Oxyphenbutazone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Category:Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]] | [[Category:Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
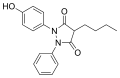
File:oxyphenbutazone.svg|Oxyphenbutazone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:45, 20 February 2025
A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
| Oxyphenbutazone | |
|---|---|

| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Oxyphenbutazone is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that was once commonly used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. It is a metabolite of phenylbutazone, another NSAID, and shares similar pharmacological effects.
Pharmacology[edit]
Oxyphenbutazone works by inhibiting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are compounds that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever. By reducing the production of prostaglandins, oxyphenbutazone helps alleviate symptoms associated with inflammatory conditions.
Medical uses[edit]
Oxyphenbutazone was primarily used to treat conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and other inflammatory disorders. It was valued for its ability to reduce pain and swelling in affected joints.
Side effects[edit]
Like other NSAIDs, oxyphenbutazone can cause a range of side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and gastric ulceration. More serious side effects can include renal impairment, hepatic dysfunction, and hematological abnormalities such as agranulocytosis.
History[edit]
Oxyphenbutazone was developed in the mid-20th century and was widely used until concerns about its safety profile led to a decline in its use. The development of newer NSAIDs with improved safety profiles has largely replaced oxyphenbutazone in clinical practice.
Regulatory status[edit]
Due to its side effect profile, oxyphenbutazone is no longer widely used and is not approved for use in many countries. It has been largely replaced by other NSAIDs that offer similar efficacy with fewer risks.
Related pages[edit]
-
Oxyphenbutazone