3-Methylfentanyl: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category:Synthetic opioids]] | [[Category:Synthetic opioids]] | ||
[[Category:Analgesics]] | [[Category:Analgesics]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:3-Methylfentanyl.svg|3-Methylfentanyl structure | |||
File:Cis-3-methylfentanyl.png|Cis-3-methylfentanyl | |||
File:Fentanyl_numbering.svg|Fentanyl numbering | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:07, 18 February 2025
A potent opioid analgesic
| 3-Methylfentanyl | |
|---|---|

| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
3-Methylfentanyl is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl. It is known for its high potency and has been associated with numerous cases of overdose and fatalities.
Chemical Structure[edit]
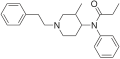
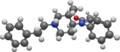
3-Methylfentanyl is structurally similar to fentanyl, with the addition of a methyl group at the 3-position of the piperidine ring. This modification increases its potency compared to fentanyl. The chemical structure can be visualized in the accompanying images.
Pharmacology[edit]
3-Methylfentanyl acts primarily as an agonist at the mu-opioid receptor, similar to other opioids. This interaction is responsible for its analgesic effects as well as its potential for abuse and overdose. The drug's high potency means that even small doses can be lethal.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of 3-Methylfentanyl involves the modification of the fentanyl molecule. The process typically includes the introduction of a methyl group to the piperidine ring, which can be achieved through various chemical reactions. Due to its potency, the synthesis of 3-Methylfentanyl is tightly regulated in many countries.
Legal Status[edit]
Due to its high potential for abuse and risk of overdose, 3-Methylfentanyl is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. It is often listed under the same legal category as fentanyl and other potent opioids.
Health Risks[edit]
The primary health risk associated with 3-Methylfentanyl is overdose, which can lead to respiratory depression, coma, and death. The drug's potency means that even small amounts can be dangerous, particularly if used without medical supervision.
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Chemical structure of 3-Methylfentanyl
-
Cis isomer of 3-Methylfentanyl
-
Numbering of the fentanyl molecule
-
3-Methylfentanyl structure
-
Cis-3-methylfentanyl
-
Fentanyl numbering