Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Exocrine | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
[[File: | | name = Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | ||
| image = [[File:Blausen_0699_PancreasAnatomy2.png|250px]] | |||
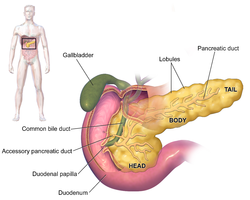
| caption = Anatomy of the pancreas | |||
| field = [[Gastroenterology]] | |||
| synonyms = EPI | |||
| symptoms = [[Steatorrhea]], [[weight loss]], [[malnutrition]], [[abdominal pain]], [[bloating]] | |||
| complications = [[Malabsorption]], [[vitamin deficiency]] | |||
| onset = Varies | |||
| duration = Long-term | |||
| causes = [[Chronic pancreatitis]], [[cystic fibrosis]], [[pancreatic cancer]], [[diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[alcohol consumption]], [[genetic disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Fecal elastase test]], [[72-hour fecal fat test]], [[serum trypsinogen]] | |||
| differential = [[Irritable bowel syndrome]], [[celiac disease]], [[Crohn's disease]] | |||
| treatment = [[Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy]], [[dietary modifications]] | |||
| medication = [[Pancrelipase]] | |||
| frequency = Common in [[cystic fibrosis]] patients, varies in general population | |||
}} | |||
'''Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency''' (EPI) is a medical condition characterized by the pancreas's inability to produce and secrete sufficient digestive enzymes into the small intestine. This leads to symptoms of malabsorption syndrome, abdominal discomfort, and bloating. EPI can be caused by various factors including chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and autoimmune disorders. | '''Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency''' (EPI) is a medical condition characterized by the pancreas's inability to produce and secrete sufficient digestive enzymes into the small intestine. This leads to symptoms of malabsorption syndrome, abdominal discomfort, and bloating. EPI can be caused by various factors including chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and autoimmune disorders. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | |||
EPI occurs when the exocrine function of the pancreas is impaired, leading to difficulties in digesting food properly due to a lack of digestive enzymes. | EPI occurs when the exocrine function of the pancreas is impaired, leading to difficulties in digesting food properly due to a lack of digestive enzymes. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
[[File:Endokrina körtlar swe 290507.png|left|thumb|Diagram of Pancreatitis, a cause of EPI]] | |||
[[File:Endokrina körtlar swe 290507.png|thumb | |||
Common causes of EPI include: | Common causes of EPI include: | ||
* '''Chronic Pancreatitis''': Long-standing inflammation of the pancreas. | * '''Chronic Pancreatitis''': Long-standing inflammation of the pancreas. | ||
* '''Cystic Fibrosis''': A genetic disorder affecting the lungs and pancreas. | * '''Cystic Fibrosis''': A genetic disorder affecting the lungs and pancreas. | ||
* '''Autoimmune Disorders''': Conditions where the immune system attacks the pancreas. | * '''Autoimmune Disorders''': Conditions where the immune system attacks the pancreas. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of EPI typically include: | Symptoms of EPI typically include: | ||
| Line 24: | Line 33: | ||
* Abdominal pain and bloating | * Abdominal pain and bloating | ||
* Fatty stools (steatorrhea) | * Fatty stools (steatorrhea) | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of EPI may involve: | Diagnosis of EPI may involve: | ||
| Line 30: | Line 38: | ||
* Fecal tests to measure enzyme levels | * Fecal tests to measure enzyme levels | ||
* [[Computed tomography|CT scans]] or [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] for structural assessment | * [[Computed tomography|CT scans]] or [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] for structural assessment | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for EPI focuses on managing symptoms and may include: | Treatment for EPI focuses on managing symptoms and may include: | ||
| Line 37: | Line 44: | ||
* Vitamins and supplements | * Vitamins and supplements | ||
* Treating the underlying cause | * Treating the underlying cause | ||
== Management and Prognosis == | == Management and Prognosis == | ||
Effective management involves: | Effective management involves: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 49: | ||
* Lifestyle changes to cope with dietary restrictions | * Lifestyle changes to cope with dietary restrictions | ||
* Psychological support for chronic illness management | * Psychological support for chronic illness management | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
While EPI itself may not be preventable, managing risk factors can be crucial, such as: | While EPI itself may not be preventable, managing risk factors can be crucial, such as: | ||
* Avoiding alcohol and smoking | * Avoiding alcohol and smoking | ||
* Managing underlying conditions like diabetes | * Managing underlying conditions like diabetes | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
* Johnson, T. & Brown, A. (2022). ''Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Review''. Journal of Gastroenterology. | * Johnson, T. & Brown, A. (2022). ''Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Review''. Journal of Gastroenterology. | ||
* Singh, V. K., & Anderson, M. A. (2023). ''Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency''. Clinical Medicine Insights. | * Singh, V. K., & Anderson, M. A. (2023). ''Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency''. Clinical Medicine Insights. | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal Disorders]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal Disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Pancreatic Diseases]] | [[Category:Pancreatic Diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{med-stub}} | {{med-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:09, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | EPI |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Steatorrhea, weight loss, malnutrition, abdominal pain, bloating |
| Complications | Malabsorption, vitamin deficiency |
| Onset | Varies |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes mellitus |
| Risks | Smoking, alcohol consumption, genetic disorders |
| Diagnosis | Fecal elastase test, 72-hour fecal fat test, serum trypsinogen |
| Differential diagnosis | Irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, Crohn's disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, dietary modifications |
| Medication | Pancrelipase |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in cystic fibrosis patients, varies in general population |
| Deaths | N/A |
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) is a medical condition characterized by the pancreas's inability to produce and secrete sufficient digestive enzymes into the small intestine. This leads to symptoms of malabsorption syndrome, abdominal discomfort, and bloating. EPI can be caused by various factors including chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and autoimmune disorders.
Introduction[edit]
EPI occurs when the exocrine function of the pancreas is impaired, leading to difficulties in digesting food properly due to a lack of digestive enzymes.
Causes[edit]

Common causes of EPI include:
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Long-standing inflammation of the pancreas.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A genetic disorder affecting the lungs and pancreas.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions where the immune system attacks the pancreas.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of EPI typically include:
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss despite a normal appetite
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Fatty stools (steatorrhea)
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of EPI may involve:
- Blood tests for nutrient deficiencies
- Fecal tests to measure enzyme levels
- CT scans or MRI for structural assessment
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for EPI focuses on managing symptoms and may include:
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)
- Dietary modifications
- Vitamins and supplements
- Treating the underlying cause
Management and Prognosis[edit]
Effective management involves:
- Regular monitoring and adjustments in therapy
- Lifestyle changes to cope with dietary restrictions
- Psychological support for chronic illness management
Prevention[edit]
While EPI itself may not be preventable, managing risk factors can be crucial, such as:
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking
- Managing underlying conditions like diabetes
References[edit]
<references />
- Johnson, T. & Brown, A. (2022). Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Gastroenterology.
- Singh, V. K., & Anderson, M. A. (2023). Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency. Clinical Medicine Insights.



