Amniotic fluid embolism: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Amniotic_fluid_embolism. | {{SI}}<br> | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Amniotic fluid embolism | |||
| image = [[File:Amniotic_fluid_embolism.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = | |||
| field = [[Obstetrics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Shortness of breath]], [[hypotension]], [[coagulopathy]], [[seizures]], [[cardiac arrest]] | |||
| complications = [[Disseminated intravascular coagulation]], [[acute respiratory distress syndrome]], [[multiple organ dysfunction syndrome]] | |||
| onset = [[Labor (childbirth)|Labor]], [[cesarean section]], or [[abortion]] | |||
| duration = | |||
| causes = Entry of [[amniotic fluid]] into maternal [[circulation]] | |||
| risks = [[Advanced maternal age]], [[placenta previa]], [[preeclampsia]], [[multiple gestation]] | |||
| diagnosis = Based on [[clinical presentation]] and [[exclusion of other causes]] | |||
| differential = [[Pulmonary embolism]], [[anaphylaxis]], [[sepsis]] | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[oxygen therapy]], [[blood transfusion]], [[mechanical ventilation]] | |||
| medication = [[Vasopressors]], [[corticosteroids]] | |||
| prognosis = High [[mortality rate]] | |||
| frequency = 1 in 40,000 deliveries | |||
}} | |||
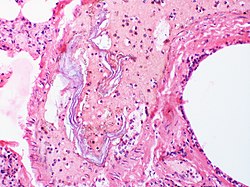
'''Amniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)''' is a rare but serious and potentially fatal condition that can occur during [[childbirth]]. It happens when amniotic fluid, fetal cells, hair, or other debris enters the maternal bloodstream, leading to a severe allergic-like reaction and [[cardiovascular collapse]]. This condition is unpredictable and can lead to significant complications, including [[coagulopathy]], [[cardiac arrest]], and [[pulmonary edema]]. | |||
== Causes and Risk Factors == | == Causes and Risk Factors == | ||
The exact cause of Amniotic Fluid Embolism is not well understood, but it is believed to occur when there is a breach in the physical barriers between the mother and fetus, such as the [[amniotic sac]] and the [[uterine veins]]. This allows amniotic fluid or fetal material to enter the maternal circulation. Risk factors for AFE are not clearly defined, but some studies suggest that advanced maternal age, [[cesarean delivery]], [[placenta previa]], and [[uterine rupture]] may increase the risk. | The exact cause of Amniotic Fluid Embolism is not well understood, but it is believed to occur when there is a breach in the physical barriers between the mother and fetus, such as the [[amniotic sac]] and the [[uterine veins]]. This allows amniotic fluid or fetal material to enter the maternal circulation. Risk factors for AFE are not clearly defined, but some studies suggest that advanced maternal age, [[cesarean delivery]], [[placenta previa]], and [[uterine rupture]] may increase the risk. | ||
== Symptoms and Diagnosis == | == Symptoms and Diagnosis == | ||
Symptoms of Amniotic Fluid Embolism can be sudden and may include acute [[shortness of breath]], [[hypotension]] (low blood pressure), [[seizures]], and [[coagulopathy]] (a disorder affecting blood clotting). Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the presentation of symptoms and the exclusion of other conditions. There is no specific test for AFE, but certain laboratory findings, such as a sudden drop in oxygen saturation and coagulation abnormalities, can support the diagnosis. | Symptoms of Amniotic Fluid Embolism can be sudden and may include acute [[shortness of breath]], [[hypotension]] (low blood pressure), [[seizures]], and [[coagulopathy]] (a disorder affecting blood clotting). Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the presentation of symptoms and the exclusion of other conditions. There is no specific test for AFE, but certain laboratory findings, such as a sudden drop in oxygen saturation and coagulation abnormalities, can support the diagnosis. | ||
== Treatment and Prognosis == | == Treatment and Prognosis == | ||
Treatment of Amniotic Fluid Embolism focuses on supportive care and managing complications. This may include [[oxygen therapy]], [[fluid resuscitation]], and [[blood transfusions]] to address hypotension and coagulopathy. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation or [[extracorporeal membrane oxygenation]] (ECMO) may be required. The prognosis of AFE varies; while some women recover completely, others may experience significant morbidity or mortality. Early recognition and aggressive management are critical for improving outcomes. | Treatment of Amniotic Fluid Embolism focuses on supportive care and managing complications. This may include [[oxygen therapy]], [[fluid resuscitation]], and [[blood transfusions]] to address hypotension and coagulopathy. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation or [[extracorporeal membrane oxygenation]] (ECMO) may be required. The prognosis of AFE varies; while some women recover completely, others may experience significant morbidity or mortality. Early recognition and aggressive management are critical for improving outcomes. | ||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
Amniotic Fluid Embolism is considered a rare condition, though its exact incidence is difficult to determine due to variations in diagnostic criteria and reporting practices. It is a leading cause of maternal mortality in the developed world, contributing to a significant proportion of deaths associated with childbirth. | Amniotic Fluid Embolism is considered a rare condition, though its exact incidence is difficult to determine due to variations in diagnostic criteria and reporting practices. It is a leading cause of maternal mortality in the developed world, contributing to a significant proportion of deaths associated with childbirth. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Currently, there are no established measures for the prevention of Amniotic Fluid Embolism due to its unpredictable nature. Management strategies focus on rapid identification and treatment of symptoms to minimize complications. | Currently, there are no established measures for the prevention of Amniotic Fluid Embolism due to its unpredictable nature. Management strategies focus on rapid identification and treatment of symptoms to minimize complications. | ||
[[Category:Obstetrics]] | [[Category:Obstetrics]] | ||
[[Category:Maternal mortality]] | [[Category:Maternal mortality]] | ||
[[Category:Medical emergencies]] | [[Category:Medical emergencies]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:01, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Amniotic fluid embolism | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Shortness of breath, hypotension, coagulopathy, seizures, cardiac arrest |
| Complications | Disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome |
| Onset | Labor, cesarean section, or abortion |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Entry of amniotic fluid into maternal circulation |
| Risks | Advanced maternal age, placenta previa, preeclampsia, multiple gestation |
| Diagnosis | Based on clinical presentation and exclusion of other causes |
| Differential diagnosis | Pulmonary embolism, anaphylaxis, sepsis |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Supportive care, oxygen therapy, blood transfusion, mechanical ventilation |
| Medication | Vasopressors, corticosteroids |
| Prognosis | High mortality rate |
| Frequency | 1 in 40,000 deliveries |
| Deaths | N/A |
Amniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE) is a rare but serious and potentially fatal condition that can occur during childbirth. It happens when amniotic fluid, fetal cells, hair, or other debris enters the maternal bloodstream, leading to a severe allergic-like reaction and cardiovascular collapse. This condition is unpredictable and can lead to significant complications, including coagulopathy, cardiac arrest, and pulmonary edema.
Causes and Risk Factors[edit]
The exact cause of Amniotic Fluid Embolism is not well understood, but it is believed to occur when there is a breach in the physical barriers between the mother and fetus, such as the amniotic sac and the uterine veins. This allows amniotic fluid or fetal material to enter the maternal circulation. Risk factors for AFE are not clearly defined, but some studies suggest that advanced maternal age, cesarean delivery, placenta previa, and uterine rupture may increase the risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis[edit]
Symptoms of Amniotic Fluid Embolism can be sudden and may include acute shortness of breath, hypotension (low blood pressure), seizures, and coagulopathy (a disorder affecting blood clotting). Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the presentation of symptoms and the exclusion of other conditions. There is no specific test for AFE, but certain laboratory findings, such as a sudden drop in oxygen saturation and coagulation abnormalities, can support the diagnosis.
Treatment and Prognosis[edit]
Treatment of Amniotic Fluid Embolism focuses on supportive care and managing complications. This may include oxygen therapy, fluid resuscitation, and blood transfusions to address hypotension and coagulopathy. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be required. The prognosis of AFE varies; while some women recover completely, others may experience significant morbidity or mortality. Early recognition and aggressive management are critical for improving outcomes.
Epidemiology[edit]
Amniotic Fluid Embolism is considered a rare condition, though its exact incidence is difficult to determine due to variations in diagnostic criteria and reporting practices. It is a leading cause of maternal mortality in the developed world, contributing to a significant proportion of deaths associated with childbirth.
Prevention[edit]
Currently, there are no established measures for the prevention of Amniotic Fluid Embolism due to its unpredictable nature. Management strategies focus on rapid identification and treatment of symptoms to minimize complications.
