Papilledema: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Papilledema | |||
| image = [[File:Papilledema.jpg|left|thumb|Papilledema as seen on fundoscopic examination]] | |||
| caption = Papilledema as seen on fundoscopic examination | |||
| field = [[Ophthalmology]], [[Neurology]] | |||
| synonyms = Papilloedema | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[visual disturbances]] | |||
| complications = [[Vision loss]], [[blindness]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Variable, depending on underlying cause | |||
| causes = [[Increased intracranial pressure]], [[brain tumor]], [[cerebral hemorrhage]], [[meningitis]], [[pseudotumor cerebri]] | |||
| risks = [[Obesity]], [[hypertension]], [[pregnancy]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Fundoscopy]], [[MRI]], [[CT scan]], [[lumbar puncture]] | |||
| differential = [[Optic neuritis]], [[ischemic optic neuropathy]], [[glaucoma]] | |||
| treatment = Addressing underlying cause, [[medications]], [[surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Varies | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Fundal_photograph_showing_severe_papilloedema_in_the_right_eye.jpg|Severe papilledema in the right eye|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Papilledema_revealed_by_scanning_laser_ophthalmoscopy_and_laser_Doppler_holography.gif|Papilledema revealed by scanning laser ophthalmoscopy|left|thumb]] | |||
'''Papilledema''' is a medical condition where the [[optic disc]] (the area at the back of the eye where the [[optic nerve]] enters) swells due to increased [[intracranial pressure]]. This condition can be a sign of serious medical conditions such as [[brain tumor]]s or [[meningitis]]. | '''Papilledema''' is a medical condition where the [[optic disc]] (the area at the back of the eye where the [[optic nerve]] enters) swells due to increased [[intracranial pressure]]. This condition can be a sign of serious medical conditions such as [[brain tumor]]s or [[meningitis]]. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Papilledema is caused by an increase in [[intracranial pressure]] due to various conditions such as [[brain tumor]]s, [[meningitis]], [[hypertensive emergency]], or [[idiopathic intracranial hypertension]]. | Papilledema is caused by an increase in [[intracranial pressure]] due to various conditions such as [[brain tumor]]s, [[meningitis]], [[hypertensive emergency]], or [[idiopathic intracranial hypertension]]. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The symptoms of papilledema can vary depending on the cause of the increased intracranial pressure. Some common symptoms include [[headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[blurred vision]], and [[diplopia]] (double vision). In severe cases, it can lead to [[vision loss]]. | The symptoms of papilledema can vary depending on the cause of the increased intracranial pressure. Some common symptoms include [[headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[blurred vision]], and [[diplopia]] (double vision). In severe cases, it can lead to [[vision loss]]. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of papilledema is usually made by an [[ophthalmologist]] using an [[ophthalmoscope]] to examine the back of the eye. Other tests such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]] may be used to determine the cause of the increased intracranial pressure. | The diagnosis of papilledema is usually made by an [[ophthalmologist]] using an [[ophthalmoscope]] to examine the back of the eye. Other tests such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]] may be used to determine the cause of the increased intracranial pressure. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment of papilledema is aimed at reducing the increased intracranial pressure. This can be achieved through medication, surgery, or other treatments depending on the cause of the increased pressure. | The treatment of papilledema is aimed at reducing the increased intracranial pressure. This can be achieved through medication, surgery, or other treatments depending on the cause of the increased pressure. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Optic disc]] | * [[Optic disc]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 37: | ||
* [[Hypertensive emergency]] | * [[Hypertensive emergency]] | ||
* [[Idiopathic intracranial hypertension]] | * [[Idiopathic intracranial hypertension]] | ||
[[Category:Eye diseases]] | [[Category:Eye diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Symptoms and signs]] | [[Category:Symptoms and signs]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:17, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Papilledema | |
|---|---|
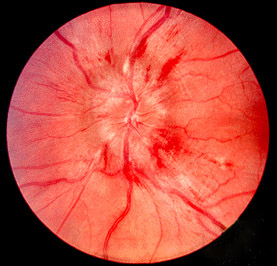 | |
| Synonyms | Papilloedema |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances |
| Complications | Vision loss, blindness |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Variable, depending on underlying cause |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Increased intracranial pressure, brain tumor, cerebral hemorrhage, meningitis, pseudotumor cerebri |
| Risks | Obesity, hypertension, pregnancy |
| Diagnosis | Fundoscopy, MRI, CT scan, lumbar puncture |
| Differential diagnosis | Optic neuritis, ischemic optic neuropathy, glaucoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Addressing underlying cause, medications, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Varies |
| Deaths | N/A |


Papilledema is a medical condition where the optic disc (the area at the back of the eye where the optic nerve enters) swells due to increased intracranial pressure. This condition can be a sign of serious medical conditions such as brain tumors or meningitis.
Causes[edit]
Papilledema is caused by an increase in intracranial pressure due to various conditions such as brain tumors, meningitis, hypertensive emergency, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of papilledema can vary depending on the cause of the increased intracranial pressure. Some common symptoms include headache, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, and diplopia (double vision). In severe cases, it can lead to vision loss.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of papilledema is usually made by an ophthalmologist using an ophthalmoscope to examine the back of the eye. Other tests such as MRI or CT scan may be used to determine the cause of the increased intracranial pressure.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of papilledema is aimed at reducing the increased intracranial pressure. This can be achieved through medication, surgery, or other treatments depending on the cause of the increased pressure.


