Prostaglandin H2: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
{{biochem-stub}} | {{biochem-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Prostaglandin_H2 == | |||
<gallery> | |||
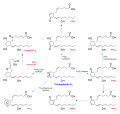
File:Prostaglandin_H2_skeletal.svg|Prostaglandin H2 skeletal structure | |||
File:Eicosanoid_synthesis.svg|Eicosanoid synthesis pathway | |||
File:Prostanoid_synthesis.svg|Prostanoid synthesis pathway | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:14, 18 February 2025
Prostaglandin H2 (often abbreviated as PGH2) is a type of prostaglandin that is a precursor to other prostaglandins. It is produced from arachidonic acid by the action of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). PGH2 is converted by specific enzymes into several other prostaglandins (such as prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin I2) and thromboxane.
Biosynthesis[edit]
The biosynthesis of PGH2 is initiated by the release of arachidonic acid from the phospholipid membrane of cells, a process catalyzed by phospholipase A2. The free arachidonic acid is then converted into PGH2 through a two-step process. First, the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX) converts arachidonic acid into prostaglandin G2 (PGG2). Then, in the second step, COX converts PGG2 into PGH2.
Role in the body[edit]
PGH2 serves as a precursor to a variety of important eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules with diverse functions in the body. These include prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α), prostaglandin I2 (PGI2, also known as prostacyclin), and thromboxane A2 (TXA2). These molecules play key roles in inflammation, fever, regulation of blood pressure, and formation of blood clots.
Clinical significance[edit]
The production of PGH2 is a target for certain drugs, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and COX-2 inhibitors. These drugs inhibit the action of COX, thereby reducing the production of PGH2 and its downstream products. This can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
See also[edit]

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Prostaglandin_H2[edit]
-
Prostaglandin H2 skeletal structure
-
Eicosanoid synthesis pathway
-
Prostanoid synthesis pathway