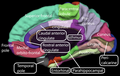
Anterior cingulate cortex
Part of the brain involved in various functions including emotion and cognition
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is a part of the brain located in the frontal lobe. It plays a crucial role in a wide range of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate, as well as higher-level functions, including decision-making, empathy, impulse control, and emotion.
Anatomy[edit]
The anterior cingulate cortex is situated in the medial aspect of the brain's frontal lobes. It forms a part of the cingulate cortex, which encircles the corpus callosum. The ACC is divided into two main areas: the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and the ventral anterior cingulate cortex (vACC).
Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex[edit]
The dACC is primarily involved in cognitive functions such as error detection, anticipation of tasks, and attention. It is connected to the prefrontal cortex and the parietal lobe, which are involved in executive functions and sensory processing, respectively.
Ventral Anterior Cingulate Cortex[edit]
The vACC is more involved in emotional regulation and is connected to the amygdala, nucleus accumbens, and the hypothalamus. These connections allow the vACC to play a role in processing emotions and regulating autonomic responses.
Functions[edit]
The anterior cingulate cortex is involved in a variety of functions:
- Emotion Regulation: The ACC is crucial in processing emotions and is involved in the regulation of emotional responses. It helps in the assessment of emotional stimuli and the generation of appropriate emotional reactions.
- Cognitive Control: The ACC is involved in cognitive processes such as conflict monitoring, error detection, and decision-making. It helps in evaluating the outcomes of actions and adjusting behavior accordingly.
- Pain Perception: The ACC is activated during the experience of pain and is thought to be involved in the emotional aspect of pain perception.
- Autonomic Functions: The ACC regulates autonomic functions such as heart rate and blood pressure, particularly in response to stress or emotional stimuli.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Dysfunction in the anterior cingulate cortex has been implicated in several psychiatric and neurological disorders:
- Depression: Abnormal activity in the ACC has been associated with major depressive disorder, particularly in the regulation of mood and emotional responses.
- Anxiety Disorders: The ACC is involved in the processing of fear and anxiety, and its dysfunction can contribute to anxiety disorders.
- Schizophrenia: Altered ACC activity has been observed in individuals with schizophrenia, affecting cognitive and emotional processing.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): The ACC's role in attention and impulse control is relevant to the symptoms of ADHD.
Imaging and Research[edit]
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans have been used to study the activity of the ACC in various tasks and conditions. These imaging techniques have provided insights into the role of the ACC in both healthy individuals and those with psychiatric disorders.
Related pages[edit]
Anterior cingulate cortex[edit]
-
MRI anterior cingulate
-
Anterior cingulate gyrus animation
-
Medial surface of cerebral cortex - gyri
-
Anterior Cingulate Cortex
-
Caudal Anterior Cingulate - DK ATLAS
-
Rostral Anterior Cingulate - DK ATLAS
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian