Pes cavus: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Pes | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
[[File:Pes cavus and os peroneum on lateral foot X-ray.jpg|thumb | | name = Pes cavus | ||
| image = [[File:Charcot-marie-tooth_foot.jpg|250px]] | |||
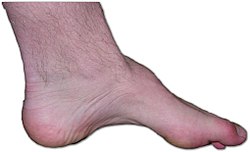
| caption = A foot with pes cavus, often associated with [[Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease]] | |||
| field = [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| synonyms = High arch, cavus foot | |||
| symptoms = High arch of the foot, [[claw toes]], pain | |||
| complications = [[Plantar fasciitis]], [[ankle instability]], [[metatarsalgia]] | |||
| onset = Can be present at birth or develop over time | |||
| duration = Long-term | |||
| causes = [[Neurological disorders]], [[muscle imbalance]], [[genetic conditions]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]], [[neuromuscular disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Flat feet]], [[normal foot arch]] | |||
| treatment = [[Orthotic devices]], [[physical therapy]], [[surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies depending on underlying cause | |||
| frequency = Relatively uncommon | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Pes cavus and os peroneum on lateral foot X-ray.jpg|left|thumb|Pes cavus foot deformity compared to a normal foot.]] | |||
'''Pes cavus''', also referred to as a "high-arched foot", is a deformity of the foot characterized by an abnormally elevated arch. Coupled with hyperextension of the toes, the foot adopts an appearance reminiscent of a claw. This condition can lead to various complications and discomforts, and can be congenital or acquired due to underlying medical conditions. | '''Pes cavus''', also referred to as a "high-arched foot", is a deformity of the foot characterized by an abnormally elevated arch. Coupled with hyperextension of the toes, the foot adopts an appearance reminiscent of a claw. This condition can lead to various complications and discomforts, and can be congenital or acquired due to underlying medical conditions. | ||
== Anatomy and Presentation == | == Anatomy and Presentation == | ||
Pes cavus is the opposite of [[flat foot|flatfoot (pes planus)]]. In a pes cavus foot: | Pes cavus is the opposite of [[flat foot|flatfoot (pes planus)]]. In a pes cavus foot: | ||
* The arch, especially the medial arch, is abnormally raised. | * The arch, especially the medial arch, is abnormally raised. | ||
* The metatarsal bones may be positioned dorsally. | * The metatarsal bones may be positioned dorsally. | ||
* Toes often exhibit a claw-like formation due to hyperextension. | * Toes often exhibit a claw-like formation due to hyperextension. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/lxx9c1B2NCE | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/lxx9c1B2NCE | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 23: | Line 35: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Pes cavus can arise from a variety of underlying causes: | Pes cavus can arise from a variety of underlying causes: | ||
* '''Congenital''': Some individuals are born with the condition. | * '''Congenital''': Some individuals are born with the condition. | ||
* '''Neurological Disorders''': Conditions like [[Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease]] or spina bifida can cause pes cavus. | * '''Neurological Disorders''': Conditions like [[Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease]] or spina bifida can cause pes cavus. | ||
* '''Trauma''': Injuries might lead to the development of this foot structure. | * '''Trauma''': Injuries might lead to the development of this foot structure. | ||
* '''Other underlying medical conditions''': Including muscular dystrophy or other neuromuscular disorders. | * '''Other underlying medical conditions''': Including muscular dystrophy or other neuromuscular disorders. | ||
== Symptoms and Complications == | == Symptoms and Complications == | ||
People with pes cavus often experience: | People with pes cavus often experience: | ||
* Pain due to uneven weight distribution. | * Pain due to uneven weight distribution. | ||
* Instability and balance issues. | * Instability and balance issues. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 48: | ||
* Increased risk of ankle sprains. | * Increased risk of ankle sprains. | ||
* Footwear fitting issues. | * Footwear fitting issues. | ||
== Diagnosis and Treatment == | == Diagnosis and Treatment == | ||
A physical examination, coupled with an assessment of the patient's medical history, typically aids in diagnosing pes cavus. In some cases, X-rays or other imaging techniques might be used. | A physical examination, coupled with an assessment of the patient's medical history, typically aids in diagnosing pes cavus. In some cases, X-rays or other imaging techniques might be used. | ||
Treatment options include: | Treatment options include: | ||
* '''Orthotics''': Custom-made insoles can provide better support and weight distribution. | * '''Orthotics''': Custom-made insoles can provide better support and weight distribution. | ||
* '''Physical Therapy''': Strengthening and stretching exercises can offer relief. | * '''Physical Therapy''': Strengthening and stretching exercises can offer relief. | ||
* '''Surgery''': In severe cases, reconstructive foot surgery might be necessary. | * '''Surgery''': In severe cases, reconstructive foot surgery might be necessary. | ||
* '''Footwear''': Specialized shoes or modifications can improve comfort. | * '''Footwear''': Specialized shoes or modifications can improve comfort. | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
Pes cavus is a notable foot deformity that can be a source of discomfort and mobility challenges for affected individuals. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can mitigate complications and enhance the quality of life. | Pes cavus is a notable foot deformity that can be a source of discomfort and mobility challenges for affected individuals. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can mitigate complications and enhance the quality of life. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Foot Anatomy]] | * [[Foot Anatomy]] | ||
* [[Orthopedics]] | * [[Orthopedics]] | ||
* [[Podiatry]] | * [[Podiatry]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* ''Pes Cavus and Its Management''. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. | * ''Pes Cavus and Its Management''. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. | ||
* ''Clinical Assessment and Treatment of Pes Cavus''. Podiatry Today. | * ''Clinical Assessment and Treatment of Pes Cavus''. Podiatry Today. | ||
* ''High-Arched Foot – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment''. WebMD. | * ''High-Arched Foot – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment''. WebMD. | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
[[Category:Medical Conditions]] | [[Category:Medical Conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Podiatry]] | [[Category:Podiatry]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Pes cavus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | High arch, cavus foot |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | High arch of the foot, claw toes, pain |
| Complications | Plantar fasciitis, ankle instability, metatarsalgia |
| Onset | Can be present at birth or develop over time |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Neurological disorders, muscle imbalance, genetic conditions |
| Risks | Family history, neuromuscular disorders |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Flat feet, normal foot arch |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Orthotic devices, physical therapy, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Relatively uncommon |
| Deaths | N/A |

Pes cavus, also referred to as a "high-arched foot", is a deformity of the foot characterized by an abnormally elevated arch. Coupled with hyperextension of the toes, the foot adopts an appearance reminiscent of a claw. This condition can lead to various complications and discomforts, and can be congenital or acquired due to underlying medical conditions.
Anatomy and Presentation[edit]
Pes cavus is the opposite of flatfoot (pes planus). In a pes cavus foot:
- The arch, especially the medial arch, is abnormally raised.
- The metatarsal bones may be positioned dorsally.
- Toes often exhibit a claw-like formation due to hyperextension.
Causes[edit]
Pes cavus can arise from a variety of underlying causes:
- Congenital: Some individuals are born with the condition.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease or spina bifida can cause pes cavus.
- Trauma: Injuries might lead to the development of this foot structure.
- Other underlying medical conditions: Including muscular dystrophy or other neuromuscular disorders.
Symptoms and Complications[edit]
People with pes cavus often experience:
- Pain due to uneven weight distribution.
- Instability and balance issues.
- Calluses on the ball, side, or heel of the foot.
- Increased risk of ankle sprains.
- Footwear fitting issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
A physical examination, coupled with an assessment of the patient's medical history, typically aids in diagnosing pes cavus. In some cases, X-rays or other imaging techniques might be used. Treatment options include:
- Orthotics: Custom-made insoles can provide better support and weight distribution.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises can offer relief.
- Surgery: In severe cases, reconstructive foot surgery might be necessary.
- Footwear: Specialized shoes or modifications can improve comfort.
Conclusion[edit]
Pes cavus is a notable foot deformity that can be a source of discomfort and mobility challenges for affected individuals. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can mitigate complications and enhance the quality of life.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
- Pes Cavus and Its Management. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery.
- Clinical Assessment and Treatment of Pes Cavus. Podiatry Today.
- High-Arched Foot – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment. WebMD.


