Estradiol furoate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[Category:Prodrugs]] | [[Category:Prodrugs]] | ||
{{Estrogen-stub}} | {{Estrogen-stub}} | ||
== Estradiol furoate == | == Estradiol furoate == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
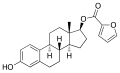
File:Estradiol furoate.svg|Estradiol furoate chemical structure | File:Estradiol furoate.svg|Estradiol furoate chemical structure | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:46, 16 March 2025
Estradiol furoate (EF) is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and an estrogen ester, specifically, the C3 furoate ester of estradiol. It is used in medicine as a component of menopausal hormone therapy. When taken by mouth, it behaves as a prodrug to estradiol.
Pharmacology[edit]
Pharmacodynamics[edit]
As an estrogen, estradiol furoate is an agonist of the estrogen receptor, a nuclear steroid hormone receptor. The pharmacodynamics of estradiol furoate are almost identical to those of estradiol, the natural and most potent endogenous estrogen.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Estradiol furoate is a prodrug of estradiol, and is converted into estradiol in the body. The furoate ester improves the lipophilicity of estradiol, which in turn improves its bioavailability when taken by mouth.
Medical uses[edit]
Estradiol furoate is used in menopausal hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal atrophy. It is used in combination with a progestogen.
Side effects[edit]
The side effects of estradiol furoate are the same as those of estradiol. These may include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, nausea, headache, and fluid retention.
History[edit]
Estradiol furoate was first described in the literature in 1965 and was introduced for medical use by 1968.
See also[edit]
Estradiol furoate[edit]
-
Estradiol furoate chemical structure