Vinyl halide
Vinyl halide is a group of organic compounds consisting of a vinyl group (a ethylene molecule missing two hydrogen atoms) attached to a halogen atom. These compounds are important in various industrial applications, particularly in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a material widely used in construction, packaging, and healthcare products. Vinyl halides are also used in the synthesis of other polymers and as intermediates in organic synthesis.
Structure and Properties[edit]
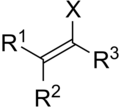
A vinyl halide molecule consists of a two-carbon vinyl group bonded to a halogen (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine). The general formula for vinyl halides is C2H3X, where X represents the halogen. The presence of the halogen atom significantly affects the physical and chemical properties of the compound, including its reactivity, boiling point, and solubility.
Types of Vinyl Halides[edit]
- Vinyl Fluoride (C2H3F): Used in the production of polyvinyl fluoride (PVF), a material with applications in protective coatings.
- Vinyl Chloride (C2H3Cl): The most significant vinyl halide, primarily used to produce PVC. It is a colorless gas with a mild, sweet odor but is toxic and carcinogenic.
- Vinyl Bromide (C2H3Br): Used in the manufacture of flame retardants and as an intermediate in organic synthesis.
- Vinyl Iodide (C2H3I): Employed in specialized organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of certain pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Production[edit]
Vinyl halides are typically produced through the halogenation of ethylene. For example, vinyl chloride is produced by combining ethylene with chlorine gas, either directly or through the reaction of ethylene with hydrogen chloride in the presence of oxygen, typically using a copper chloride catalyst.
Applications[edit]
The primary application of vinyl halides is in the production of polymers. PVC, derived from vinyl chloride, is the most well-known example, used in a wide range of products from pipes and cable insulation to medical devices and clothing. Other vinyl halides serve as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Health and Environmental Concerns[edit]
Vinyl halides, particularly vinyl chloride, pose significant health risks. Exposure to vinyl chloride gas can cause a range of health issues, including liver damage and an increased risk of cancer. Consequently, the production and handling of vinyl halides are subject to strict regulatory controls to protect human health and the environment.
Regulation and Safety[edit]
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and regulations to limit exposure to vinyl halides, especially vinyl chloride. These regulations cover permissible exposure limits in the workplace, emission standards, and requirements for the handling and disposal of these compounds.
See Also[edit]
-
Vinyl halide
-
Carbometalation
-
Takai Mechanism
-
Stork-Zhao Olefination
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian