Intestinal ischemia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Intestinal ischemia | |||
| image = [[File:Ischemicbowel.PNG|250px]] | |||
| caption = Ischemic bowel as seen on [[CT scan]] | |||
| field = [[Gastroenterology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Abdominal pain]], [[vomiting]], [[diarrhea]], [[bloody stool]] | |||
| complications = [[Sepsis]], [[perforation]], [[peritonitis]], [[death]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| causes = [[Atherosclerosis]], [[embolism]], [[thrombosis]], [[hypotension]] | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[high blood pressure]], [[high cholesterol]], [[diabetes]], [[age]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], [[angiography]], [[colonoscopy]] | |||
| differential = [[Gastroenteritis]], [[appendicitis]], [[inflammatory bowel disease]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[angioplasty]], [[anticoagulant]]s, [[antibiotics]] | |||
| medication = [[Anticoagulant]]s, [[vasodilator]]s | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Mesenteriale_Ischaemie_mit_Pneumatosis_intestinalis_und_Gas_in_Mesenterial-_und_Lebervenen_80M_-_CT_-_001.jpg|Mesenteric ischemia with pneumatosis intestinalis and gas in mesenteric and hepatic veins|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Intestinal ischemia''' refers to a medical condition characterized by an inadequate blood supply to the [[intestine]], leading to inflammation and injury of the intestinal tissues. This condition can affect the [[small intestine]], [[large intestine]], or both. | '''Intestinal ischemia''' refers to a medical condition characterized by an inadequate blood supply to the [[intestine]], leading to inflammation and injury of the intestinal tissues. This condition can affect the [[small intestine]], [[large intestine]], or both. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Intestinal ischemia is often caused by a blockage in the [[arteries]] that supply blood to the intestine. This blockage can be due to: | Intestinal ischemia is often caused by a blockage in the [[arteries]] that supply blood to the intestine. This blockage can be due to: | ||
* [[Blood clot]]s: These can form in the heart or a large artery, then travel through the bloodstream and block a smaller artery in the intestine. | * [[Blood clot]]s: These can form in the heart or a large artery, then travel through the bloodstream and block a smaller artery in the intestine. | ||
* [[Atherosclerosis]]: This is a condition where fatty deposits build up on the inner walls of the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. | * [[Atherosclerosis]]: This is a condition where fatty deposits build up on the inner walls of the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. | ||
* [[Vasculitis]]: This is an inflammation of the blood vessels that can cause blockages. | * [[Vasculitis]]: This is an inflammation of the blood vessels that can cause blockages. | ||
* [[Hernia]]: A hernia can cause a portion of the intestine to become twisted or kinked, blocking blood flow. | * [[Hernia]]: A hernia can cause a portion of the intestine to become twisted or kinked, blocking blood flow. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of intestinal ischemia can vary depending on the severity and location of the condition. They may include: | Symptoms of intestinal ischemia can vary depending on the severity and location of the condition. They may include: | ||
* [[Abdominal pain]]: This is often severe and sudden in onset. | * [[Abdominal pain]]: This is often severe and sudden in onset. | ||
* [[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]] | * [[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 33: | ||
* [[Blood in the stool]] | * [[Blood in the stool]] | ||
* [[Fever]] | * [[Fever]] | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of intestinal ischemia typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include: | Diagnosis of intestinal ischemia typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include: | ||
* [[Blood tests]]: These can help identify signs of infection or inflammation. | * [[Blood tests]]: These can help identify signs of infection or inflammation. | ||
* [[Imaging tests]]: These may include [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], or [[ultrasound]] to visualize the blood vessels and intestines. | * [[Imaging tests]]: These may include [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], or [[ultrasound]] to visualize the blood vessels and intestines. | ||
* [[Angiography]]: This is a procedure that uses dye and special X-rays to show the inside of the blood vessels. | * [[Angiography]]: This is a procedure that uses dye and special X-rays to show the inside of the blood vessels. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for intestinal ischemia aims to restore blood flow to the intestine as quickly as possible. This may involve: | Treatment for intestinal ischemia aims to restore blood flow to the intestine as quickly as possible. This may involve: | ||
* [[Medication]]: Drugs can be used to dissolve blood clots, reduce inflammation, or treat infection. | * [[Medication]]: Drugs can be used to dissolve blood clots, reduce inflammation, or treat infection. | ||
* [[Surgery]]: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the blockage or repair damaged sections of the intestine. | * [[Surgery]]: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the blockage or repair damaged sections of the intestine. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for intestinal ischemia depends on the extent of the condition and the patient's overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis significantly. | The prognosis for intestinal ischemia depends on the extent of the condition and the patient's overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis significantly. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Ischemia]] | * [[Ischemia]] | ||
* [[Abdominal pain]] | * [[Abdominal pain]] | ||
* [[Blood clot]] | * [[Blood clot]] | ||
* [[Atherosclerosis]] | * [[Atherosclerosis]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal disorders]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Vascular diseases]] | [[Category:Vascular diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:16, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Intestinal ischemia | |
|---|---|
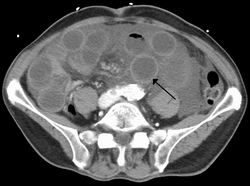
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, bloody stool |
| Complications | Sepsis, perforation, peritonitis, death |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Atherosclerosis, embolism, thrombosis, hypotension |
| Risks | Smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, age |
| Diagnosis | CT scan, MRI, angiography, colonoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Gastroenteritis, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, angioplasty, anticoagulants, antibiotics |
| Medication | Anticoagulants, vasodilators |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Intestinal ischemia refers to a medical condition characterized by an inadequate blood supply to the intestine, leading to inflammation and injury of the intestinal tissues. This condition can affect the small intestine, large intestine, or both.
Causes[edit]
Intestinal ischemia is often caused by a blockage in the arteries that supply blood to the intestine. This blockage can be due to:
- Blood clots: These can form in the heart or a large artery, then travel through the bloodstream and block a smaller artery in the intestine.
- Atherosclerosis: This is a condition where fatty deposits build up on the inner walls of the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow.
- Vasculitis: This is an inflammation of the blood vessels that can cause blockages.
- Hernia: A hernia can cause a portion of the intestine to become twisted or kinked, blocking blood flow.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of intestinal ischemia can vary depending on the severity and location of the condition. They may include:
- Abdominal pain: This is often severe and sudden in onset.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Blood in the stool
- Fever
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of intestinal ischemia typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include:
- Blood tests: These can help identify signs of infection or inflammation.
- Imaging tests: These may include CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound to visualize the blood vessels and intestines.
- Angiography: This is a procedure that uses dye and special X-rays to show the inside of the blood vessels.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for intestinal ischemia aims to restore blood flow to the intestine as quickly as possible. This may involve:
- Medication: Drugs can be used to dissolve blood clots, reduce inflammation, or treat infection.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the blockage or repair damaged sections of the intestine.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for intestinal ischemia depends on the extent of the condition and the patient's overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis significantly.


