Leishmaniasis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Leishmaniasis | |||
| image = [[File:Skin_ulcer_due_to_leishmaniasis,_hand_of_Central_American_adult_3MG0037_lores.jpg|alt=Skin ulcer due to leishmaniasis on the hand of a Central American adult]] | |||
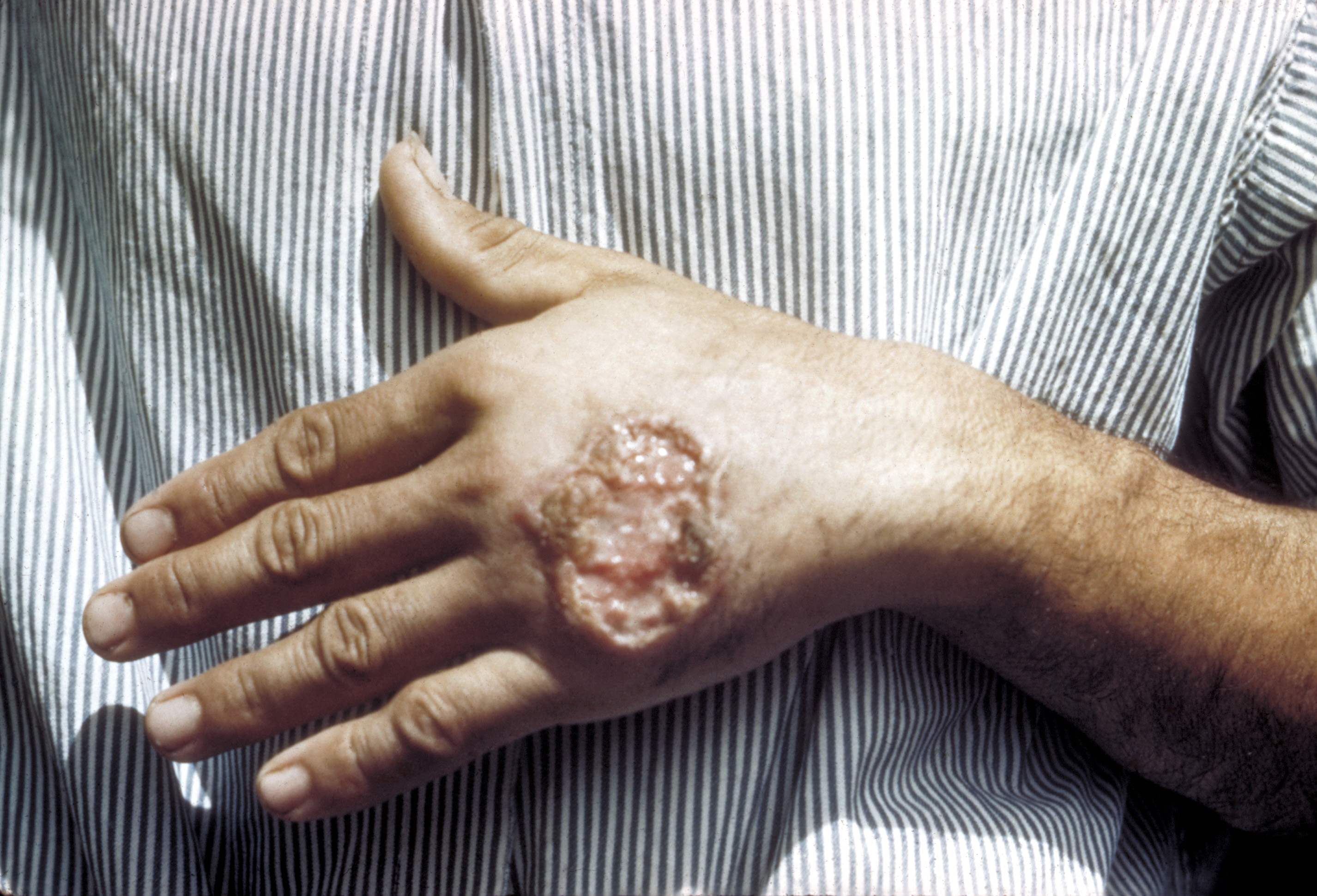
| caption = Skin ulcer due to leishmaniasis on the hand of a Central American adult | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Skin ulcer]], [[fever]], [[weight loss]], [[enlarged spleen]] | |||
| complications = [[Anemia]], [[secondary infections]] | |||
| onset = Weeks to months after [[sandfly]] bite | |||
| duration = Months to years | |||
| causes = [[Leishmania]] [[parasite]] spread by [[sandfly]] bites | |||
| risks = [[Malnutrition]], [[poverty]], [[deforestation]], [[urbanization]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Microscopy]], [[culture]], [[PCR]] | |||
| differential = [[Tuberculosis]], [[syphilis]], [[leprosy]], [[fungal infections]] | |||
| prevention = [[Insect repellent]], [[bed nets]], [[protective clothing]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antimonial]] drugs, [[amphotericin B]], [[miltefosine]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, can be fatal if untreated | |||
| frequency = 4 to 12 million people currently infected | |||
| deaths = 20,000 to 30,000 per year | |||
}} | |||
'''Other Names: ''' | '''Other Names: ''' | ||
Kala-azar; Visceral leishmaniasis (subtype); Cutaneous leishmaniasis (subtype) | Kala-azar; Visceral leishmaniasis (subtype); Cutaneous leishmaniasis (subtype) | ||
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease that is found in parts of the tropics, subtropics, and southern Europe. | |||
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease that is found in parts of the tropics, subtropics, and southern Europe. | [[File:Leishmaniasis ulcer.jpg|left|thumb|Cutaneous leishmaniasis ulcer]] | ||
[[File:Leishmaniasis ulcer.jpg|thumb | |||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 33: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== '''Cause''' == | == '''Cause''' == | ||
[[File:Leishmania LifeCycle.gif|thumb]] | [[File:Leishmania LifeCycle.gif|left|thumb]] | ||
Leishmaniasis is caused by infection with [[Leishmania parasites]], which are spread by the bite of '''phlebotomine sand flies'''. | Leishmaniasis is caused by infection with [[Leishmania parasites]], which are spread by the bite of '''phlebotomine sand flies'''. | ||
Overall, infection in people is caused by more than 20 species (types) of Leishmania parasites, which are spread by about 30 species of phlebotomine sand flies; particular species of the parasite are spread by particular sand flies. The sand fly vectors generally are the most active during twilight, evening, and night-time hours (from dusk to dawn). | Overall, infection in people is caused by more than 20 species (types) of Leishmania parasites, which are spread by about 30 species of phlebotomine sand flies; particular species of the parasite are spread by particular sand flies. The sand fly vectors generally are the most active during twilight, evening, and night-time hours (from dusk to dawn). | ||
== '''Types''' == | == '''Types''' == | ||
There are several different forms of leishmaniasis in people. The most common forms are '''cutaneous leishmaniasis''', which causes skin sores, and '''visceral leishmaniasis''', which affects several internal organs (usually spleen, liver, and bone marrow). | There are several different forms of leishmaniasis in people. The most common forms are '''cutaneous leishmaniasis''', which causes skin sores, and '''visceral leishmaniasis''', which affects several internal organs (usually spleen, liver, and bone marrow). | ||
== '''Epidemiology & Risk Factors''' == | == '''Epidemiology & Risk Factors''' == | ||
Leishmaniasis is found in people in focal areas of approximately 90 countries in the tropics, subtropics, and southern Europe. The ecologic settings range from rain forests to deserts. Leishmaniasis usually is more common in rural than in urban areas, but it is found in the outskirts of some cities. Climate and other environmental changes have the potential to expand the geographic range of the sand fly vectors and the areas in the world where leishmaniasis is found. | Leishmaniasis is found in people in focal areas of approximately 90 countries in the tropics, subtropics, and southern Europe. The ecologic settings range from rain forests to deserts. Leishmaniasis usually is more common in rural than in urban areas, but it is found in the outskirts of some cities. Climate and other environmental changes have the potential to expand the geographic range of the sand fly vectors and the areas in the world where leishmaniasis is found. | ||
The number of new cases may vary or change over time and are difficult to estimate. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, estimates of the number of new cases per year have ranged from approximately 700,000 to 1.2 million or more. For visceral leishmaniasis, the estimated number of new cases per year may have decreased to <100,000, but previous estimates ranged up to 400,000 or more cases. | The number of new cases may vary or change over time and are difficult to estimate. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, estimates of the number of new cases per year have ranged from approximately 700,000 to 1.2 million or more. For visceral leishmaniasis, the estimated number of new cases per year may have decreased to <100,000, but previous estimates ranged up to 400,000 or more cases. | ||
== '''Symptoms''' == | == '''Symptoms''' == | ||
For most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. | For most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. | ||
80%-99% of people have these symptoms | 80%-99% of people have these symptoms | ||
* Abnormal bleeding(Bleeding tendency) | * Abnormal bleeding(Bleeding tendency) | ||
| Line 45: | Line 58: | ||
* Skin ulcer(Open skin sore) | * Skin ulcer(Open skin sore) | ||
* Splenomegaly(Increased spleen size) | * Splenomegaly(Increased spleen size) | ||
30%-79% of people have these symptoms | 30%-79% of people have these symptoms | ||
* Anemia(Low number of red blood cells or hemoglobin) | * Anemia(Low number of red blood cells or hemoglobin) | ||
| Line 54: | Line 66: | ||
* [[Pallor]] | * [[Pallor]] | ||
* Weight loss | * Weight loss | ||
5%-29% of people have these symptoms | 5%-29% of people have these symptoms | ||
* [[Anorexia]] | * [[Anorexia]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 71: | ||
* Leukopenia(Decreased blood leukocyte number) | * Leukopenia(Decreased blood leukocyte number) | ||
* Thrombocytopenia(Low platelet count) | * Thrombocytopenia(Low platelet count) | ||
== '''Diagnosis''' == | == '''Diagnosis''' == | ||
Various laboratory methods can be used to diagnose | Various laboratory methods can be used to diagnose leishmaniasis—to detect the parasite as well as to identify the Leishmania species (type). | ||
Tissue specimens—such as from skin sores (for cutaneous leishmaniasis) or from [[bone marrow]] (for visceral leishmaniasis)—can be examined for the parasite under a [[microscope]], in special cultures, and by molecular tests. | |||
Tissue | |||
Blood tests that detect [[antibody]] (an immune response) to the parasite can be helpful for cases of visceral leishmaniasis; tests to look for the parasite (or its DNA) itself usually also are done. | Blood tests that detect [[antibody]] (an immune response) to the parasite can be helpful for cases of visceral leishmaniasis; tests to look for the parasite (or its DNA) itself usually also are done. | ||
Several different [[polymerase chain reaction]] (PCR) tests are available for the detection of ''Leishmania'' DNA. | Several different [[polymerase chain reaction]] (PCR) tests are available for the detection of ''Leishmania'' DNA. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
[[File:Paromomycin structure.svg|thumb | [[File:Paromomycin structure.svg|left|thumb|[[Paromomycin]] is an inexpensive (US$10) and effective treatment for leishmaniasis.]] | ||
The treatment is determined by where the disease is acquired, the species of ''Leishmania'', and the type of infection. | The treatment is determined by where the disease is acquired, the species of ''Leishmania'', and the type of infection. | ||
For visceral leishmaniasis in India, South America, and the Mediterranean, [[liposomal amphotericin B]] is the recommended treatment and is often used as a single dose. | For visceral leishmaniasis in India, South America, and the Mediterranean, [[liposomal amphotericin B]] is the recommended treatment and is often used as a single dose. | ||
| Line 79: | Line 87: | ||
Pentamidine is effective for ''L. guyanensis''.ral [[fluconazole]] or [[itraconazole]] appears effective in ''L. major'' and ''L. tropica'' | Pentamidine is effective for ''L. guyanensis''.ral [[fluconazole]] or [[itraconazole]] appears effective in ''L. major'' and ''L. tropica'' | ||
The medication(s) listed below have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as orphan products for treatment of this condition. | The medication(s) listed below have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as orphan products for treatment of this condition. | ||
* '''[[Amphotericin B Liposomal]] '''(Brand name: | * '''[[Amphotericin B Liposomal]] '''(Brand name: AmBisome®) Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. | ||
* '''[[miltefosine]] '''(Brand name: Impavido)Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani; cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis, Leishmania guyanensis, and Leishmania panamensis; and mucosal leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis. | * '''[[miltefosine]] '''(Brand name: Impavido)Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani; cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis, Leishmania guyanensis, and Leishmania panamensis; and mucosal leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis. | ||
{{Protozoal diseases}} | {{Protozoal diseases}} | ||
{{Portal bar|Medicine}} | {{Portal bar|Medicine}} | ||
[[Category:Leishmaniasis| ]] | [[Category:Leishmaniasis| ]] | ||
[[Category:Dog diseases]] | [[Category:Dog diseases]] | ||
| Line 94: | Line 99: | ||
[[Category:RTTID]] | [[Category:RTTID]] | ||
[[Category:Zoonoses]] | [[Category:Zoonoses]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:18, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Leishmaniasis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Skin ulcer, fever, weight loss, enlarged spleen |
| Complications | Anemia, secondary infections |
| Onset | Weeks to months after sandfly bite |
| Duration | Months to years |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Leishmania parasite spread by sandfly bites |
| Risks | Malnutrition, poverty, deforestation, urbanization |
| Diagnosis | Microscopy, culture, PCR |
| Differential diagnosis | Tuberculosis, syphilis, leprosy, fungal infections |
| Prevention | Insect repellent, bed nets, protective clothing |
| Treatment | Antimonial drugs, amphotericin B, miltefosine |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, can be fatal if untreated |
| Frequency | 4 to 12 million people currently infected |
| Deaths | 20,000 to 30,000 per year |
Other Names:
Kala-azar; Visceral leishmaniasis (subtype); Cutaneous leishmaniasis (subtype)
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease that is found in parts of the tropics, subtropics, and southern Europe.

Cause[edit]

Leishmaniasis is caused by infection with Leishmania parasites, which are spread by the bite of phlebotomine sand flies. Overall, infection in people is caused by more than 20 species (types) of Leishmania parasites, which are spread by about 30 species of phlebotomine sand flies; particular species of the parasite are spread by particular sand flies. The sand fly vectors generally are the most active during twilight, evening, and night-time hours (from dusk to dawn).
Types[edit]
There are several different forms of leishmaniasis in people. The most common forms are cutaneous leishmaniasis, which causes skin sores, and visceral leishmaniasis, which affects several internal organs (usually spleen, liver, and bone marrow).
Epidemiology & Risk Factors[edit]
Leishmaniasis is found in people in focal areas of approximately 90 countries in the tropics, subtropics, and southern Europe. The ecologic settings range from rain forests to deserts. Leishmaniasis usually is more common in rural than in urban areas, but it is found in the outskirts of some cities. Climate and other environmental changes have the potential to expand the geographic range of the sand fly vectors and the areas in the world where leishmaniasis is found. The number of new cases may vary or change over time and are difficult to estimate. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, estimates of the number of new cases per year have ranged from approximately 700,000 to 1.2 million or more. For visceral leishmaniasis, the estimated number of new cases per year may have decreased to <100,000, but previous estimates ranged up to 400,000 or more cases.
Symptoms[edit]
For most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. 80%-99% of people have these symptoms
- Abnormal bleeding(Bleeding tendency)
- Abnormal macrophage morphology
- Abnormal oral mucosa morphology(Abnormality of lining of mouth)
- Hepatomegaly(Enlarged liver)
- Lymphadenopathy(Swollen lymph nodes)
- Night sweats
- Pancytopenia(Low blood cell count)
- Papule
- Recurrent fever(Episodic fever)
- Rhinitis(Nasal inflammation)
- Skin plaque
- Skin ulcer(Open skin sore)
- Splenomegaly(Increased spleen size)
30%-79% of people have these symptoms
- Anemia(Low number of red blood cells or hemoglobin)
- Arthralgia(Joint pain)
- Elevated hepatic transaminase(High liver enzymes)
- Hypoalbuminemia(Low blood albumin)
- Increased circulating antibody level
- Pallor
- Weight loss
5%-29% of people have these symptoms
- Anorexia
- Fatigue(Tired)
- Leukopenia(Decreased blood leukocyte number)
- Thrombocytopenia(Low platelet count)
Diagnosis[edit]
Various laboratory methods can be used to diagnose leishmaniasis—to detect the parasite as well as to identify the Leishmania species (type). Tissue specimens—such as from skin sores (for cutaneous leishmaniasis) or from bone marrow (for visceral leishmaniasis)—can be examined for the parasite under a microscope, in special cultures, and by molecular tests. Blood tests that detect antibody (an immune response) to the parasite can be helpful for cases of visceral leishmaniasis; tests to look for the parasite (or its DNA) itself usually also are done. Several different polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests are available for the detection of Leishmania DNA.
Treatment[edit]

The treatment is determined by where the disease is acquired, the species of Leishmania, and the type of infection. For visceral leishmaniasis in India, South America, and the Mediterranean, liposomal amphotericin B is the recommended treatment and is often used as a single dose.
Rates of cure with a single dose of amphotericin have been reported as 95%.
In India, almost all infections are resistant to pentavalent antimonials. In Africa, a combination of pentavalent antimonials and paromomycin is recommended. Miltefosine, an oral medication, is effective against both visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis. A number of topical treatments may be used for cutaneous leishmaniasis. Which treatments are effective depends on the strain, with topical paromomycin effective for L. major, L. tropica, L. mexicana, L. panamensis, and L. braziliensis. Pentamidine is effective for L. guyanensis.ral fluconazole or itraconazole appears effective in L. major and L. tropica The medication(s) listed below have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as orphan products for treatment of this condition.
- Amphotericin B Liposomal (Brand name: AmBisome®) Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis.
- miltefosine (Brand name: Impavido)Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani; cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis, Leishmania guyanensis, and Leishmania panamensis; and mucosal leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis.
| Parasitic disease caused by Excavata protozoa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|


