Anaplastic astrocytoma
Rare genetic disorder affecting albumin production
| Medical conditions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This medical condition related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
|
Analbuminaemia is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the absence or severe reduction of albumin in the blood plasma. Albumin is a vital protein produced by the liver, playing a crucial role in maintaining the oncotic pressure necessary for proper distribution of body fluids between body tissues and the bloodstream. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
Pathophysiology
Albumin is the most abundant protein in human plasma, accounting for about 60% of the total plasma protein. It is essential for maintaining the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which prevents the leakage of fluid from the blood vessels into the tissues. In individuals with analbuminaemia, the absence of albumin leads to a compensatory increase in other plasma proteins, such as globulins, to maintain oncotic pressure. However, this compensation is often inadequate, leading to various clinical manifestations.
Clinical Features
Patients with analbuminaemia may present with a range of symptoms, although some individuals remain asymptomatic. Common clinical features include:
- Edema: Due to the reduced oncotic pressure, fluid may accumulate in the interstitial spaces, leading to swelling, particularly in the lower extremities.
- Hyperlipidemia: Elevated levels of lipids in the blood are often observed, as albumin plays a role in lipid transport.
- Fatigue and muscle weakness: These symptoms may result from the body's inability to maintain proper fluid and electrolyte balance.
- Hypotension: Low blood pressure can occur due to the reduced blood volume.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of analbuminaemia is typically made through laboratory tests that reveal low or undetectable levels of albumin in the blood. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the albumin gene (ALB) responsible for the condition.
Management
There is no specific treatment for analbuminaemia. Management focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
- Dietary modifications to manage hyperlipidemia.
- Diuretics to reduce edema.
- Monitoring and managing blood pressure.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with analbuminaemia varies. Some individuals may lead relatively normal lives with minimal symptoms, while others may experience significant complications. Regular monitoring and supportive care are essential to manage the condition effectively.
Genetics
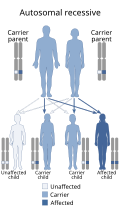
Analbuminaemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene, one from each parent, to be affected. Carriers, who have only one copy of the mutation, typically do not show symptoms.
Related pages
Gallery
-
Diagram illustrating autosomal recessive inheritance.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian