Brain herniation: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Brain herniation | |||
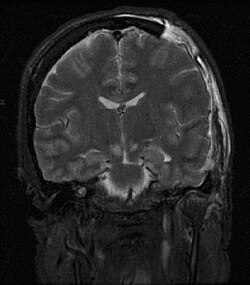
| image = [[File:Brain_herniation_MRI.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = MRI showing brain herniation | |||
| field = [[Neurology]], [[Neurosurgery]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[vomiting]], [[altered mental status]], [[coma]] | |||
| complications = [[Brain damage]], [[death]] | |||
| onset = Sudden | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| types = [[Subfalcine herniation]], [[transtentorial herniation]], [[tonsillar herniation]] | |||
| causes = [[Traumatic brain injury]], [[stroke]], [[brain tumor]], [[abscess]] | |||
| risks = Increased [[intracranial pressure]] | |||
==Types== | | diagnosis = [[CT scan]], [[MRI]] | ||
| differential = [[Intracerebral hemorrhage]], [[cerebral edema]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[osmotic therapy]], [[hyperventilation]] | |||
| prognosis = Poor if untreated | |||
| frequency = Common in severe [[head injury]] | |||
}} | |||
== Brain Herniation == | |||
[[File:Brain_herniation_types-2.svg|Types of brain herniation|left|thumb]] | |||
'''Brain herniation''' occurs when there is a displacement of brain tissue due to increased intracranial pressure. This condition is a medical emergency and can lead to severe neurological damage or death if not treated promptly. | |||
== | == Types of Brain Herniation == | ||
Brain herniation can be classified into several types based on the location and direction of the herniation: | |||
=== Subfalcine Herniation === | |||
* | [[File:Subfalcine-herniation-001.jpg|Subfalcine herniation|left|thumb]] | ||
Subfalcine herniation, also known as cingulate herniation, occurs when the cingulate gyrus is displaced under the falx cerebri. This is the most common type of herniation and can compress the [[anterior cerebral artery]], leading to ischemia. | |||
=== Transtentorial Herniation === | |||
Transtentorial herniation can be further divided into uncal and central herniation: | |||
* '''Uncal Herniation''': This occurs when the uncus of the temporal lobe is pushed downward through the tentorial notch. It can compress the [[oculomotor nerve]], leading to a dilated pupil on the affected side, and can also compress the [[brainstem]]. | |||
* '''Central Herniation''': This involves downward displacement of the brainstem and diencephalon through the tentorial notch, potentially leading to [[decerebrate posturing]] and [[coma]]. | |||
=== Tonsillar Herniation === | |||
Tonsillar herniation occurs when the cerebellar tonsils are pushed downward through the foramen magnum. This can compress the [[medulla oblongata]], affecting vital functions such as respiration and cardiac function. | |||
=== External Herniation === | |||
External herniation occurs when brain tissue is displaced through a defect in the skull, often due to trauma or surgery. | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | |||
The symptoms of brain herniation depend on the type and severity of the herniation. Common signs include: | |||
* Altered level of consciousness | |||
* Headache | * Headache | ||
* | * Vomiting | ||
* Pupillary changes | |||
==Diagnosis== | * Abnormal posturing, such as [[File:Decorticate.PNG|Decorticate posturing|left|thumb]] | ||
Diagnosis of brain herniation | == Diagnosis == | ||
[[File:Brain_injury_with_herniation_MRI.jpg|Brain injury with herniation on MRI|left|thumb]] | |||
==Treatment== | Diagnosis of brain herniation is typically made using imaging studies such as [[computed tomography]] (CT) or [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI). These imaging modalities can reveal the displacement of brain structures and the presence of any mass lesions or edema. | ||
Treatment of brain herniation | [[File:Brain_herniation_MRI.jpg|MRI showing brain herniation|left|thumb]] | ||
== Treatment == | |||
* | Treatment of brain herniation focuses on reducing intracranial pressure and addressing the underlying cause. This may include: | ||
* | * Surgical intervention to remove mass lesions or relieve pressure | ||
* | * Administration of [[osmotic diuretics]] such as [[mannitol]] | ||
* Hyperventilation to reduce carbon dioxide levels and decrease intracranial pressure | |||
==Prognosis== | * Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation | ||
The prognosis for brain herniation | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for brain herniation varies depending on the cause, severity, and timeliness of treatment. Early intervention can improve outcomes, but severe herniation can result in permanent neurological deficits or death. | |||
== | == See also == | ||
* [[Intracranial pressure]] | |||
* [[Cerebral edema]] | |||
* [[Traumatic brain injury]] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
[[Category:Neurosurgery]] | [[Category:Neurosurgery]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:12, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Brain herniation | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, vomiting, altered mental status, coma |
| Complications | Brain damage, death |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Subfalcine herniation, transtentorial herniation, tonsillar herniation |
| Causes | Traumatic brain injury, stroke, brain tumor, abscess |
| Risks | Increased intracranial pressure |
| Diagnosis | CT scan, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral edema |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, osmotic therapy, hyperventilation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Poor if untreated |
| Frequency | Common in severe head injury |
| Deaths | N/A |
Brain Herniation[edit]

Brain herniation occurs when there is a displacement of brain tissue due to increased intracranial pressure. This condition is a medical emergency and can lead to severe neurological damage or death if not treated promptly.
Types of Brain Herniation[edit]
Brain herniation can be classified into several types based on the location and direction of the herniation:
Subfalcine Herniation[edit]

Subfalcine herniation, also known as cingulate herniation, occurs when the cingulate gyrus is displaced under the falx cerebri. This is the most common type of herniation and can compress the anterior cerebral artery, leading to ischemia.
Transtentorial Herniation[edit]
Transtentorial herniation can be further divided into uncal and central herniation:
- Uncal Herniation: This occurs when the uncus of the temporal lobe is pushed downward through the tentorial notch. It can compress the oculomotor nerve, leading to a dilated pupil on the affected side, and can also compress the brainstem.
- Central Herniation: This involves downward displacement of the brainstem and diencephalon through the tentorial notch, potentially leading to decerebrate posturing and coma.
Tonsillar Herniation[edit]
Tonsillar herniation occurs when the cerebellar tonsils are pushed downward through the foramen magnum. This can compress the medulla oblongata, affecting vital functions such as respiration and cardiac function.
External Herniation[edit]
External herniation occurs when brain tissue is displaced through a defect in the skull, often due to trauma or surgery.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
The symptoms of brain herniation depend on the type and severity of the herniation. Common signs include:
- Altered level of consciousness
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Pupillary changes
- Abnormal posturing, such as
Decorticate posturing
Diagnosis[edit]

Diagnosis of brain herniation is typically made using imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These imaging modalities can reveal the displacement of brain structures and the presence of any mass lesions or edema.

Treatment[edit]
Treatment of brain herniation focuses on reducing intracranial pressure and addressing the underlying cause. This may include:
- Surgical intervention to remove mass lesions or relieve pressure
- Administration of osmotic diuretics such as mannitol
- Hyperventilation to reduce carbon dioxide levels and decrease intracranial pressure
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for brain herniation varies depending on the cause, severity, and timeliness of treatment. Early intervention can improve outcomes, but severe herniation can result in permanent neurological deficits or death.
