Holoprosencephaly: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Holoprosencephaly | |||
| image = [[File:EmbryonicBrain.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram of embryonic brain development | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]], [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Facial dysmorphism]], [[Cleft lip and palate]], [[Cyclopia]], [[Microcephaly]] | |||
| complications = [[Developmental delay]], [[Seizures]], [[Endocrine disorders]] | |||
| onset = [[Prenatal]] | |||
| duration = Lifelong | |||
| causes = Genetic mutations, [[Chromosomal abnormalities]], [[Environmental factors]] | |||
| risks = [[Maternal diabetes]], [[Alcohol consumption during pregnancy]], [[Retinoic acid]] exposure | |||
| diagnosis = [[Prenatal ultrasound]], [[MRI]], [[Genetic testing]] | |||
| differential = [[Septo-optic dysplasia]], [[Agenesis of the corpus callosum]], [[Microcephaly]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[Surgical intervention]], [[Hormone replacement therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies widely; often poor in severe cases | |||
| frequency = 1 in 10,000 to 20,000 live births | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Holoprosencephaly_fetus_14_weks_US_by_Dr._W._Moroder.jpg|Holoprosencephaly|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Holoprosencephaly''' is a [[congenital disorder]] that affects the development of the [[brain]] in the early stages of [[pregnancy]]. This condition is characterized by the failure of the [[prosencephalon]] (the forebrain of the embryo) to develop. As a result, the brain does not divide into two hemispheres, leading to defects in the structure and function of the brain. | '''Holoprosencephaly''' is a [[congenital disorder]] that affects the development of the [[brain]] in the early stages of [[pregnancy]]. This condition is characterized by the failure of the [[prosencephalon]] (the forebrain of the embryo) to develop. As a result, the brain does not divide into two hemispheres, leading to defects in the structure and function of the brain. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Holoprosencephaly is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Mutations in certain genes, such as [[SHH]], [[ZIC2]], [[SIX3]], and [[TGIF1]], have been associated with this condition. Environmental factors, such as maternal diabetes, alcohol use during pregnancy, and certain infections, can also increase the risk of holoprosencephaly. | Holoprosencephaly is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Mutations in certain genes, such as [[SHH]], [[ZIC2]], [[SIX3]], and [[TGIF1]], have been associated with this condition. Environmental factors, such as maternal diabetes, alcohol use during pregnancy, and certain infections, can also increase the risk of holoprosencephaly. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of holoprosencephaly can vary widely, depending on the severity of the brain malformation. In severe cases, symptoms can include [[microcephaly]] (small head size), [[hydrocephalus]] (buildup of fluid in the brain), [[seizures]], and intellectual disability. In milder cases, symptoms can include [[hypotelorism]] (closely spaced eyes), [[cleft lip]] and/or [[cleft palate]], and mild learning disabilities. | The symptoms of holoprosencephaly can vary widely, depending on the severity of the brain malformation. In severe cases, symptoms can include [[microcephaly]] (small head size), [[hydrocephalus]] (buildup of fluid in the brain), [[seizures]], and intellectual disability. In milder cases, symptoms can include [[hypotelorism]] (closely spaced eyes), [[cleft lip]] and/or [[cleft palate]], and mild learning disabilities. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Holoprosencephaly can often be diagnosed before birth through [[ultrasound]] imaging. After birth, the diagnosis can be confirmed through [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) or [[computed tomography]] (CT) scans of the brain. | Holoprosencephaly can often be diagnosed before birth through [[ultrasound]] imaging. After birth, the diagnosis can be confirmed through [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) or [[computed tomography]] (CT) scans of the brain. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
There is currently no cure for holoprosencephaly. Treatment is supportive and depends on the symptoms. This can include medications to manage seizures, shunt surgery for hydrocephalus, and therapies to address developmental delays. | There is currently no cure for holoprosencephaly. Treatment is supportive and depends on the symptoms. This can include medications to manage seizures, shunt surgery for hydrocephalus, and therapies to address developmental delays. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for individuals with holoprosencephaly depends on the severity of the brain malformation. Those with severe forms of the condition often do not survive past infancy. Those with milder forms can live into adulthood, but may have intellectual and physical disabilities. | The prognosis for individuals with holoprosencephaly depends on the severity of the brain malformation. Those with severe forms of the condition often do not survive past infancy. Those with milder forms can live into adulthood, but may have intellectual and physical disabilities. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Congenital disorder]] | * [[Congenital disorder]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 34: | ||
* [[Genetic disorder]] | * [[Genetic disorder]] | ||
* [[Pregnancy]] | * [[Pregnancy]] | ||
[[Category:Congenital disorders]] | [[Category:Congenital disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Brain disorders]] | [[Category:Brain disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Genetic disorders]] | [[Category:Genetic disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Pregnancy]] | [[Category:Pregnancy]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:16, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Holoprosencephaly | |
|---|---|
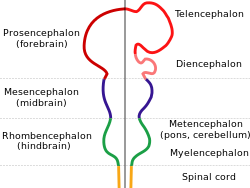
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Facial dysmorphism, Cleft lip and palate, Cyclopia, Microcephaly |
| Complications | Developmental delay, Seizures, Endocrine disorders |
| Onset | Prenatal |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations, Chromosomal abnormalities, Environmental factors |
| Risks | Maternal diabetes, Alcohol consumption during pregnancy, Retinoic acid exposure |
| Diagnosis | Prenatal ultrasound, MRI, Genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Septo-optic dysplasia, Agenesis of the corpus callosum, Microcephaly |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, Surgical intervention, Hormone replacement therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies widely; often poor in severe cases |
| Frequency | 1 in 10,000 to 20,000 live births |
| Deaths | N/A |

Holoprosencephaly is a congenital disorder that affects the development of the brain in the early stages of pregnancy. This condition is characterized by the failure of the prosencephalon (the forebrain of the embryo) to develop. As a result, the brain does not divide into two hemispheres, leading to defects in the structure and function of the brain.
Causes[edit]
Holoprosencephaly is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Mutations in certain genes, such as SHH, ZIC2, SIX3, and TGIF1, have been associated with this condition. Environmental factors, such as maternal diabetes, alcohol use during pregnancy, and certain infections, can also increase the risk of holoprosencephaly.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of holoprosencephaly can vary widely, depending on the severity of the brain malformation. In severe cases, symptoms can include microcephaly (small head size), hydrocephalus (buildup of fluid in the brain), seizures, and intellectual disability. In milder cases, symptoms can include hypotelorism (closely spaced eyes), cleft lip and/or cleft palate, and mild learning disabilities.
Diagnosis[edit]
Holoprosencephaly can often be diagnosed before birth through ultrasound imaging. After birth, the diagnosis can be confirmed through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans of the brain.
Treatment[edit]
There is currently no cure for holoprosencephaly. Treatment is supportive and depends on the symptoms. This can include medications to manage seizures, shunt surgery for hydrocephalus, and therapies to address developmental delays.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with holoprosencephaly depends on the severity of the brain malformation. Those with severe forms of the condition often do not survive past infancy. Those with milder forms can live into adulthood, but may have intellectual and physical disabilities.


