Decision-making
Decision-making
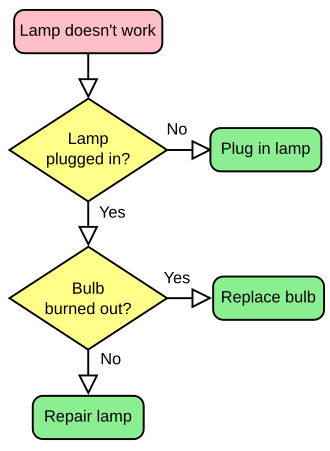
Decision-making is a cognitive process that results in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It is a crucial aspect of human behavior and is essential in various fields, including medicine, business, and personal life.
Overview[edit]
Decision-making involves identifying and choosing alternatives based on the values and preferences of the decision-maker. It is a process that can be rational or irrational, and it can be influenced by a variety of factors, including emotions, cognitive biases, and social influences.
In the context of medicine, decision-making is particularly important as it can directly impact patient outcomes. Medical professionals must often make quick decisions under pressure, balancing the risks and benefits of different treatment options.
Types of Decision-making[edit]
Rational Decision-making[edit]
Rational decision-making is a structured or systematic approach to making decisions. It involves logical reasoning and often follows a step-by-step process:
1. Define the problem 2. Identify the criteria 3. Weigh the criteria 4. Generate alternatives 5. Rate each alternative on each criterion 6. Compute the optimal decision
Intuitive Decision-making[edit]
Intuitive decision-making relies on a person's instincts and gut feelings. It is often used in situations where time is limited, and there is no clear rational choice. Intuition can be developed through experience and is often used by experts in their fields.
Collaborative Decision-making[edit]
Collaborative decision-making involves multiple stakeholders working together to reach a consensus. This approach is common in organizational settings and can lead to more comprehensive and accepted decisions.
Factors Influencing Decision-making[edit]
Cognitive Biases[edit]
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Common biases include confirmation bias, anchoring, and overconfidence.
Emotions[edit]
Emotions can significantly influence decision-making. For example, fear can lead to risk-averse decisions, while excitement might lead to risk-taking.
Social Influences[edit]
Social factors, such as peer pressure and cultural norms, can also impact decision-making processes.
Decision-making in Medicine[edit]
In the medical field, decision-making is critical and often involves ethical considerations. Physicians must weigh the potential benefits and harms of treatments, consider patient preferences, and adhere to medical guidelines.
[edit]
Shared decision-making is a collaborative process that allows patients and their healthcare providers to make health care decisions together. It takes into account the best scientific evidence available, as well as the patient's values and preferences.
Also see[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
