Hyoid bone fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hyoid bone fracture | |||
| image = [[File:Hyoid_bone_-_animation.gif|alt=Animation of the hyoid bone]] | |||
| caption = Animation of the hyoid bone | |||
| field = [[Otolaryngology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| symptoms = [[Neck pain]], [[dysphagia]], [[dysphonia]], [[stridor]] | |||
| complications = [[Airway obstruction]], [[aspiration]], [[infection]] | |||
| onset = | |||
| duration = | |||
| types = | |||
| causes = [[Blunt trauma]], [[strangulation]], [[hanging]] | |||
| risks = | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = [[Airway management]], [[surgical intervention]] | |||
| medication = [[Analgesics]], [[antibiotics]] | |||
| prognosis = | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Hyoid bone - close-up - animation.gif|left|thumb]] [[File:Gray186.png|thumb]] [[File:Gray1194.png|thumb]]<br>Hyoid Bone Fracture | |||
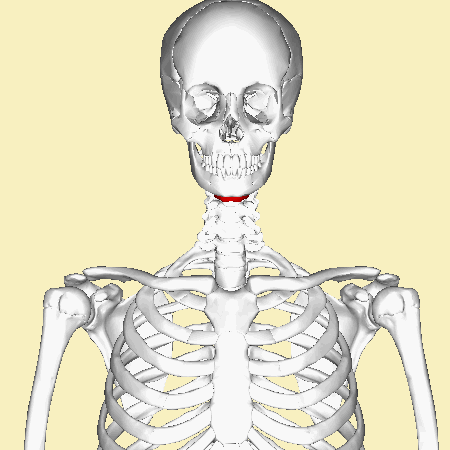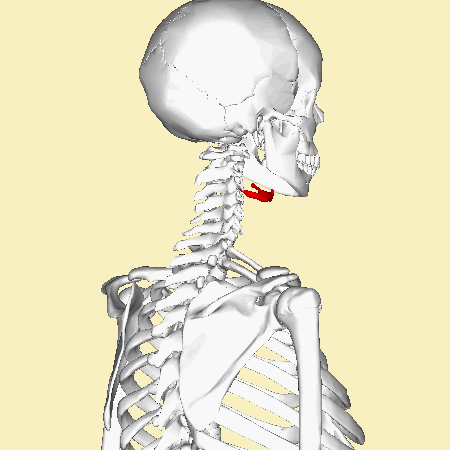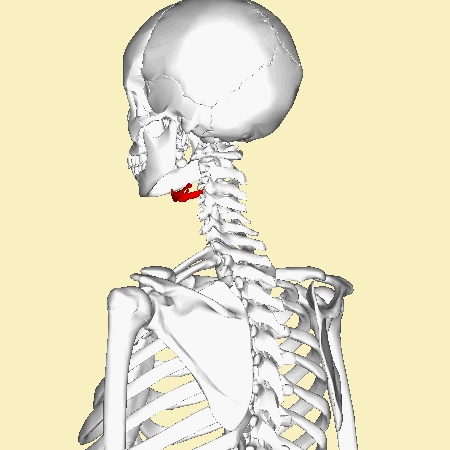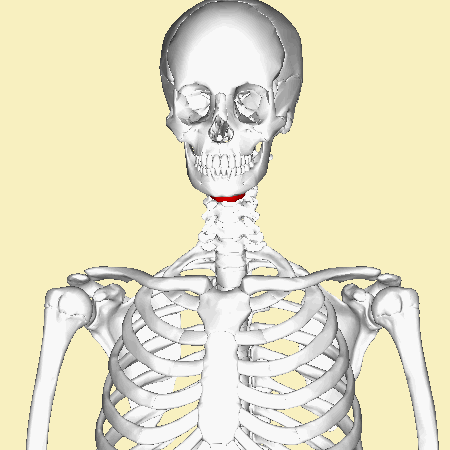
A '''[[hyoid bone fracture]]''' is a rare injury that involves a break in the hyoid bone, a U-shaped bone located in the anterior neck. This type of fracture is uncommon due to the protected position of the hyoid bone, which is situated above the larynx and below the mandible. | A '''[[hyoid bone fracture]]''' is a rare injury that involves a break in the hyoid bone, a U-shaped bone located in the anterior neck. This type of fracture is uncommon due to the protected position of the hyoid bone, which is situated above the larynx and below the mandible. | ||
==Anatomy of the Hyoid Bone== | ==Anatomy of the Hyoid Bone== | ||
The [[hyoid bone]] is a unique structure in the human body. It is not directly attached to any other bones, making it the only bone that is "free-floating." The hyoid bone serves as an attachment site for muscles associated with swallowing and speech. It consists of a central body and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser cornua. | The [[hyoid bone]] is a unique structure in the human body. It is not directly attached to any other bones, making it the only bone that is "free-floating." The hyoid bone serves as an attachment site for muscles associated with swallowing and speech. It consists of a central body and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser cornua. | ||
==Causes of Hyoid Bone Fracture== | ==Causes of Hyoid Bone Fracture== | ||
Hyoid bone fractures are typically caused by direct trauma to the neck. Common causes include: | Hyoid bone fractures are typically caused by direct trauma to the neck. Common causes include: | ||
* '''[[Strangulation]]''': Manual strangulation or hanging can exert significant force on the neck, leading to a fracture. | * '''[[Strangulation]]''': Manual strangulation or hanging can exert significant force on the neck, leading to a fracture. | ||
* '''[[Blunt trauma]]''': Accidents, such as motor vehicle collisions or sports injuries, can result in a fracture if the neck is impacted. | * '''[[Blunt trauma]]''': Accidents, such as motor vehicle collisions or sports injuries, can result in a fracture if the neck is impacted. | ||
* '''[[Penetrating trauma]]''': Stab wounds or gunshot injuries to the neck may also fracture the hyoid bone. | * '''[[Penetrating trauma]]''': Stab wounds or gunshot injuries to the neck may also fracture the hyoid bone. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of a hyoid bone fracture may include: | Symptoms of a hyoid bone fracture may include: | ||
* Pain in the neck, especially when swallowing or speaking | * Pain in the neck, especially when swallowing or speaking | ||
* Swelling and bruising in the neck area | * Swelling and bruising in the neck area | ||
| Line 24: | Line 38: | ||
* Hoarseness or changes in voice | * Hoarseness or changes in voice | ||
* Respiratory distress in severe cases | * Respiratory distress in severe cases | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of a hyoid bone fracture typically involves: | Diagnosis of a hyoid bone fracture typically involves: | ||
* '''[[Physical examination]]''': A healthcare provider will assess the neck for tenderness, swelling, and other signs of injury. | * '''[[Physical examination]]''': A healthcare provider will assess the neck for tenderness, swelling, and other signs of injury. | ||
* '''[[Imaging studies]]''': X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the fracture and assess the extent of the injury. | * '''[[Imaging studies]]''': X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the fracture and assess the extent of the injury. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for a hyoid bone fracture depends on the severity of the injury: | Treatment for a hyoid bone fracture depends on the severity of the injury: | ||
* '''[[Conservative management]]''': Mild fractures may be treated with rest, pain management, and dietary modifications to ease swallowing. | * '''[[Conservative management]]''': Mild fractures may be treated with rest, pain management, and dietary modifications to ease swallowing. | ||
* '''[[Surgical intervention]]''': Severe fractures or those associated with airway compromise may require surgical repair. | * '''[[Surgical intervention]]''': Severe fractures or those associated with airway compromise may require surgical repair. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for a hyoid bone fracture is generally good, especially with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Most individuals recover fully without long-term complications. | The prognosis for a hyoid bone fracture is generally good, especially with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Most individuals recover fully without long-term complications. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Hyoid bone]] | * [[Hyoid bone]] | ||
* [[Neck trauma]] | * [[Neck trauma]] | ||
* [[Strangulation]] | * [[Strangulation]] | ||
* [[Dysphagia]] | * [[Dysphagia]] | ||
{{Medical conditions}} | {{Medical conditions}} | ||
[[Category:Fractures]] | [[Category:Fractures]] | ||
[[Category:Neck injuries]] | [[Category:Neck injuries]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:20, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hyoid bone fracture | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Neck pain, dysphagia, dysphonia, stridor |
| Complications | Airway obstruction, aspiration, infection |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Blunt trauma, strangulation, hanging |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Airway management, surgical intervention |
| Medication | Analgesics, antibiotics |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |



Hyoid Bone Fracture
A hyoid bone fracture is a rare injury that involves a break in the hyoid bone, a U-shaped bone located in the anterior neck. This type of fracture is uncommon due to the protected position of the hyoid bone, which is situated above the larynx and below the mandible.
Anatomy of the Hyoid Bone[edit]
The hyoid bone is a unique structure in the human body. It is not directly attached to any other bones, making it the only bone that is "free-floating." The hyoid bone serves as an attachment site for muscles associated with swallowing and speech. It consists of a central body and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser cornua.
Causes of Hyoid Bone Fracture[edit]
Hyoid bone fractures are typically caused by direct trauma to the neck. Common causes include:
- Strangulation: Manual strangulation or hanging can exert significant force on the neck, leading to a fracture.
- Blunt trauma: Accidents, such as motor vehicle collisions or sports injuries, can result in a fracture if the neck is impacted.
- Penetrating trauma: Stab wounds or gunshot injuries to the neck may also fracture the hyoid bone.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of a hyoid bone fracture may include:
- Pain in the neck, especially when swallowing or speaking
- Swelling and bruising in the neck area
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Respiratory distress in severe cases
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a hyoid bone fracture typically involves:
- Physical examination: A healthcare provider will assess the neck for tenderness, swelling, and other signs of injury.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the fracture and assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for a hyoid bone fracture depends on the severity of the injury:
- Conservative management: Mild fractures may be treated with rest, pain management, and dietary modifications to ease swallowing.
- Surgical intervention: Severe fractures or those associated with airway compromise may require surgical repair.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for a hyoid bone fracture is generally good, especially with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Most individuals recover fully without long-term complications.
See also[edit]