SR-14968: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
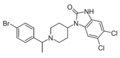
File:SR-14968 structure.png|SR-14968 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:33, 20 February 2025
SR-14968 is a drug that belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, which means it specifically targets and inhibits the COX-2 enzyme. This enzyme is responsible for the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals that promote inflammation, pain, and fever in the body. By inhibiting COX-2, SR-14968 helps to reduce these symptoms.
Pharmacology[edit]
SR-14968 works by selectively inhibiting the COX-2 enzyme. This enzyme is one of two cyclooxygenase enzymes (the other being COX-1) that convert arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are involved in the body's inflammatory response, and by inhibiting their production, SR-14968 can help to reduce inflammation and associated symptoms such as pain and fever.
Unlike traditional NSAIDs, which inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, SR-14968 is a selective COX-2 inhibitor. This means it does not inhibit the COX-1 enzyme, which is responsible for protecting the stomach lining and regulating blood clotting. As a result, SR-14968 may cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects than traditional NSAIDs.
Clinical Use[edit]
SR-14968 is used in the treatment of conditions where inflammation is a significant component, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It may also be used for pain relief in other conditions.
Side Effects[edit]
As with all NSAIDs, SR-14968 can cause side effects. These may include gastrointestinal issues such as stomach pain, heartburn, and nausea, as well as more serious side effects such as ulcers and bleeding. It may also increase the risk of heart attack or stroke, particularly in people with pre-existing heart disease or risk factors for heart disease.
See Also[edit]
-
SR-14968