato. Throughout history, the Atlantic Ocean has been a significant route for navigation and trade between the Americas, Europe, and Africa. The Age of Discovery, from the late 15th century to the 18th century, was a period where European powers explored and colonized many parts of the world, significantly across the Atlantic.
Economy[edit]
The Atlantic Ocean plays a crucial role in the world economy, especially in the areas of shipping, fishing, and offshore oil and gas production. Major ports along the Atlantic coast include New York City, London, and Rotterdam. The Atlantic is also crucial for transatlantic cable routes providing telecommunications between the Americas and Europe/Africa.
Environment[edit]
The Atlantic Ocean faces several environmental challenges, including overfishing, marine pollution, and habitat destruction. Climate change is also affecting the Atlantic, with changes in water temperature and currents having impacts on marine life and weather patterns.
Flora and Fauna[edit]
The Atlantic Ocean has a diverse range of marine life, including numerous species of fish, marine mammals like whales and dolphins, and sea turtles. Coral reefs, particularly in the Caribbean Sea, are vital habitats that support a diverse ecosystem.
See also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
