Food coating: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[[Category:Food Processing]] | [[Category:Food Processing]] | ||
[[Category:Cooking Techniques]] | [[Category:Cooking Techniques]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Turbine_à_chocolat.JPG|Turbine à chocolat | |||
File:ধানের_মুড়কি_(Murki_from_paddy).jpg|Murki from paddy | |||
File:IQF_Frozen_Vegetable_Sauce_Coated.jpg|IQF Frozen Vegetable Sauce Coated | |||
File:Suikerboon-2.JPG|Suikerboon | |||
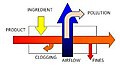
File:Food_Coating_As_A_System.jpg|Food Coating As A System | |||
File:Temperature_Influence_On_Coating.jpg|Temperature Influence On Coating | |||
File:Coating_Process_Diagram.jpg|Coating Process Diagram | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:18, 25 February 2025

Food coating refers to the process of covering or enveloping food items with a layer of material that can enhance flavor, improve texture, or serve as a barrier to moisture and gas exchange, thereby extending the shelf life of the product. This technique is widely used in the food processing industry and encompasses a variety of methods and materials, depending on the desired outcome and the type of food being coated.
Types of Food Coatings[edit]
Food coatings can be broadly classified into several types based on their composition and purpose:
Batter[edit]
A batter is a semi-liquid mixture that can be made from flour, water, eggs, and sometimes leavening agents or other ingredients. It is commonly used for coating foods before frying to create a crispy outer layer. Examples include the batter for fried chicken, tempura, and fish and chips.
Breading[edit]
Breading involves coating food with breadcrumbs or other dry particles before cooking. This method is often used in conjunction with battering, where the food is first dipped in batter and then rolled in breadcrumbs. Breading adds texture and flavor to the surface of the food, as seen in dishes like schnitzel and breaded cutlets.
Sugar Coating[edit]
Sugar coating is applied to confections and sweets, such as candy, chocolate, and gum, to add sweetness, texture, and a glossy appearance. This can be achieved through various techniques, including panning, where the items are tumbled in sugar until a desired thickness is reached.
Chocolate Coating[edit]
Chocolate coating involves covering confections, fruits, or baked goods with a layer of chocolate. This not only adds flavor but also helps in preserving the freshness of the coated item by acting as a barrier against air and moisture.
Glazing[edit]
Glazing refers to the application of a thin, shiny layer on the surface of food. Glazes can be made from a variety of substances, including sugar, honey, chocolate, and certain types of icings. They are typically applied to baked goods, such as doughnuts, pastries, and cakes, to improve appearance and taste.
Enrobing[edit]
Enrobing is a process similar to chocolate coating but can involve other coatings like fondant, icing, or other confectionery coatings. The food item passes through a curtain of the coating material, ensuring it is completely covered. This technique is commonly used in the production of chocolate-covered nuts, fruits, and cookies.
Applications in the Food Industry[edit]
Food coating is employed in various sectors of the food industry for different purposes:
- Confectionery Industry: Enhancing the appeal and taste of sweets and chocolates.
- Snack Food Industry: Improving texture and flavor of snack items, such as chips and nuts.
- Bakery and Pastry Sector: Adding visual appeal and taste to baked goods.
- Meat and Seafood Processing: Providing a protective layer to meat and seafood, improving texture and flavor after cooking.
Challenges and Considerations[edit]
While food coating offers numerous benefits, there are challenges and considerations that manufacturers must address:
- Allergen Control: Ensuring that the coating materials do not introduce allergens to the food product.
- Nutritional Impact: Balancing the desire for taste and texture enhancement with the need to maintain nutritional value.
- Shelf Life: Optimizing the coating process to extend shelf life without compromising food safety or quality.
- Environmental Impact: Minimizing waste and ensuring that the materials used in coatings are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion[edit]
Food coating is a versatile and essential technique in the food processing industry, offering numerous benefits in terms of flavor, texture, and shelf life enhancement. As consumer preferences continue to evolve, the innovation and application of food coatings will likely continue to expand, driving further advancements in food technology and processing.
-
Turbine à chocolat
-
Murki from paddy
-
IQF Frozen Vegetable Sauce Coated
-
Suikerboon
-
Food Coating As A System
-
Temperature Influence On Coating
-
Coating Process Diagram