Flurazepam: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{intro}} Flurazepam is an orally available benzodiazepine used for therapy of insomnia. {{livtox}} As with most benzodiazepines, flurazepam therapy has not been asso..." |
CSV import |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{{benzodiazepines}} | {{benzodiazepines}} | ||
{{coststubd}} | {{coststubd}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
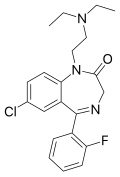
File:Flurazepam.svg|Chemical structure of Flurazepam | |||
File:Flurazepam3d.png|3D model of Flurazepam | |||
File:Dalmane15mg.jpg|Dalmane 15 mg capsules | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:03, 18 February 2025
Information about Flurazepam[edit]
Flurazepam is an orally available benzodiazepine used for therapy of insomnia.
Liver safety of Flurazepam[edit]
As with most benzodiazepines, flurazepam therapy has not been associated with serum aminotransferase or alkaline phosphatase elevations; clinically apparent liver injury from flurazepam has been reported, but is very rare.
Mechanism of action of Flurazepam[edit]
Flurazepam (flur az' e pam) is a benzodiazepine used as a sleeping aid in the therapy of insomnia. The sedating and soporific activity of the benzodiazepines is mediated by their ability to enhance gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission through binding to the GABA-A receptor.
FDA approval information for Flurazepam[edit]
Flurazepam was approved in the United States in 1970 for the short term management of insomnia. For many years flurazepam was one of the most prescribed medications for sleep. Currently, it is less commonly used, having been replaced by benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine analogues with shorter half-life and better tolerance. Flurazepam is available in multiple generic forms and formerly under the brand name of Dalmane in capsules of 15 and 30 mg. The recommended dose for adults is 15 to 30 mg shortly before bedtime. Chronic use is often followed by tolerance and decrease in effectiveness.
Side effects of Flurazepam[edit]
The most common side effects of flurazepam are dose related and include daytime drowsiness, lethargy, and dizziness. Flurazepam and other benzodiazepines are classified as schedule IV controlled substances, indicating that they are capable of causing dependence, tolerance and abuse.
Benzodiazipines[edit]
- Alprazolam
- Chlordiazepoxide
- Diazepam (Oral)
- Estazolam
- Flurazepam
- Lorazepam
- Midazolam
- Oxazepam
- Quazepam
- Temazepam
- Triazolam
Anticonvulsants Drugs[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Flurazepam
-
3D model of Flurazepam
-
Dalmane 15 mg capsules