Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
[[File:Fulminating_ADEM_showing_many_lesions.png| | | name = Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | ||
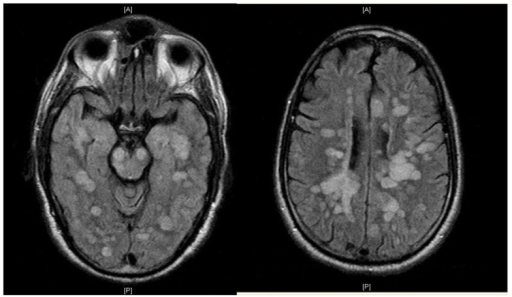
| image = [[File:Fulminating_ADEM_showing_many_lesions.png|alt=Brain MRI showing multiple lesions]] | |||
| caption = MRI of the brain showing multiple lesions typical of ADEM | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| synonyms = Post-infectious encephalomyelitis, post-vaccinal encephalomyelitis | |||
| symptoms = [[Fever]], [[headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[seizures]], [[confusion]], [[ataxia]], [[vision problems]] | |||
| complications = [[Seizures]], [[coma]], [[death]] | |||
| onset = Rapid, often following an infection or vaccination | |||
| duration = Days to weeks | |||
| causes = Often follows a [[viral infection]] or [[vaccination]] | |||
| risks = Recent [[infection]], [[vaccination]], [[autoimmune disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[lumbar puncture]], [[blood tests]] | |||
| differential = [[Multiple sclerosis]], [[neuromyelitis optica]], [[viral encephalitis]] | |||
| treatment = [[Corticosteroids]], [[plasmapheresis]], [[intravenous immunoglobulin]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment, but can vary | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Acute_hemorrhagic_Leukoencephalitis_in_a_patient_with_Multiple_sclerosis_(MRI).png|thumb|Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis in a patient with multiple sclerosis (MRI)]] | [[File:Acute_hemorrhagic_Leukoencephalitis_in_a_patient_with_Multiple_sclerosis_(MRI).png|thumb|Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis in a patient with multiple sclerosis (MRI)]] | ||
'''Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis''' ('''ADEM''') is an [[autoimmune disease]] marked by a sudden, widespread attack of [[inflammation]] in the [[brain]] and [[spinal cord]]. It is characterized by a brief but intense episode of [[inflammation]] in the [[central nervous system]] (CNS), often following a [[viral infection]] or [[vaccination]]. | '''Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis''' ('''ADEM''') is an [[autoimmune disease]] marked by a sudden, widespread attack of [[inflammation]] in the [[brain]] and [[spinal cord]]. It is characterized by a brief but intense episode of [[inflammation]] in the [[central nervous system]] (CNS), often following a [[viral infection]] or [[vaccination]]. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
ADEM is believed to be an [[autoimmune]] response where the body's [[immune system]] mistakenly attacks its own [[myelin]], the protective covering of [[nerve fibers]] in the [[central nervous system]]. This results in [[demyelination]], which disrupts the normal transmission of [[nerve impulses]]. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve [[molecular mimicry]], where the immune system confuses [[myelin]] with [[viral antigens]]. | ADEM is believed to be an [[autoimmune]] response where the body's [[immune system]] mistakenly attacks its own [[myelin]], the protective covering of [[nerve fibers]] in the [[central nervous system]]. This results in [[demyelination]], which disrupts the normal transmission of [[nerve impulses]]. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve [[molecular mimicry]], where the immune system confuses [[myelin]] with [[viral antigens]]. | ||
==Clinical Presentation== | ==Clinical Presentation== | ||
Patients with ADEM typically present with a rapid onset of [[neurological symptoms]] such as [[headache]], [[fever]], [[nausea]], and [[vomiting]]. [[Neurological deficits]] may include [[ataxia]], [[hemiparesis]], [[optic neuritis]], and [[altered mental status]]. In severe cases, [[seizures]] and [[coma]] may occur. | Patients with ADEM typically present with a rapid onset of [[neurological symptoms]] such as [[headache]], [[fever]], [[nausea]], and [[vomiting]]. [[Neurological deficits]] may include [[ataxia]], [[hemiparesis]], [[optic neuritis]], and [[altered mental status]]. In severe cases, [[seizures]] and [[coma]] may occur. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis of ADEM is primarily clinical, supported by [[magnetic resonance imaging]] ([[MRI]]) findings. MRI typically shows multiple [[lesions]] in the [[white matter]] of the [[brain]] and [[spinal cord]]. These lesions are often [[bilateral]] and [[asymmetrical]]. [[Cerebrospinal fluid]] (CSF) analysis may show elevated [[protein]] levels and [[pleocytosis]]. | The diagnosis of ADEM is primarily clinical, supported by [[magnetic resonance imaging]] ([[MRI]]) findings. MRI typically shows multiple [[lesions]] in the [[white matter]] of the [[brain]] and [[spinal cord]]. These lesions are often [[bilateral]] and [[asymmetrical]]. [[Cerebrospinal fluid]] (CSF) analysis may show elevated [[protein]] levels and [[pleocytosis]]. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The mainstay of treatment for ADEM is high-dose [[corticosteroids]], such as [[methylprednisolone]], to reduce [[inflammation]] and [[immune system]] activity. In cases where patients do not respond to steroids, [[intravenous immunoglobulin]] (IVIG) or [[plasmapheresis]] may be considered. Supportive care is also crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications. | The mainstay of treatment for ADEM is high-dose [[corticosteroids]], such as [[methylprednisolone]], to reduce [[inflammation]] and [[immune system]] activity. In cases where patients do not respond to steroids, [[intravenous immunoglobulin]] (IVIG) or [[plasmapheresis]] may be considered. Supportive care is also crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for ADEM is generally favorable, with most patients experiencing significant recovery within weeks to months. However, some individuals may have residual [[neurological deficits]]. Recurrence is rare, distinguishing ADEM from [[multiple sclerosis]], which is a chronic condition with recurrent episodes. | The prognosis for ADEM is generally favorable, with most patients experiencing significant recovery within weeks to months. However, some individuals may have residual [[neurological deficits]]. Recurrence is rare, distinguishing ADEM from [[multiple sclerosis]], which is a chronic condition with recurrent episodes. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Multiple sclerosis]] | * [[Multiple sclerosis]] | ||
* [[Autoimmune disease]] | * [[Autoimmune disease]] | ||
* [[Demyelinating disease]] | * [[Demyelinating disease]] | ||
* [[Central nervous system]] | * [[Central nervous system]] | ||
[[Category:Autoimmune diseases]] | [[Category:Autoimmune diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
[[Category:Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system]] | [[Category:Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:51, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Post-infectious encephalomyelitis, post-vaccinal encephalomyelitis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, seizures, confusion, ataxia, vision problems |
| Complications | Seizures, coma, death |
| Onset | Rapid, often following an infection or vaccination |
| Duration | Days to weeks |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Often follows a viral infection or vaccination |
| Risks | Recent infection, vaccination, autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | MRI, lumbar puncture, blood tests |
| Differential diagnosis | Multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, viral encephalitis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, plasmapheresis, intravenous immunoglobulin |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment, but can vary |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is an autoimmune disease marked by a sudden, widespread attack of inflammation in the brain and spinal cord. It is characterized by a brief but intense episode of inflammation in the central nervous system (CNS), often following a viral infection or vaccination.
Pathophysiology[edit]
ADEM is believed to be an autoimmune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own myelin, the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This results in demyelination, which disrupts the normal transmission of nerve impulses. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve molecular mimicry, where the immune system confuses myelin with viral antigens.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with ADEM typically present with a rapid onset of neurological symptoms such as headache, fever, nausea, and vomiting. Neurological deficits may include ataxia, hemiparesis, optic neuritis, and altered mental status. In severe cases, seizures and coma may occur.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of ADEM is primarily clinical, supported by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. MRI typically shows multiple lesions in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. These lesions are often bilateral and asymmetrical. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis may show elevated protein levels and pleocytosis.
Treatment[edit]
The mainstay of treatment for ADEM is high-dose corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone, to reduce inflammation and immune system activity. In cases where patients do not respond to steroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasmapheresis may be considered. Supportive care is also crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for ADEM is generally favorable, with most patients experiencing significant recovery within weeks to months. However, some individuals may have residual neurological deficits. Recurrence is rare, distinguishing ADEM from multiple sclerosis, which is a chronic condition with recurrent episodes.