Brodmann area
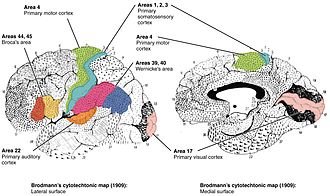



Brodmann area refers to regions of the cerebral cortex that are defined based on their cytoarchitectonic characteristics—that is, their organization of cells. These areas were first mapped and described by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann in the early 20th century, and they are still used today to describe the location of functions and structures in the brain. Brodmann's work involved the microscopic examination of the neocortex, leading to the identification of 52 distinct regions based on differences in the layers of neurons and their organization.
History[edit]
Korbinian Brodmann, born in 1868, was a German neurologist who made significant contributions to the understanding of the functional division of the cerebral cortex. His seminal work, "Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues" (Comparative Localization Studies in the Cerebral Cortex, based on the Cellular Architecture), published in 1909, laid the foundation for what would become known as Brodmann areas. Brodmann's meticulous study of the brain led to the classification of cortical areas based on their distinct cellular structures and organization, a method that was revolutionary at the time.
Brodmann Areas[edit]
Brodmann identified 52 areas, although not all are universally recognized or used today. These areas are numbered from 1 to 52, often referred to by their number, such as Brodmann area 1 (BA1), which is located in the postcentral gyrus and is involved in somatosensory processing. Other well-known Brodmann areas include:
- Brodmann area 4: Located in the precentral gyrus, this area is known as the primary motor cortex and is involved in the voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
- Brodmann area 17: This area corresponds to the primary visual cortex, located in the occipital lobe, and is crucial for processing visual information.
- Brodmann area 25: Situated in the cingulate cortex, this area is implicated in various functions, including emotion and cognition.
Significance and Applications[edit]
The mapping of Brodmann areas has been fundamental in the field of neuroscience for understanding the localization of brain functions. These areas are used as a reference in various fields, including neurology, psychiatry, and neuropsychology, to discuss brain structure-function relationships. With the advent of modern imaging techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI), the correlation between Brodmann areas and functional brain activity can be explored in vivo, providing insights into the neural basis of behavior, cognition, and neurological diseases.
Limitations and Criticisms[edit]
While Brodmann's classification has been invaluable in neuroscience, it is not without its limitations. The delineation of areas based solely on cytoarchitectonic features does not always align with functional boundaries. Additionally, there is considerable individual variability in the exact location and size of these areas across different brains. Recent studies have also identified functional areas within the brain that do not correspond to any specific Brodmann area, suggesting that the map is not exhaustive.
Conclusion[edit]
Brodmann areas continue to be a crucial framework for understanding the organization and function of the cerebral cortex. Despite its limitations, Brodmann's map remains a fundamental tool in neuroscience, providing a common language for researchers to discuss cortical structure and function. As neuroscientific techniques evolve, the integration of Brodmann's anatomical classification with functional and connectomic data promises to deepen our understanding of the complex workings of the human brain.

This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian