Coombs test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical test | |||
| name = Coombs test | |||
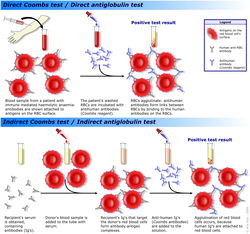
| image = Coombs test schematic.png | |||
| caption = Schematic representation of the Coombs test | |||
| purpose = Detects antibodies that act against the surface of red blood cells | |||
}} | |||
The '''Coombs test''', also known as the '''antiglobulin test''', is a clinical blood test used to detect antibodies that may bind to the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). It is primarily used in the diagnosis of [[hemolytic anemia]], [[hemolytic disease of the newborn]], and in [[blood transfusion]] compatibility testing. | |||
==Types of Coombs Test== | |||
There are two main types of Coombs tests: | |||
== | ===Direct Coombs Test=== | ||
The '''Direct Coombs Test''' (DCT), also known as the '''Direct Antiglobulin Test''' (DAT), is used to detect antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of red blood cells. This test is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia and hemolytic disease of the newborn. | |||
[[File:Algorithm in positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT, or direct Coombs test).png|thumb|Algorithm in positive direct antiglobulin test]] | |||
== | ===Indirect Coombs Test=== | ||
The '''Indirect Coombs Test''' (ICT) is used to detect antibodies that are present in the serum and are capable of binding to red blood cells. This test is often used in prenatal testing of pregnant women and in testing blood prior to transfusion. | |||
The Coombs test | ==Procedure== | ||
The Coombs test involves the following steps: | |||
1. '''Sample Collection''': A blood sample is collected from the patient. | |||
2. '''Addition of Coombs Reagent''': The Coombs reagent, which contains anti-human globulin, is added to the blood sample. | |||
3. '''Observation for Agglutination''': The sample is observed for agglutination (clumping) of red blood cells, which indicates a positive result. | |||
The Coombs test | ==Clinical Significance== | ||
The Coombs test is significant in several clinical scenarios: | |||
[[ | |||
[[ | * '''Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia''': The direct Coombs test can confirm the presence of antibodies that are causing the destruction of red blood cells. | ||
[[ | * '''Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn''': The test can detect antibodies in the mother that may attack the red blood cells of the fetus. | ||
[[Category: | * '''Blood Transfusion''': The indirect Coombs test is used to screen for antibodies in the recipient's serum that may react with donor red blood cells. | ||
==Limitations== | |||
While the Coombs test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has limitations. False positives can occur due to non-specific binding, and false negatives may occur if the antibody levels are too low to detect. | |||
==Also see== | |||
* [[Hemolytic anemia]] | |||
* [[Blood transfusion]] | |||
* [[Hemolytic disease of the newborn]] | |||
* [[Autoimmune disease]] | |||
{{Medical tests}} | |||
[[Category:Blood tests]] | |||
[[Category:Immunology]] | [[Category:Immunology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:47, 11 December 2024
The Coombs test, also known as the antiglobulin test, is a clinical blood test used to detect antibodies that may bind to the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). It is primarily used in the diagnosis of hemolytic anemia, hemolytic disease of the newborn, and in blood transfusion compatibility testing.
Types of Coombs Test[edit]
There are two main types of Coombs tests:
Direct Coombs Test[edit]
The Direct Coombs Test (DCT), also known as the Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT), is used to detect antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of red blood cells. This test is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia and hemolytic disease of the newborn.

Indirect Coombs Test[edit]
The Indirect Coombs Test (ICT) is used to detect antibodies that are present in the serum and are capable of binding to red blood cells. This test is often used in prenatal testing of pregnant women and in testing blood prior to transfusion.
Procedure[edit]
The Coombs test involves the following steps:
1. Sample Collection: A blood sample is collected from the patient. 2. Addition of Coombs Reagent: The Coombs reagent, which contains anti-human globulin, is added to the blood sample. 3. Observation for Agglutination: The sample is observed for agglutination (clumping) of red blood cells, which indicates a positive result.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The Coombs test is significant in several clinical scenarios:
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: The direct Coombs test can confirm the presence of antibodies that are causing the destruction of red blood cells.
- Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn: The test can detect antibodies in the mother that may attack the red blood cells of the fetus.
- Blood Transfusion: The indirect Coombs test is used to screen for antibodies in the recipient's serum that may react with donor red blood cells.
Limitations[edit]
While the Coombs test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has limitations. False positives can occur due to non-specific binding, and false negatives may occur if the antibody levels are too low to detect.
Also see[edit]
| Medical tests | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This medical test related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
|