Varenicline
Medication used to treat nicotine addiction
| Varenicline | |
|---|---|
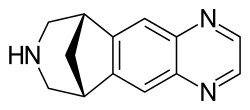
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Varenicline is a medication used to treat nicotine addiction. It is marketed under the brand name Chantix in the United States and Champix in other countries. Varenicline is a prescription medication that helps people stop smoking by reducing withdrawal symptoms and decreasing the pleasurable effects of cigarettes and other tobacco products.
Mechanism of action[edit]
Varenicline is a partial agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtype _4_2. This receptor is believed to play a key role in the addictive properties of nicotine. By partially stimulating these receptors, varenicline reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms associated with smoking cessation. Additionally, it blocks nicotine from binding to these receptors, thereby reducing the rewarding effects of smoking.
Medical uses[edit]
Varenicline is primarily used as an aid to smoking cessation. It is typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive program that includes counseling and support. The standard course of treatment lasts for 12 weeks, but it may be extended for an additional 12 weeks to increase the likelihood of long-term abstinence.
Side effects[edit]
Common side effects of varenicline include nausea, headache, difficulty sleeping, and abnormal dreams. Some users may experience mood changes, depression, or suicidal thoughts. It is important for patients to be monitored for any changes in mood or behavior while taking this medication.
History[edit]
Varenicline was developed by Pfizer and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2006. It has since become a widely used treatment for smoking cessation, although its use has been subject to some controversy due to reports of psychiatric side effects.
Research[edit]
Ongoing research is examining the effectiveness of varenicline in combination with other smoking cessation therapies, as well as its potential use in treating other forms of addiction. Studies are also investigating the long-term safety and efficacy of varenicline.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
Varenicline[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Varenicline
-
Ball-and-stick model of Varenicline
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian

