Flexion teardrop fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Flexion teardrop fracture | |||
| image = [[File:Teardrop_fracture.jpg|250px]] | |||
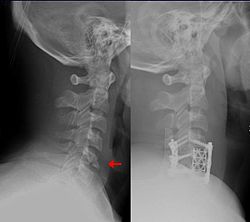
| caption = X-ray of a flexion teardrop fracture | |||
| field = [[Orthopedic surgery]] | |||
| symptoms = Severe neck pain, [[neurological deficit]] | |||
| complications = [[Spinal cord injury]], [[paralysis]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, typically due to trauma | |||
| duration = Varies, depending on severity and treatment | |||
| causes = High-energy [[trauma]], such as [[motor vehicle accident]] | |||
| risks = [[Osteoporosis]], [[high-impact sports]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[X-ray]], [[CT scan]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Cervical fracture]], [[cervical dislocation]] | |||
| prevention = Use of [[seat belts]], [[protective gear]] in sports | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical stabilization]], [[immobilization]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on severity and presence of neurological injury | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Flexion teardrop fracture''' is a severe type of [[cervical fracture]] that is often associated with spinal cord injury. This fracture is characterized by a fragment of the anterior part of a cervical vertebra taking on a "teardrop" shape and being displaced anteriorly. It is typically caused by a high-energy, hyperflexion injury to the neck, such as those sustained in car accidents or falls. | '''Flexion teardrop fracture''' is a severe type of [[cervical fracture]] that is often associated with spinal cord injury. This fracture is characterized by a fragment of the anterior part of a cervical vertebra taking on a "teardrop" shape and being displaced anteriorly. It is typically caused by a high-energy, hyperflexion injury to the neck, such as those sustained in car accidents or falls. | ||
==Etiology== | ==Etiology== | ||
Flexion teardrop fractures are usually the result of high-energy trauma. The most common causes are [[motor vehicle accidents]], falls from a height, and sports injuries. The mechanism of injury is typically a forceful, sudden flexion of the neck. | Flexion teardrop fractures are usually the result of high-energy trauma. The most common causes are [[motor vehicle accidents]], falls from a height, and sports injuries. The mechanism of injury is typically a forceful, sudden flexion of the neck. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
The flexion teardrop fracture occurs when the neck is forcefully flexed, causing the anterior portion of the vertebral body to compress and fracture. The posterior ligamentous complex, including the [[anterior longitudinal ligament]], [[posterior longitudinal ligament]], and [[ligamentum flavum]], is often disrupted, leading to instability of the cervical spine. | The flexion teardrop fracture occurs when the neck is forcefully flexed, causing the anterior portion of the vertebral body to compress and fracture. The posterior ligamentous complex, including the [[anterior longitudinal ligament]], [[posterior longitudinal ligament]], and [[ligamentum flavum]], is often disrupted, leading to instability of the cervical spine. | ||
==Clinical Presentation== | ==Clinical Presentation== | ||
Patients with a flexion teardrop fracture often present with severe neck pain and neurological deficits due to spinal cord injury. These can include quadriplegia, loss of sensation below the level of the injury, and [[autonomic dysreflexia]], a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high blood pressure and a slowed heart rate. | Patients with a flexion teardrop fracture often present with severe neck pain and neurological deficits due to spinal cord injury. These can include quadriplegia, loss of sensation below the level of the injury, and [[autonomic dysreflexia]], a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high blood pressure and a slowed heart rate. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of a flexion teardrop fracture is typically made through [[radiography]], with a lateral cervical spine X-ray being the most commonly used imaging study. The characteristic "teardrop" fragment can often be seen on this X-ray. In some cases, a [[computed tomography]] (CT) scan or [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) may be used to better visualize the fracture and assess for associated injuries. | Diagnosis of a flexion teardrop fracture is typically made through [[radiography]], with a lateral cervical spine X-ray being the most commonly used imaging study. The characteristic "teardrop" fragment can often be seen on this X-ray. In some cases, a [[computed tomography]] (CT) scan or [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) may be used to better visualize the fracture and assess for associated injuries. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment of a flexion teardrop fracture typically involves stabilization of the cervical spine to prevent further injury. This can be achieved through the use of a cervical collar or halo vest, or through surgical intervention. Surgery may involve [[anterior cervical discectomy and fusion]] (ACDF), in which the damaged vertebra is removed and the surrounding vertebrae are fused together, or [[posterior cervical fusion]], in which rods and screws are used to stabilize the spine from the back. | Treatment of a flexion teardrop fracture typically involves stabilization of the cervical spine to prevent further injury. This can be achieved through the use of a cervical collar or halo vest, or through surgical intervention. Surgery may involve [[anterior cervical discectomy and fusion]] (ACDF), in which the damaged vertebra is removed and the surrounding vertebrae are fused together, or [[posterior cervical fusion]], in which rods and screws are used to stabilize the spine from the back. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for patients with a flexion teardrop fracture is often poor, due to the high incidence of associated spinal cord injury. However, with prompt diagnosis and treatment, some patients may regain function and lead productive lives. | The prognosis for patients with a flexion teardrop fracture is often poor, due to the high incidence of associated spinal cord injury. However, with prompt diagnosis and treatment, some patients may regain function and lead productive lives. | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic fractures]] | [[Category:Orthopedic fractures]] | ||
[[Category:Spinal cord injury]] | [[Category:Spinal cord injury]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:38, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Flexion teardrop fracture | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Severe neck pain, neurological deficit |
| Complications | Spinal cord injury, paralysis |
| Onset | Sudden, typically due to trauma |
| Duration | Varies, depending on severity and treatment |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | High-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle accident |
| Risks | Osteoporosis, high-impact sports |
| Diagnosis | X-ray, CT scan, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Cervical fracture, cervical dislocation |
| Prevention | Use of seat belts, protective gear in sports |
| Treatment | Surgical stabilization, immobilization, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity and presence of neurological injury |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Flexion teardrop fracture is a severe type of cervical fracture that is often associated with spinal cord injury. This fracture is characterized by a fragment of the anterior part of a cervical vertebra taking on a "teardrop" shape and being displaced anteriorly. It is typically caused by a high-energy, hyperflexion injury to the neck, such as those sustained in car accidents or falls.
Etiology[edit]
Flexion teardrop fractures are usually the result of high-energy trauma. The most common causes are motor vehicle accidents, falls from a height, and sports injuries. The mechanism of injury is typically a forceful, sudden flexion of the neck.
Pathophysiology[edit]
The flexion teardrop fracture occurs when the neck is forcefully flexed, causing the anterior portion of the vertebral body to compress and fracture. The posterior ligamentous complex, including the anterior longitudinal ligament, posterior longitudinal ligament, and ligamentum flavum, is often disrupted, leading to instability of the cervical spine.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with a flexion teardrop fracture often present with severe neck pain and neurological deficits due to spinal cord injury. These can include quadriplegia, loss of sensation below the level of the injury, and autonomic dysreflexia, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high blood pressure and a slowed heart rate.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a flexion teardrop fracture is typically made through radiography, with a lateral cervical spine X-ray being the most commonly used imaging study. The characteristic "teardrop" fragment can often be seen on this X-ray. In some cases, a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to better visualize the fracture and assess for associated injuries.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of a flexion teardrop fracture typically involves stabilization of the cervical spine to prevent further injury. This can be achieved through the use of a cervical collar or halo vest, or through surgical intervention. Surgery may involve anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF), in which the damaged vertebra is removed and the surrounding vertebrae are fused together, or posterior cervical fusion, in which rods and screws are used to stabilize the spine from the back.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with a flexion teardrop fracture is often poor, due to the high incidence of associated spinal cord injury. However, with prompt diagnosis and treatment, some patients may regain function and lead productive lives.
