Watson syndrome

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Watson syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pulmonary stenosis, café-au-lait spots, short stature, learning disabilities |
| Complications | |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Mutations in the NF1 gene |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Neurofibromatosis type I, Noonan syndrome |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Symptomatic management |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally good with management |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
Other Names[edit]
Alagille syndrome, Hepatic ductular hypoplasia; Watson Alagille syndrome; Alagille-Watson syndrome; Cholestasis with peripheral pulmonary stenosis; Arteriohepatic dysplasia; Paucity of interlobular bile ducts; Cardio-vertebral syndrome; Watson-Miller syndrome; Hepatofacioneurocardiovertebral syndrome
Clinical features[edit]
- Alagille syndrome is a genetic syndrome that can affect the liver and other parts of the body.
- Signs and symptoms of Alagille syndrome are generally noticed in infancy or early childhood.
- Type of symptoms and severity varies greatly, even among people in the same family, so that in some cases the symptoms are severe, and in others, very mild.
- The liver problems may be the first symptoms of the syndrome, and may include yellow color of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice); itchy skin; bumps on the skin caused by deposits of cholesterol and fats (xanthomas); pale, loose bowel movements; and poor growth.
- Alagille syndrome can also affect other parts of the body including the heart, brain, kidneys, blood vessels, eyes, face, and skeleton.
- People with Alagille syndrome may have distinctive facial features too, including a broad, prominent forehead, deep-set eyes, and a small, pointed chin.
- While there is no known cure for Alagille syndrome, there are treatments that can help control symptoms.
- Possible treatments may include medication that increases the flow of bile and careful management of diet to minimize nutrition and vitamin related problems.
- In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Cause[edit]
The liver problems result from having fewer small bile ducts than normal in the liver. This leads to bile building-up inside the liver, which in turn causes liver scarring and damage. Alagille syndrome is caused by changes or mutations in the JAG1 and NOTCH2 genes.
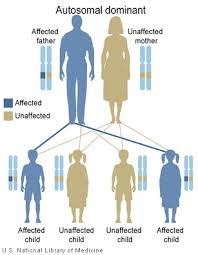
Inheritance[edit]
Inheritance is autosomal dominant. However, in about half of cases the mutation occurs as a new change ("de novo") without being inherited from either parents.
Symptoms[edit]
Alagille syndrome is a complex multisystem disease involving the liver, brain, heart, eyes, face, and skeleton. Symptoms typically present in infancy or early childhood. The severity of the syndrome varies greatly, even within the same family. Symptoms range from so mild as to go unnoticed to severe enough to require heart and/or liver transplants. 80%-99% of people have these symptoms
- Cholestasis
- Corneal dystrophy
- Failure to thrive
- Hepatomegaly
- Reduced number of intrahepatic bile ducts
Treatment[edit]
Many doctors may be necessary for the best management of Alagille syndrome, including specialists in medical genetics, gastroenterology (for digestive system and liver problems), nephrology (for kidney problems), nutrition, cardiology (for heart problems), ophthalmology (for eye problems), liver transplantation, and child development. Treatment may include: Medication that increases bile flow (ursodeoxycholic acid) and that reduces the itching, such as cholestyramine, rifampin, and naltrexone. Biliary diversion procedures (partial internal biliary diversion and ileal exclusion) that interrupt the normal bile circulation between the intestines and liver resulting in the bile being eliminated and therefore lowering the blood bile levels. These procedures relieve symptoms of liver disease, such as itching, and improve the quality of life, but do not prevent the progression of liver disease. Vitamin and special nutrition supplementation to support proper growth and development. Liver Transplantation to increase life span and improve liver function for those with end stage liver disease. Watson syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by Lisch nodules of the ocular iris, axillary/inguinal freckling, pulmonary valvular stenosis, relative macrocephaly, short stature, and neurofibromas. Watson syndrome is allelic to NF1, the same gene associated with neurofibromatosis type 1.
See also[edit]
Latest research (Pubmed)[edit]

Mitchell E, Gilbert M, Loomes KM. Clin Liver Dis. 2018 Nov;22(4):625-641. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Aug 22. PMID: 30266153 Review. Alagille syndrome is a complex multisystem autosomal dominant disorder with a wide variability in penetrance of clinical features.
Jesina D. Neonatal Netw. 2017 Nov 1;36(6):343-347. doi: 10.1891/0730-0832.36.6.343. PMID: 29185945 Review. Alagille syndrome (AGS) is a highly complex, multisystem, autosomal dominant disorder that is caused by a defect in the Notch signaling pathway.
Wakim El-Khoury J, Venetz JP, Rutz T, Sciarra A, Unger S, Sempoux C, Moradpour D, Fraga M. Rev Med Suisse. 2019 Aug 28;15(660):1506-1510. PMID: 31496175 Review. French. Alagille syndrome is a rare disorder with low physician awareness. Inherited mutations affect the Notch pathway. Although the molecular basis of Alagille syndrome is well defined, no specific targeted therapy exists
Turnpenny PD, Ellard S. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012 Mar;20(3):251-7. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.181. Epub 2011 Sep 21. PMID: 21934706 Free PMC article. Review. Alagille syndrome (ALGS), also known as arteriohepatic dysplasia, is a multisystem disorder due to defects in components of the Notch signalling pathway, most commonly due to mutation in JAG1 (ALGS type 1), but in a small proportion of cases mutation in NOTCH2.
Frequently asked questions[edit]
- What are the symptoms of Alagille syndrome?
See above - Jaundice, xanthomas, pale, loose bowel movements and poor growth etc.
- Is there a cure for Alagille syndrome?
No, there is no cure but there are many treatments as noted above including supportive care, vitamins, medications and or liver transplantation.
- What is Alagille syndrome life expectancy?
The life expectancy varies - about 75% of people diagnosed with the syndrome in childhood live to at least age 20.
- Is Alagille syndrome detectable prior to birth?
- Yes. Prenatal genetic testing can detect the Alagille syndrome as it is a genetic disorder.
The diagnosis of Alagille syndrome can be confirmed in many cases by molecular genetic testing, which reveals the presence of a JAG1 or NOTCH2 gene mutation.
- Is Alagille syndrome rare?
Yes. It is a rare genetic disorder. It affects about 1 in 70,000 newborns.
Answer these questions[edit]
- Can you live with Alagille syndrome?
- What does the 20th chromosome do?
- What do people with Alagille syndrome look like?
- Is Alagille syndrome a disability?
- Does Alagille syndrome affect development?
- What is ALGS?
- What is posterior Embryotoxon?
External links[edit]

| Phakomatosis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Deficiencies of intracellular signaling peptides and proteins | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This article is a Genodermatoses stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian