Slipping rib syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Slipping rib syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Slipping_Rib_Syndrome_Example.svg|250px]] | |||
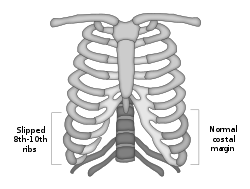
| caption = Illustration of Slipping Rib Syndrome | |||
| synonyms = Rib-tip syndrome, Clicking rib, Displaced rib cartilage | |||
| specialty = [[Orthopedics]], [[Rheumatology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Chest pain]], [[Upper abdominal pain]], [[Back pain]], "popping" or "clicking" sensation | |||
| onset = Any age, but more common in adults | |||
| duration = Can be chronic or intermittent | |||
| causes = Hypermobile rib cartilage, trauma, repetitive motion | |||
| risks = [[Athletes]], [[Trauma]], [[Hypermobility]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[Hooking maneuver]], [[Ultrasound]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Costochondritis]], [[Tietze syndrome]], [[Intercostal neuralgia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[Pain management]], [[Surgery]] | |||
| medication = [[NSAIDs]], [[Analgesics]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Slipping rib syndrome''' is a medical condition where the [[ribs]] move out of their normal position, causing pain in the [[thoracic]] or [[abdominal]] region. This condition is also known as [[rib tip syndrome]], [[twelfth rib syndrome]], [[clicking rib]], [[rib subluxation]], or [[traumatic intercostal neuritis]]. | '''Slipping rib syndrome''' is a medical condition where the [[ribs]] move out of their normal position, causing pain in the [[thoracic]] or [[abdominal]] region. This condition is also known as [[rib tip syndrome]], [[twelfth rib syndrome]], [[clicking rib]], [[rib subluxation]], or [[traumatic intercostal neuritis]]. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The main symptom of slipping rib syndrome is persistent pain in the lower chest or upper abdomen. This pain can be sharp, dull, or aching, and it may be accompanied by a clicking or popping sensation. Other symptoms can include difficulty breathing, discomfort when bending or twisting, and tenderness in the affected area. | The main symptom of slipping rib syndrome is persistent pain in the lower chest or upper abdomen. This pain can be sharp, dull, or aching, and it may be accompanied by a clicking or popping sensation. Other symptoms can include difficulty breathing, discomfort when bending or twisting, and tenderness in the affected area. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Slipping rib syndrome can be caused by a variety of factors. These include [[physical trauma]] to the chest or abdomen, [[hypermobility]] of the ribs, [[degeneration]] of the [[cartilage]] or [[ligaments]] that hold the ribs in place, and certain [[medical conditions]] such as [[fibromyalgia]] or [[chronic fatigue syndrome]]. | Slipping rib syndrome can be caused by a variety of factors. These include [[physical trauma]] to the chest or abdomen, [[hypermobility]] of the ribs, [[degeneration]] of the [[cartilage]] or [[ligaments]] that hold the ribs in place, and certain [[medical conditions]] such as [[fibromyalgia]] or [[chronic fatigue syndrome]]. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of slipping rib syndrome can be challenging, as the symptoms can mimic other conditions such as [[gallbladder disease]], [[ulcers]], or [[heart disease]]. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, during which the doctor may perform the [[hooking maneuver]] to reproduce the symptoms. Imaging tests such as [[X-rays]], [[CT scans]], or [[MRI scans]] may also be used to rule out other conditions. | Diagnosis of slipping rib syndrome can be challenging, as the symptoms can mimic other conditions such as [[gallbladder disease]], [[ulcers]], or [[heart disease]]. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, during which the doctor may perform the [[hooking maneuver]] to reproduce the symptoms. Imaging tests such as [[X-rays]], [[CT scans]], or [[MRI scans]] may also be used to rule out other conditions. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for slipping rib syndrome typically involves conservative measures such as [[pain management]], [[physical therapy]], and [[lifestyle modifications]]. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to reposition the displaced rib. | Treatment for slipping rib syndrome typically involves conservative measures such as [[pain management]], [[physical therapy]], and [[lifestyle modifications]]. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to reposition the displaced rib. | ||
== Slipping_rib_syndrome images == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Rib_anatomy.png|Anatomy of the ribs | |||
File:SRS_hooking_maneuver_model.jpg|Model demonstrating the hooking maneuver for slipping rib syndrome | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Rib (anatomy)]] | * [[Rib (anatomy)]] | ||
* [[Thoracic diaphragm]] | * [[Thoracic diaphragm]] | ||
* [[Intercostal muscles]] | * [[Intercostal muscles]] | ||
* [[Costochondritis]] | * [[Costochondritis]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Syndromes]] | [[Category:Syndromes]] | ||
[[Category:Pain]] | [[Category:Pain]] | ||
[[Category:Ribs]] | [[Category:Ribs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:31, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Slipping rib syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Rib-tip syndrome, Clicking rib, Displaced rib cartilage |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Orthopedics, Rheumatology |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, Upper abdominal pain, Back pain, "popping" or "clicking" sensation |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Any age, but more common in adults |
| Duration | Can be chronic or intermittent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Hypermobile rib cartilage, trauma, repetitive motion |
| Risks | Athletes, Trauma, Hypermobility |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, Hooking maneuver, Ultrasound, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Costochondritis, Tietze syndrome, Intercostal neuralgia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, Pain management, Surgery |
| Medication | NSAIDs, Analgesics |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Slipping rib syndrome is a medical condition where the ribs move out of their normal position, causing pain in the thoracic or abdominal region. This condition is also known as rib tip syndrome, twelfth rib syndrome, clicking rib, rib subluxation, or traumatic intercostal neuritis.
Symptoms[edit]
The main symptom of slipping rib syndrome is persistent pain in the lower chest or upper abdomen. This pain can be sharp, dull, or aching, and it may be accompanied by a clicking or popping sensation. Other symptoms can include difficulty breathing, discomfort when bending or twisting, and tenderness in the affected area.
Causes[edit]
Slipping rib syndrome can be caused by a variety of factors. These include physical trauma to the chest or abdomen, hypermobility of the ribs, degeneration of the cartilage or ligaments that hold the ribs in place, and certain medical conditions such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of slipping rib syndrome can be challenging, as the symptoms can mimic other conditions such as gallbladder disease, ulcers, or heart disease. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, during which the doctor may perform the hooking maneuver to reproduce the symptoms. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may also be used to rule out other conditions.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for slipping rib syndrome typically involves conservative measures such as pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to reposition the displaced rib.
Slipping_rib_syndrome images[edit]
-
Anatomy of the ribs
-
Model demonstrating the hooking maneuver for slipping rib syndrome
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />




