Sinus bradycardia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
* [[Angina Pectoris|Chest pains]] | * [[Angina Pectoris|Chest pains]] | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Causes of sinus bradycardia include: | Causes of sinus bradycardia include: | ||
* Physiological responses, such as high physical fitness or [[Sleep and Health|sleep]] | * Physiological responses, such as high physical fitness or [[Sleep and Health|sleep]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:35, 26 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Sinus bradycardia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Sinus bradyarrhythmia |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Dizziness, fatigue, syncope |
| Complications | Heart failure, cardiac arrest |
| Onset | Can occur at any age |
| Duration | Can be transient or persistent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Increased vagal tone, medications, hypothyroidism, hypothermia, myocardial infarction |
| Risks | Athletic training, age, hypothyroidism |
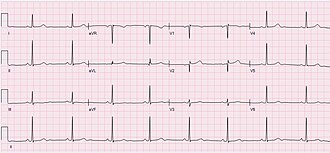
| Diagnosis | Electrocardiogram (ECG) |
| Differential diagnosis | Atrioventricular block, sick sinus syndrome |
| Prevention | Avoidance of causative factors |
| Treatment | Atropine, pacemaker |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in athletes |
| Deaths | N/A |
Sinus Bradycardia: Understanding a Slow Heart Rate[edit]
Sinus bradycardia is a cardiac condition characterized by a slower than normal heart rate, typically defined as less than 60 beats per minute (bpm) in adults. This article explores sinus bradycardia, its significance, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
Introduction[edit]
Sinus bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia that originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is known as the heart's natural pacemaker. While a heart rate below 60 bpm is considered bradycardic, it may be normal for some individuals, particularly athletes or those with a high level of physical fitness.
Normal Heart Rate Range[edit]
The typical resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 bpm. Rates slower than 60 bpm may be considered bradycardic but can be normal and healthy if they occur without any symptoms, particularly during sleep or in physically fit individuals.
Symptoms of Sinus Bradycardia[edit]
While many individuals with sinus bradycardia are asymptomatic, some may experience:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting or near-fainting spells
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pains
Causes[edit]
Causes of sinus bradycardia include:
- Physiological responses, such as high physical fitness or sleep
- Hypothyroidism
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Aging heart tissue
- Medications that affect heart rate, like beta-blockers
- Inflammatory diseases, such as myocarditis
- Neurological conditions that affect the heart
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of sinus bradycardia involves a review of the patient's medical history, a physical exam, and typically an electrocardiogram (ECG). An ECG can confirm a slow heart rate and determine if the rhythm is regular and originates from the SA node.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for sinus bradycardia is usually not necessary unless it is causing symptoms or is a result of an underlying health condition. In symptomatic cases, the treatment approach may include:
- Adjusting medications that may be contributing to the slow heart rate
- Treating any underlying conditions
- Pacemaker implantation in cases where bradycardia is chronic and symptomatic
When to Seek Medical Attention[edit]
Medical attention should be sought if sinus bradycardia is accompanied by symptoms such as fainting, persistent dizziness, or chest pain, as these may indicate a more serious condition.
Conclusion[edit]
Sinus bradycardia can be a benign condition or an indicator of underlying health issues. Understanding when a slow heart rate is a normal variant versus when it signifies a medical concern is important for proper management and treatment.


