Joubert syndrome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Joubert syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Syndrome_de_Joubert_IRM_PAMJ-22-127-g001.jpg]] | |||
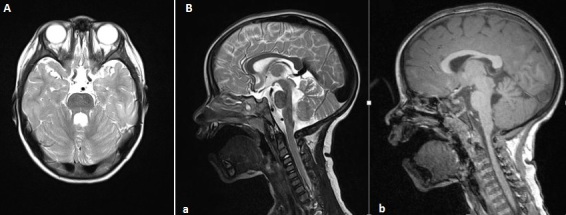
| caption = MRI showing the "molar tooth sign" characteristic of Joubert syndrome | |||
| field = [[Neurology]], [[Genetics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Hypotonia]], [[ataxia]], [[developmental delay]], [[abnormal eye movements]], [[breathing abnormalities]] | |||
| onset = [[Infancy]] | |||
| duration = [[Lifelong]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[MRI]], [[genetic testing]] | |||
| differential = [[Dandy-Walker malformation]], [[cerebellar hypoplasia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[physical therapy]], [[occupational therapy]], [[speech therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = [[Variable]], depends on severity and associated features | |||
| frequency = 1 in 80,000 to 1 in 100,000 | |||
| deaths = Rare, depends on severity and complications | |||
}} | |||
'''Joubert syndrome''' is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the underdevelopment of the [[cerebellar vermis]], a part of the brain that controls balance and coordination. This condition is part of a group of disorders known as [[ciliopathies]], which are caused by defects in the function of cellular structures called [[cilia]]. | |||
== Signs and Symptoms == | == Signs and Symptoms == | ||
Individuals with Joubert syndrome typically present with a range of symptoms, including: | Individuals with Joubert syndrome typically present with a range of symptoms, including: | ||
| Line 8: | Line 25: | ||
* Abnormal eye movements, such as [[nystagmus]] | * Abnormal eye movements, such as [[nystagmus]] | ||
* Breathing abnormalities, including episodes of rapid breathing (hyperpnea) and apnea | * Breathing abnormalities, including episodes of rapid breathing (hyperpnea) and apnea | ||
== Genetics == | == Genetics == | ||
Joubert syndrome is genetically heterogeneous, meaning it can be caused by mutations in several different genes. Some of the genes associated with Joubert syndrome include: | Joubert syndrome is genetically heterogeneous, meaning it can be caused by mutations in several different genes. Some of the genes associated with Joubert syndrome include: | ||
| Line 15: | Line 31: | ||
* [[TMEM67]] | * [[TMEM67]] | ||
* [[CC2D2A]] | * [[CC2D2A]] | ||
These genes are involved in the function and structure of cilia, which are essential for various cellular processes. | These genes are involved in the function and structure of cilia, which are essential for various cellular processes. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of Joubert syndrome is based on clinical features and neuroimaging findings. A key diagnostic feature is the "molar tooth sign" observed on [[MRI]] scans, which results from the abnormal development of the cerebellar vermis and brainstem. | The diagnosis of Joubert syndrome is based on clinical features and neuroimaging findings. A key diagnostic feature is the "molar tooth sign" observed on [[MRI]] scans, which results from the abnormal development of the cerebellar vermis and brainstem. | ||
== Management == | == Management == | ||
There is no cure for Joubert syndrome, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include: | There is no cure for Joubert syndrome, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include: | ||
| Line 27: | Line 40: | ||
* Speech therapy to address communication difficulties | * Speech therapy to address communication difficulties | ||
* Regular monitoring and management of breathing abnormalities | * Regular monitoring and management of breathing abnormalities | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for individuals with Joubert syndrome varies widely depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of associated conditions. Some individuals may have mild symptoms and lead relatively normal lives, while others may have significant developmental and physical challenges. | The prognosis for individuals with Joubert syndrome varies widely depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of associated conditions. Some individuals may have mild symptoms and lead relatively normal lives, while others may have significant developmental and physical challenges. | ||
== See also == | |||
== | |||
* [[Cerebellar vermis]] | * [[Cerebellar vermis]] | ||
* [[Ciliopathy]] | * [[Ciliopathy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:37, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Joubert syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hypotonia, ataxia, developmental delay, abnormal eye movements, breathing abnormalities |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Infancy |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, MRI, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Dandy-Walker malformation, cerebellar hypoplasia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and associated features |
| Frequency | 1 in 80,000 to 1 in 100,000 |
| Deaths | Rare, depends on severity and complications |
Joubert syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the underdevelopment of the cerebellar vermis, a part of the brain that controls balance and coordination. This condition is part of a group of disorders known as ciliopathies, which are caused by defects in the function of cellular structures called cilia.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
Individuals with Joubert syndrome typically present with a range of symptoms, including:
- Hypotonia (low muscle tone)
- Ataxia (lack of muscle coordination)
- Developmental delays
- Abnormal eye movements, such as nystagmus
- Breathing abnormalities, including episodes of rapid breathing (hyperpnea) and apnea
Genetics[edit]
Joubert syndrome is genetically heterogeneous, meaning it can be caused by mutations in several different genes. Some of the genes associated with Joubert syndrome include:
These genes are involved in the function and structure of cilia, which are essential for various cellular processes.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of Joubert syndrome is based on clinical features and neuroimaging findings. A key diagnostic feature is the "molar tooth sign" observed on MRI scans, which results from the abnormal development of the cerebellar vermis and brainstem.
Management[edit]
There is no cure for Joubert syndrome, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include:
- Physical therapy to improve motor skills and coordination
- Occupational therapy to assist with daily activities
- Speech therapy to address communication difficulties
- Regular monitoring and management of breathing abnormalities
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with Joubert syndrome varies widely depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of associated conditions. Some individuals may have mild symptoms and lead relatively normal lives, while others may have significant developmental and physical challenges.
See also[edit]
External Links[edit]
| Diseases of cilia | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
See also: ciliary proteins
|
| Deficiencies of intracellular signaling peptides and proteins | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


