Binge drinking: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
|||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
File:Hotel Rocamar 2009.jpg|Binge drinking | File:Hotel Rocamar 2009.jpg|Binge drinking | ||
File:William Hogarth - A Midnight Modern Conversation.jpg|Binge drinking | File:William Hogarth - A Midnight Modern Conversation.jpg|Binge drinking | ||
File:Stonehenge trouble on stones.jpg|Binge drinking | File:Stonehenge trouble on stones.jpg|Binge drinking | ||
File:William Hogarth - Gin Lane.jpg|Binge drinking | File:William Hogarth - Gin Lane.jpg|Binge drinking | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Alcohol use disorder]] | * [[Alcohol use disorder]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:48, 27 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Binge drinking | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Intoxication, hangover, blackouts, alcohol poisoning |
| Complications | Alcohol use disorder, liver disease, cardiovascular disease, neurological damage, injuries, violence |
| Onset | Typically begins in adolescence or early adulthood |
| Duration | Episodes last several hours |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Excessive alcohol consumption |
| Risks | Peer pressure, social norms, mental health disorders, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Based on drinking patterns and blood alcohol concentration |
| Differential diagnosis | Alcohol use disorder, alcohol dependence |
| Prevention | Education, policy interventions, behavioral interventions |
| Treatment | Counseling, support groups, medication |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; risk of developing alcohol use disorder |
| Frequency | Common among young adults and college students |
| Deaths | N/A |
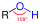
Binge drinking is a pattern of alcohol consumption that brings the blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level to 0.08% or more. This pattern of drinking is typically observed in adults over the age of 21 and is often associated with a range of negative health and social consequences.
Definition[edit]
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) defines binge drinking as a pattern of drinking alcohol that brings the blood alcohol concentration (BAC) to 0.08% or above. For a typical adult, this pattern corresponds to consuming five or more drinks (male), or four or more drinks (female), in about two hours.
Health Risks[edit]
Binge drinking poses significant health risks, including the development of alcohol use disorder, liver disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer. It can also lead to poor decision making, risky behavior, and accidents or injuries.
Social and Economic Impact[edit]
The social and economic impacts of binge drinking are substantial. These include lost productivity, healthcare costs, crime, and other social problems. Binge drinking can also lead to domestic violence, child neglect and abuse, and absenteeism in the workplace.
Prevention and Treatment[edit]
Prevention and treatment of binge drinking involve a combination of public health interventions, policy changes, and individual counseling. These may include alcohol education programs, cognitive behavioral therapy, and medication.
Gallery[edit]
-
Binge drinking
-
Binge drinking
-
Binge drinking
-
Binge drinking
-
Binge drinking
-
Binge drinking
See Also[edit]