Anterior cingulate cortex: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Part of the brain involved in various functions including emotion and cognition}} | |||
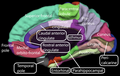
The '''anterior cingulate cortex''' (ACC) is a part of the brain | The '''anterior cingulate cortex''' (ACC) is a part of the [[brain]] located in the [[frontal lobe]]. It plays a crucial role in a wide range of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as higher-level functions, including [[decision-making]], [[empathy]], [[impulse control]], and [[emotion]]. | ||
== | ==Anatomy== | ||
The anterior cingulate cortex is part of the [[cingulate cortex]], which | The anterior cingulate cortex is situated in the medial aspect of the brain's frontal lobes. It forms a part of the [[cingulate cortex]], which encircles the [[corpus callosum]]. The ACC is divided into two main areas: the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and the ventral anterior cingulate cortex (vACC). | ||
== | ===Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex=== | ||
The | The dACC is primarily involved in cognitive functions such as [[error detection]], [[anticipation of tasks]], and [[attention]]. It is connected to the [[prefrontal cortex]] and the [[parietal lobe]], which are involved in executive functions and sensory processing, respectively. | ||
===Ventral Anterior Cingulate Cortex=== | |||
The vACC is more involved in emotional regulation and is connected to the [[amygdala]], [[nucleus accumbens]], and the [[hypothalamus]]. These connections allow the vACC to play a role in processing emotions and regulating autonomic responses. | |||
==Functions== | |||
The anterior cingulate cortex is involved in a variety of functions: | |||
* ''' | * '''Emotion Regulation''': The ACC is crucial in processing emotions and is involved in the regulation of emotional responses. It helps in the assessment of emotional stimuli and the generation of appropriate emotional reactions. | ||
* ''' | * '''Cognitive Control''': The ACC is involved in cognitive processes such as [[conflict monitoring]], [[error detection]], and [[decision-making]]. It helps in evaluating the outcomes of actions and adjusting behavior accordingly. | ||
* '''Pain Perception''': The ACC is activated during the experience of pain and is thought to be involved in the emotional aspect of pain perception. | |||
* '''Autonomic Functions''': The ACC regulates autonomic functions such as heart rate and blood pressure, particularly in response to stress or emotional stimuli. | |||
==Clinical Significance== | ==Clinical Significance== | ||
Dysfunction in the anterior cingulate cortex has been implicated in several psychiatric and neurological disorders: | |||
* '''Depression''': | * '''[[Depression]]''': Abnormal activity in the ACC has been associated with major depressive disorder, particularly in the regulation of mood and emotional responses. | ||
* '''Anxiety Disorders''': The ACC is involved in the | * '''[[Anxiety Disorders]]''': The ACC is involved in the processing of fear and anxiety, and its dysfunction can contribute to anxiety disorders. | ||
* '''Schizophrenia''': | * '''[[Schizophrenia]]''': Altered ACC activity has been observed in individuals with schizophrenia, affecting cognitive and emotional processing. | ||
* ''' | * '''[[Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder]] (ADHD)''': The ACC's role in attention and impulse control is relevant to the symptoms of ADHD. | ||
==Research | ==Imaging and Research== | ||
Functional [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (fMRI) and [[positron emission tomography]] (PET) scans have been used to study the activity of the ACC in various tasks and conditions. These imaging techniques have provided insights into the role of the ACC in both healthy individuals and those with psychiatric disorders. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Cingulate cortex]] | |||
* [[Prefrontal cortex]] | |||
* [[Amygdala]] | |||
* [[Nucleus accumbens]] | |||
* [[Hypothalamus]] | |||
[[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | [[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Frontal lobe]] | [[Category:Frontal lobe]] | ||
[[Category:Brain]] | |||
== Anterior cingulate cortex == | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:MRI_anterior_cingulate.png|MRI anterior cingulate | |||
File:Anterior_cingulate_gyrus_animation.gif|Anterior cingulate gyrus animation | |||
File:MRI_anterior_cingulate.png|MRI | |||
File:Anterior_cingulate_gyrus_animation.gif| | |||
File:Medial_surface_of_cerebral_cortex_-_gyri.png|Medial surface of cerebral cortex - gyri | File:Medial_surface_of_cerebral_cortex_-_gyri.png|Medial surface of cerebral cortex - gyri | ||
File:Anterior_Cingulate_Cortex.png|Anterior | File:Anterior_Cingulate_Cortex.png|Anterior Cingulate Cortex | ||
File:Caudal_Anterior_Cingulate_-_DK_ATLAS.png|Caudal | File:Caudal_Anterior_Cingulate_-_DK_ATLAS.png|Caudal Anterior Cingulate - DK ATLAS | ||
File:Rostral_Anterior_Cingulate_-_DK_ATLAS.png|Rostral | File:Rostral_Anterior_Cingulate_-_DK_ATLAS.png|Rostral Anterior Cingulate - DK ATLAS | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:24, 23 February 2025
Part of the brain involved in various functions including emotion and cognition
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is a part of the brain located in the frontal lobe. It plays a crucial role in a wide range of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as higher-level functions, including decision-making, empathy, impulse control, and emotion.
Anatomy[edit]
The anterior cingulate cortex is situated in the medial aspect of the brain's frontal lobes. It forms a part of the cingulate cortex, which encircles the corpus callosum. The ACC is divided into two main areas: the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and the ventral anterior cingulate cortex (vACC).
Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex[edit]
The dACC is primarily involved in cognitive functions such as error detection, anticipation of tasks, and attention. It is connected to the prefrontal cortex and the parietal lobe, which are involved in executive functions and sensory processing, respectively.
Ventral Anterior Cingulate Cortex[edit]
The vACC is more involved in emotional regulation and is connected to the amygdala, nucleus accumbens, and the hypothalamus. These connections allow the vACC to play a role in processing emotions and regulating autonomic responses.
Functions[edit]
The anterior cingulate cortex is involved in a variety of functions:
- Emotion Regulation: The ACC is crucial in processing emotions and is involved in the regulation of emotional responses. It helps in the assessment of emotional stimuli and the generation of appropriate emotional reactions.
- Cognitive Control: The ACC is involved in cognitive processes such as conflict monitoring, error detection, and decision-making. It helps in evaluating the outcomes of actions and adjusting behavior accordingly.
- Pain Perception: The ACC is activated during the experience of pain and is thought to be involved in the emotional aspect of pain perception.
- Autonomic Functions: The ACC regulates autonomic functions such as heart rate and blood pressure, particularly in response to stress or emotional stimuli.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Dysfunction in the anterior cingulate cortex has been implicated in several psychiatric and neurological disorders:
- Depression: Abnormal activity in the ACC has been associated with major depressive disorder, particularly in the regulation of mood and emotional responses.
- Anxiety Disorders: The ACC is involved in the processing of fear and anxiety, and its dysfunction can contribute to anxiety disorders.
- Schizophrenia: Altered ACC activity has been observed in individuals with schizophrenia, affecting cognitive and emotional processing.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): The ACC's role in attention and impulse control is relevant to the symptoms of ADHD.
Imaging and Research[edit]
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans have been used to study the activity of the ACC in various tasks and conditions. These imaging techniques have provided insights into the role of the ACC in both healthy individuals and those with psychiatric disorders.
Related pages[edit]
Anterior cingulate cortex[edit]
-
MRI anterior cingulate
-
Anterior cingulate gyrus animation
-
Medial surface of cerebral cortex - gyri
-
Anterior Cingulate Cortex
-
Caudal Anterior Cingulate - DK ATLAS
-
Rostral Anterior Cingulate - DK ATLAS