Carotid-cavernous fistula: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Carotid-cavernous fistula | |||
| image = [[File:Gray571.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram of the [[cavernous sinus]] and surrounding structures | |||
| field = [[Neurology]], [[Ophthalmology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pulsatile exophthalmos]], [[conjunctival chemosis]], [[diplopia]], [[headache]] | |||
| complications = [[Vision loss]], [[cerebral hemorrhage]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| causes = [[Trauma]], [[aneurysm]], [[arteriosclerosis]] | |||
| risks = [[Head injury]], [[connective tissue disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Angiography]], [[CT scan]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Cavernous sinus thrombosis]], [[orbital cellulitis]], [[thyroid eye disease]] | |||
| treatment = [[Endovascular therapy]], [[surgery]], [[radiation therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Corkscrew_blood_vessels_in_left_eye.jpg|Corkscrew blood vessels in left eye.|thumb]]] | |||
[[File:1471-2415-12-28-1Cerebral_angiogram.jpg|Cerebral angiogram showing carotid-cavernous fistula.||thumb]]] | |||
A carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) is an abnormal connection between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus, a venous structure located at the base of the skull. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, making it an important topic in the field of neurology and vascular surgery. | A carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) is an abnormal connection between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus, a venous structure located at the base of the skull. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, making it an important topic in the field of neurology and vascular surgery. | ||
=== Causes === | === Causes === | ||
CCFs can be either congenital or acquired. Congenital CCFs are present at birth and are usually associated with certain genetic conditions. Acquired CCFs, on the other hand, are typically caused by trauma, such as a head injury or a car accident. Other possible causes include certain medical conditions, such as atherosclerosis or connective tissue disorders. | CCFs can be either congenital or acquired. Congenital CCFs are present at birth and are usually associated with certain genetic conditions. Acquired CCFs, on the other hand, are typically caused by trauma, such as a head injury or a car accident. Other possible causes include certain medical conditions, such as atherosclerosis or connective tissue disorders. | ||
=== Symptoms === | === Symptoms === | ||
The symptoms of a carotid-cavernous fistula can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include: | The symptoms of a carotid-cavernous fistula can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include: | ||
* Proptosis (bulging of the eye) | |||
* Redness and swelling of the eye | |||
* Double vision or other visual disturbances | |||
* Headache | |||
* Eye pain | |||
* Auditory symptoms, such as pulsatile tinnitus | |||
=== Diagnosis === | === Diagnosis === | ||
Diagnosing a carotid-cavernous fistula usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A thorough evaluation of the patient's symptoms and medical history is important in order to determine the likelihood of a CCF. Physical examination may reveal signs such as proptosis or a bruit (abnormal sound) over the affected artery. Imaging tests, such as angiography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can provide detailed information about the location and severity of the fistula. | Diagnosing a carotid-cavernous fistula usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A thorough evaluation of the patient's symptoms and medical history is important in order to determine the likelihood of a CCF. Physical examination may reveal signs such as proptosis or a bruit (abnormal sound) over the affected artery. Imaging tests, such as angiography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can provide detailed information about the location and severity of the fistula. | ||
=== Treatment === | === Treatment === | ||
The treatment of a carotid-cavernous fistula depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and the patient's overall health. In some cases, conservative management may be sufficient, involving close monitoring of the condition and symptomatic treatment. However, more severe cases may require intervention. | The treatment of a carotid-cavernous fistula depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and the patient's overall health. In some cases, conservative management may be sufficient, involving close monitoring of the condition and symptomatic treatment. However, more severe cases may require intervention. | ||
Endovascular treatment is a common approach for CCFs. This involves the use of catheters and embolic materials to block the abnormal connection between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus. Surgical treatment may also be considered in certain cases, particularly if the fistula is large or complex. | Endovascular treatment is a common approach for CCFs. This involves the use of catheters and embolic materials to block the abnormal connection between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus. Surgical treatment may also be considered in certain cases, particularly if the fistula is large or complex. | ||
=== Complications === | === Complications === | ||
If left untreated, carotid-cavernous fistulas can lead to various complications. These may include: | If left untreated, carotid-cavernous fistulas can lead to various complications. These may include: | ||
- Vision loss or blindness | - Vision loss or blindness | ||
- Intracranial hemorrhage | - Intracranial hemorrhage | ||
- Neurological deficits | - Neurological deficits | ||
- Infection | - Infection | ||
Therefore, early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in order to prevent these complications. | Therefore, early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in order to prevent these complications. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Carotid artery]] | * [[Carotid artery]] | ||
* [[Cavernous sinus]] | * [[Cavernous sinus]] | ||
* [[Vascular surgery]] | * [[Vascular surgery]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
[[Category:Vascular surgery]] | [[Category:Vascular surgery]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:09, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Carotid-cavernous fistula | |
|---|---|
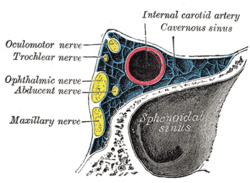
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pulsatile exophthalmos, conjunctival chemosis, diplopia, headache |
| Complications | Vision loss, cerebral hemorrhage |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, aneurysm, arteriosclerosis |
| Risks | Head injury, connective tissue disorders |
| Diagnosis | Angiography, CT scan, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Cavernous sinus thrombosis, orbital cellulitis, thyroid eye disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Endovascular therapy, surgery, radiation therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

]

]
A carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) is an abnormal connection between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus, a venous structure located at the base of the skull. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, making it an important topic in the field of neurology and vascular surgery.
Causes[edit]
CCFs can be either congenital or acquired. Congenital CCFs are present at birth and are usually associated with certain genetic conditions. Acquired CCFs, on the other hand, are typically caused by trauma, such as a head injury or a car accident. Other possible causes include certain medical conditions, such as atherosclerosis or connective tissue disorders.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of a carotid-cavernous fistula can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Proptosis (bulging of the eye)
- Redness and swelling of the eye
- Double vision or other visual disturbances
- Headache
- Eye pain
- Auditory symptoms, such as pulsatile tinnitus
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing a carotid-cavernous fistula usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A thorough evaluation of the patient's symptoms and medical history is important in order to determine the likelihood of a CCF. Physical examination may reveal signs such as proptosis or a bruit (abnormal sound) over the affected artery. Imaging tests, such as angiography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can provide detailed information about the location and severity of the fistula.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of a carotid-cavernous fistula depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and the patient's overall health. In some cases, conservative management may be sufficient, involving close monitoring of the condition and symptomatic treatment. However, more severe cases may require intervention. Endovascular treatment is a common approach for CCFs. This involves the use of catheters and embolic materials to block the abnormal connection between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus. Surgical treatment may also be considered in certain cases, particularly if the fistula is large or complex.
Complications[edit]
If left untreated, carotid-cavernous fistulas can lead to various complications. These may include: - Vision loss or blindness - Intracranial hemorrhage - Neurological deficits - Infection Therefore, early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in order to prevent these complications.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />