Paramethadione
An anticonvulsant medication
| Paramethadione | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Paramethadione is a medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy. It belongs to the class of drugs known as oxazolidinediones, which are used as anticonvulsants. Paramethadione is specifically indicated for the management of absence seizures, also known as petit mal seizures.
Pharmacology
Paramethadione works by reducing the frequency of seizures. It is believed to act on the central nervous system by modulating the activity of neurons to prevent the abnormal electrical activity that leads to seizures. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve the stabilization of neuronal membranes.
Medical uses
Paramethadione is used in the treatment of absence seizures, which are characterized by brief, sudden lapses in attention and activity. These seizures are most common in children and can interfere with learning and daily activities. Paramethadione helps to control these seizures, allowing individuals to lead more normal lives.
Side effects
Like many anticonvulsants, paramethadione can cause a range of side effects. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea. More serious side effects can include blood dyscrasias, such as agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia, as well as liver toxicity. Patients taking paramethadione require regular monitoring of blood counts and liver function.
History
Paramethadione was developed in the mid-20th century as part of a class of anticonvulsants known as oxazolidinediones. It was one of the first drugs used specifically for the treatment of absence seizures. However, due to its side effect profile and the development of newer anticonvulsants with better safety profiles, its use has declined over the years.
Chemical properties
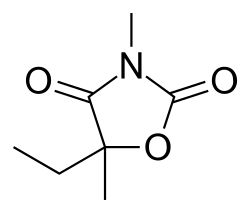
Paramethadione is a derivative of trimethadione, another anticonvulsant. It is chemically classified as an oxazolidinedione, with the chemical formula C7H11NO3. The structure of paramethadione includes a five-membered oxazolidine ring, which is a key feature of this class of drugs.
Related pages
-
Paramethadione
-
Paramethadione
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
