Paramethadione: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category:Anticonvulsants]] | [[Category:Anticonvulsants]] | ||
[[Category:Oxazolidinediones]] | [[Category:Oxazolidinediones]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Paramethadione.svg|Paramethadione | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:09, 20 February 2025
An anticonvulsant medication
| Paramethadione | |
|---|---|
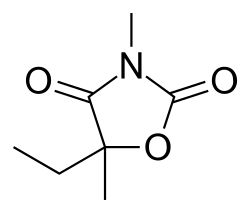
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Paramethadione is a medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy. It belongs to the class of drugs known as oxazolidinediones, which are used as anticonvulsants. Paramethadione is specifically indicated for the management of absence seizures, also known as petit mal seizures.
Pharmacology
Paramethadione works by reducing the frequency of seizures. It is believed to act on the central nervous system by modulating the activity of neurons to prevent the abnormal electrical activity that leads to seizures. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve the stabilization of neuronal membranes.
Medical uses
Paramethadione is used in the treatment of absence seizures, which are characterized by brief, sudden lapses in attention and activity. These seizures are most common in children and can interfere with learning and daily activities. Paramethadione helps to control these seizures, allowing individuals to lead more normal lives.
Side effects
Like many anticonvulsants, paramethadione can cause a range of side effects. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea. More serious side effects can include blood dyscrasias, such as agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia, as well as liver toxicity. Patients taking paramethadione require regular monitoring of blood counts and liver function.
History
Paramethadione was developed in the mid-20th century as part of a class of anticonvulsants known as oxazolidinediones. It was one of the first drugs used specifically for the treatment of absence seizures. However, due to its side effect profile and the development of newer anticonvulsants with better safety profiles, its use has declined over the years.
Chemical properties
Paramethadione is a derivative of trimethadione, another anticonvulsant. It is chemically classified as an oxazolidinedione, with the chemical formula C7H11NO3. The structure of paramethadione includes a five-membered oxazolidine ring, which is a key feature of this class of drugs.
Related pages
-
Paramethadione
