Trophoblastic neoplasm: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Trophoblastic neoplasm | |||
| image = [[File:Intermediate_trophoblast_3_-_low_mag.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Micrograph of an intermediate trophoblast, as may be seen in a trophoblastic neoplasm. H&E stain. | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = Gestational trophoblastic disease | |||
| symptoms = Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, enlarged uterus | |||
| complications = [[Metastasis]], [[hemorrhage]], [[infertility]] | |||
| onset = Reproductive age | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| types = [[Hydatidiform mole]], [[Choriocarcinoma]], [[Placental site trophoblastic tumor]], [[Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor]] | |||
| causes = Abnormal fertilization | |||
| risks = Prior molar pregnancy, advanced maternal age, history of miscarriage | |||
| diagnosis = [[Ultrasound]], [[hCG]] levels, [[histopathology]] | |||
| differential = [[Ectopic pregnancy]], [[miscarriage]], [[ovarian tumor]] | |||
| prevention = None | |||
| treatment = [[Chemotherapy]], [[surgery]] | |||
| medication = [[Methotrexate]], [[Dactinomycin]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A group of rare tumors involving trophoblastic tissue}} | {{Short description|A group of rare tumors involving trophoblastic tissue}} | ||
'''Trophoblastic neoplasms''' are a group of rare tumors that involve the [[trophoblast]], the layer of cells that surrounds the embryo and contributes to the formation of the [[placenta]]. These neoplasms are part of a broader category known as [[gestational trophoblastic disease]] (GTD), which includes both benign and malignant conditions. | '''Trophoblastic neoplasms''' are a group of rare tumors that involve the [[trophoblast]], the layer of cells that surrounds the embryo and contributes to the formation of the [[placenta]]. These neoplasms are part of a broader category known as [[gestational trophoblastic disease]] (GTD), which includes both benign and malignant conditions. | ||
==Types== | ==Types== | ||
Trophoblastic neoplasms can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and clinical implications: | Trophoblastic neoplasms can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and clinical implications: | ||
===Hydatidiform mole=== | ===Hydatidiform mole=== | ||
A [[hydatidiform mole]] is a benign form of trophoblastic disease that can be either complete or partial. It is characterized by abnormal growth of trophoblastic tissue and can lead to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease if not treated. | A [[hydatidiform mole]] is a benign form of trophoblastic disease that can be either complete or partial. It is characterized by abnormal growth of trophoblastic tissue and can lead to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease if not treated. | ||
===Invasive mole=== | ===Invasive mole=== | ||
An [[invasive mole]] is a type of trophoblastic neoplasm that occurs when a hydatidiform mole invades the muscular layer of the uterus. It can cause significant bleeding and may require chemotherapy for treatment. | An [[invasive mole]] is a type of trophoblastic neoplasm that occurs when a hydatidiform mole invades the muscular layer of the uterus. It can cause significant bleeding and may require chemotherapy for treatment. | ||
===Choriocarcinoma=== | ===Choriocarcinoma=== | ||
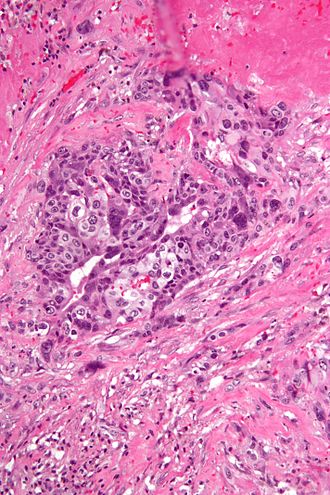
[[Choriocarcinoma]] is a highly malignant form of trophoblastic neoplasm that can occur after any type of pregnancy. It is characterized by rapid growth and early metastasis, often to the lungs and brain. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy. | [[Choriocarcinoma]] is a highly malignant form of trophoblastic neoplasm that can occur after any type of pregnancy. It is characterized by rapid growth and early metastasis, often to the lungs and brain. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy. | ||
[[File:Choriocarcinoma_-2-_high_mag.jpg|left|thumb|High magnification micrograph of choriocarcinoma.]] | |||
[[File:Choriocarcinoma_-2-_high_mag.jpg|thumb | |||
===Placental site trophoblastic tumor=== | ===Placental site trophoblastic tumor=== | ||
A [[placental site trophoblastic tumor]] (PSTT) is a rare form of trophoblastic neoplasm that arises from the placental implantation site. It is less responsive to chemotherapy compared to other types and may require surgical intervention. | A [[placental site trophoblastic tumor]] (PSTT) is a rare form of trophoblastic neoplasm that arises from the placental implantation site. It is less responsive to chemotherapy compared to other types and may require surgical intervention. | ||
===Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor=== | ===Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor=== | ||
An [[epithelioid trophoblastic tumor]] (ETT) is another rare variant that resembles carcinoma and can occur years after a normal pregnancy. It is often treated with surgery and chemotherapy. | An [[epithelioid trophoblastic tumor]] (ETT) is another rare variant that resembles carcinoma and can occur years after a normal pregnancy. It is often treated with surgery and chemotherapy. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of trophoblastic neoplasms typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Measurement of [[human chorionic gonadotropin]] (hCG) levels is crucial, as elevated levels can indicate the presence of trophoblastic disease. | Diagnosis of trophoblastic neoplasms typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Measurement of [[human chorionic gonadotropin]] (hCG) levels is crucial, as elevated levels can indicate the presence of trophoblastic disease. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment strategies for trophoblastic neoplasms depend on the type and stage of the disease. Chemotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for malignant forms such as choriocarcinoma, while surgical intervention may be necessary for localized tumors like PSTT and ETT. | Treatment strategies for trophoblastic neoplasms depend on the type and stage of the disease. Chemotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for malignant forms such as choriocarcinoma, while surgical intervention may be necessary for localized tumors like PSTT and ETT. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for patients with trophoblastic neoplasms varies based on the type and extent of the disease. Early detection and treatment generally lead to favorable outcomes, especially for choriocarcinoma, which is highly sensitive to chemotherapy. | The prognosis for patients with trophoblastic neoplasms varies based on the type and extent of the disease. Early detection and treatment generally lead to favorable outcomes, especially for choriocarcinoma, which is highly sensitive to chemotherapy. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Gestational trophoblastic disease]] | * [[Gestational trophoblastic disease]] | ||
* [[Human chorionic gonadotropin]] | * [[Human chorionic gonadotropin]] | ||
* [[Placenta]] | * [[Placenta]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* Seckl, M. J., Sebire, N. J., & Berkowitz, R. S. (2010). Gestational trophoblastic disease. The Lancet, 376(9742), 717-729. | * Seckl, M. J., Sebire, N. J., & Berkowitz, R. S. (2010). Gestational trophoblastic disease. The Lancet, 376(9742), 717-729. | ||
* Lurain, J. R. (2010). Gestational trophoblastic disease II: classification and management of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 203(1), 11-18. | * Lurain, J. R. (2010). Gestational trophoblastic disease II: classification and management of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 203(1), 11-18. | ||
[[Category:Trophoblastic neoplasms]] | [[Category:Trophoblastic neoplasms]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:32, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Trophoblastic neoplasm | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Gestational trophoblastic disease |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, enlarged uterus |
| Complications | Metastasis, hemorrhage, infertility |
| Onset | Reproductive age |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | Hydatidiform mole, Choriocarcinoma, Placental site trophoblastic tumor, Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor |
| Causes | Abnormal fertilization |
| Risks | Prior molar pregnancy, advanced maternal age, history of miscarriage |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound, hCG levels, histopathology |
| Differential diagnosis | Ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, ovarian tumor |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, surgery |
| Medication | Methotrexate, Dactinomycin |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A group of rare tumors involving trophoblastic tissue
Trophoblastic neoplasms are a group of rare tumors that involve the trophoblast, the layer of cells that surrounds the embryo and contributes to the formation of the placenta. These neoplasms are part of a broader category known as gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), which includes both benign and malignant conditions.
Types[edit]
Trophoblastic neoplasms can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and clinical implications:
Hydatidiform mole[edit]
A hydatidiform mole is a benign form of trophoblastic disease that can be either complete or partial. It is characterized by abnormal growth of trophoblastic tissue and can lead to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease if not treated.
Invasive mole[edit]
An invasive mole is a type of trophoblastic neoplasm that occurs when a hydatidiform mole invades the muscular layer of the uterus. It can cause significant bleeding and may require chemotherapy for treatment.
Choriocarcinoma[edit]
Choriocarcinoma is a highly malignant form of trophoblastic neoplasm that can occur after any type of pregnancy. It is characterized by rapid growth and early metastasis, often to the lungs and brain. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy.
Placental site trophoblastic tumor[edit]
A placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT) is a rare form of trophoblastic neoplasm that arises from the placental implantation site. It is less responsive to chemotherapy compared to other types and may require surgical intervention.
Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor[edit]
An epithelioid trophoblastic tumor (ETT) is another rare variant that resembles carcinoma and can occur years after a normal pregnancy. It is often treated with surgery and chemotherapy.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of trophoblastic neoplasms typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Measurement of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels is crucial, as elevated levels can indicate the presence of trophoblastic disease.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment strategies for trophoblastic neoplasms depend on the type and stage of the disease. Chemotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for malignant forms such as choriocarcinoma, while surgical intervention may be necessary for localized tumors like PSTT and ETT.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with trophoblastic neoplasms varies based on the type and extent of the disease. Early detection and treatment generally lead to favorable outcomes, especially for choriocarcinoma, which is highly sensitive to chemotherapy.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- Seckl, M. J., Sebire, N. J., & Berkowitz, R. S. (2010). Gestational trophoblastic disease. The Lancet, 376(9742), 717-729.
- Lurain, J. R. (2010). Gestational trophoblastic disease II: classification and management of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 203(1), 11-18.