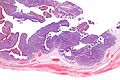
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary
| Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, bloating, pelvic mass |
| Complications | Metastasis |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Age, family history, genetic factors |
| Diagnosis | Pelvic examination, Ultrasound, CT scan, Biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Other types of ovarian cancer |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, Chemotherapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary is a rare type of ovarian cancer that resembles urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. It is characterized by the presence of transitional cells, which are similar to the cells lining the urinary tract.
Epidemiology[edit]
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary is an uncommon malignancy, accounting for less than 2% of all ovarian cancers. It typically occurs in postmenopausal women, with a median age of diagnosis around 60 years.
Pathophysiology[edit]
The exact pathogenesis of transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary is not well understood. It is hypothesized that these tumors may arise from surface epithelial-stromal tumors of the ovary, specifically from the Brenner tumor, which contains transitional cell elements. The tumor cells exhibit a transitional or urothelial phenotype, which is distinct from the more common serous carcinoma of the ovary.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary often present with non-specific symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and the presence of a pelvic mass. These symptoms are similar to those of other types of ovarian cancer, making early diagnosis challenging.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. A pelvic examination may reveal an adnexal mass. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound and CT scan are used to assess the extent of the disease. Definitive diagnosis is made through histopathological examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen, where the presence of transitional cell morphology is confirmed.
Differential Diagnosis[edit]
The differential diagnosis for transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary includes other types of ovarian neoplasms, such as:
Treatment[edit]
The primary treatment for transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary is surgical resection, which may include total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and omentectomy. Chemotherapy is often administered postoperatively, with regimens similar to those used for other epithelial ovarian cancers, such as carboplatin and paclitaxel.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary varies depending on the stage at diagnosis and the response to treatment. Early-stage disease has a better prognosis, while advanced-stage disease may have a poorer outcome. Overall, the prognosis is similar to that of other epithelial ovarian cancers.
See also[edit]
| Oncology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This oncology-related article is a stub.
|
Transitional_cell_carcinoma_of_the_ovary[edit]
-
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary - very low magnification
-
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary - low magnification
-
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary - very high magnification
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian