Bonnet–Dechaume–Blanc syndrome

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Bonnet–Dechaume–Blanc syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Wyburn-Mason syndrome |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Neurology, Ophthalmology |
| Symptoms | Arteriovenous malformations in the retina, midbrain, and facial skin |
| Complications | Intracerebral hemorrhage, seizures, vision loss |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, MRI, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Sturge-Weber syndrome, Von Hippel-Lindau disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention, radiotherapy, laser therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on severity and complications |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A rare congenital disorder affecting the eyes and brain
Bonnet–Dechaume–Blanc syndrome (BDBS), also known as Wyburn-Mason syndrome, is a rare congenital disorder characterized by arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) that primarily affect the retina and the brain. This condition is part of the phakomatoses group of disorders, which are neurocutaneous syndromes involving the central nervous system and the skin.
Presentation[edit]
BDBS is typically identified by the presence of AVMs in the retina and the cerebral vasculature. These malformations can lead to a variety of symptoms depending on their size and location.
Ocular Manifestations[edit]

The ocular manifestations of BDBS include retinal AVMs, which can be detected through ophthalmoscopy or fluorescein angiography. These AVMs may cause visual disturbances such as decreased visual acuity, visual field defects, or even retinal detachment.
Neurological Manifestations[edit]

Neurologically, patients may present with symptoms due to cerebral AVMs, such as headaches, seizures, or intracerebral hemorrhage. The location of the AVMs in the brain can lead to specific neurological deficits, including hemiparesis or aphasia.
Visual Field Defects[edit]

Patients with BDBS may experience visual field defects such as homonymous hemianopia, which is a loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes. This occurs due to the involvement of the visual pathways in the brain.
Pathophysiology[edit]
The exact cause of BDBS is not well understood, but it is believed to result from developmental anomalies in the embryonic vasculature. The AVMs are thought to arise from a failure of the normal regression of embryonic vascular connections, leading to direct arterial-to-venous shunts without intervening capillaries.
Diagnosis[edit]
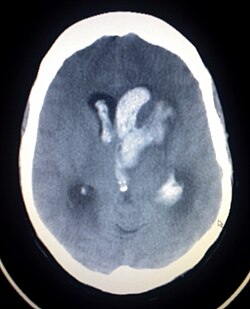
Diagnosis of BDBS is primarily clinical, supported by imaging studies. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans can reveal cerebral AVMs, while fluorescein angiography is used to visualize retinal AVMs.

Management[edit]
There is no cure for BDBS, and management is primarily symptomatic and supportive. Treatment options may include:
- Laser photocoagulation or cryotherapy for retinal AVMs to prevent complications such as retinal detachment.
- Surgical intervention or endovascular therapy for cerebral AVMs to reduce the risk of hemorrhage.
- Anticonvulsants for seizure management.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis of BDBS varies depending on the severity and location of the AVMs. Early detection and management of complications can improve outcomes, but the condition can lead to significant morbidity due to visual and neurological impairments.
See also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian