Acute pericarditis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular diseases]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Inflammations]] | [[Category:Inflammations]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
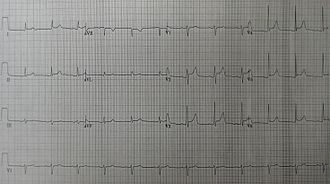
File:PericarditisECG.JPG|ECG showing signs of acute pericarditis | |||
File:Acute_pericarditis.jpg|Illustration of acute pericarditis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 02:05, 17 February 2025
Inflammation of the pericardium
Acute pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. It is a common condition that can cause significant chest pain and other symptoms.
Signs and symptoms
The primary symptom of acute pericarditis is sharp, stabbing chest pain that may radiate to the neck, shoulder, or back. The pain is often worsened by lying down or taking a deep breath and relieved by sitting up and leaning forward. Other symptoms may include fever, cough, and dyspnea (shortness of breath).
Causes
Acute pericarditis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Viral infections (most common)
- Bacterial infections
- Fungal infections
- Autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Trauma or injury to the chest
- Cancer
- Kidney failure
- Certain medications
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of acute pericarditis is typically based on clinical presentation and may be supported by diagnostic tests such as:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) - often shows characteristic changes such as widespread ST elevation
- Echocardiogram - can assess for pericardial effusion
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests - to check for markers of inflammation and infection
Treatment
Treatment of acute pericarditis depends on the underlying cause but often includes:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen
- Colchicine to reduce inflammation
- Corticosteroids in certain cases
- Treatment of the underlying cause, such as antibiotics for bacterial infections
Complications
Complications of acute pericarditis can include:
Prognosis
The prognosis for acute pericarditis is generally good, especially when treated promptly. Most patients recover fully, although some may experience recurrent episodes.
Related pages
Gallery
-
Illustration of acute pericarditis
-
ECG showing signs of acute pericarditis
-
Illustration of acute pericarditis

