WNT4 deficiency: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
{{genetic-disorder-stub}} | {{genetic-disorder-stub}} | ||
{{stb}} | {{stb}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ovary_nih.jpg | |||
File:Ideogram_human_chromosome_1.svg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:52, 17 February 2025
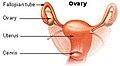
WNT4 deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that affects females and it results in the underdevelopment and sometimes absence of the uterus and vagina. WNT4 deficiency is caused by mutations of the WNT4 gene. Abnormally high androgen levels are found in the blood and can initiate and promote the development of male sex characteristics. This is seen as male pattern of hair growth on the chest and face. Those with this genetic defect develop breasts but do not have their period. Mayer–Rokitansky–Küster–Hauser syndrome is a related but distinct syndrome. Some women who have an initial diagnosis of MRKH have later been found to have WNT4 deficiency. Most women with MRKH syndrome do not have genetic mutations of the WNT4 gene. The failure to begin the menstrual cycle may be the initial clinical sign of WNT4 deficiency. WNT4 deficiency can cause significant psychological challenges and counseling is recommended.<ref> ,
WNT4 Deficiency - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders) Full text, NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), Accessed on: 2018-01-22.
</ref><ref>Biason-Lauber, A.,
WNT4 deficiency--a clinical phenotype distinct from the classic Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome: a case report, Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), Vol. 22(Issue: 1), pp. 224–229, DOI: 10.1093/humrep/del360, PMID: 16959810,</ref>
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
| Vaginal anatomy | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

This article is a genetic disorder stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |