Thioester
Thioester is a type of organic compound that is derived from carboxylic acids and thiols. They are the sulfur analogs of esters and are important in many biological processes, including the synthesis of fatty acids and polyketides.
Structure and Bonding[edit]
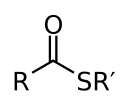
Thioesters are characterized by the presence of a sulfur atom, which replaces the oxygen atom found in regular esters. This results in a C-S-CO-R structure, where R represents any organic group. The C-S bond in thioesters is generally weaker than the C-O bond in esters, which has implications for their reactivity.
Synthesis[edit]
Thioesters can be synthesized in several ways. One common method is the reaction of a carboxylic acid with a thiol in the presence of a dehydrating agent. Another method is the reaction of an acyl chloride with a thiol. Thioesters can also be formed from alcohols and thiols using a Fischer esterification reaction.
Reactivity[edit]
Thioesters are more reactive than their oxygen counterparts due to the weaker C-S bond. They undergo many of the same reactions as esters, including hydrolysis, transesterification, and Claisen condensation. However, they also participate in unique reactions such as the Perkin reaction and the Dieckmann condensation.
Biological Importance[edit]
Thioesters play a crucial role in biology. They are involved in the synthesis of fatty acids and polyketides, and are key intermediates in the citric acid cycle. They also participate in protein synthesis and signal transduction.
See Also[edit]
|
|
|
-
Thioester 2D Structure
-
Formation of Amides
-
Native Chemical Ligation Mechanism
-
Fukuyama Coupling
-
Acetyl-CoA 2D Structure
-
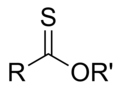
Thionoester General Structure
-
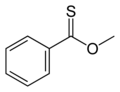
Methyl Thionobenzoate 2D Skeletal
-
Thionoester from Thioacyl Chloride 2D Skeletal
-
Transesterification of Thionoesters
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian