Urethral intercourse: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category:Sexual practices]] | [[Category:Sexual practices]] | ||
[[Category:Human sexuality]] | [[Category:Human sexuality]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Female_reproductive_system_lateral_1.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:04, 16 February 2025
Urethral Intercourse[edit]
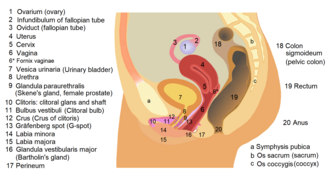
Urethral intercourse refers to the insertion of an object, typically a penis, into the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This practice is considered a form of sexual activity and is distinct from more common forms of intercourse such as vaginal intercourse or anal intercourse.
Anatomy and Physiology[edit]
The urethra is a part of both the urinary system and, in males, the reproductive system. In females, the urethra is significantly shorter, measuring approximately 4 cm in length, and opens above the vaginal opening. In males, the urethra is longer, approximately 20 cm, and passes through the penis.
The primary function of the urethra is to transport urine from the bladder to the external urethral orifice. In males, it also serves as a conduit for semen during ejaculation. The urethral lining is delicate and not designed to accommodate penetration, which can lead to potential health risks.
Health Risks[edit]
Engaging in urethral intercourse can pose several health risks, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to the introduction of bacteria into the urethra.
- Urethral trauma or injury, which can result in pain, bleeding, or scarring.
- Increased risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) if proper protection is not used.
Medical professionals generally advise against urethral intercourse due to these potential complications.
Cultural and Social Aspects[edit]
Urethral intercourse is not a widely practiced or socially accepted form of sexual activity. It is often considered a form of sexual fetishism or paraphilia. Discussions about urethral intercourse are typically limited to specific communities or forums that explore unconventional sexual practices.
Related Pages[edit]
